The Decline In Excessive Heat Warnings: Causes And Implications
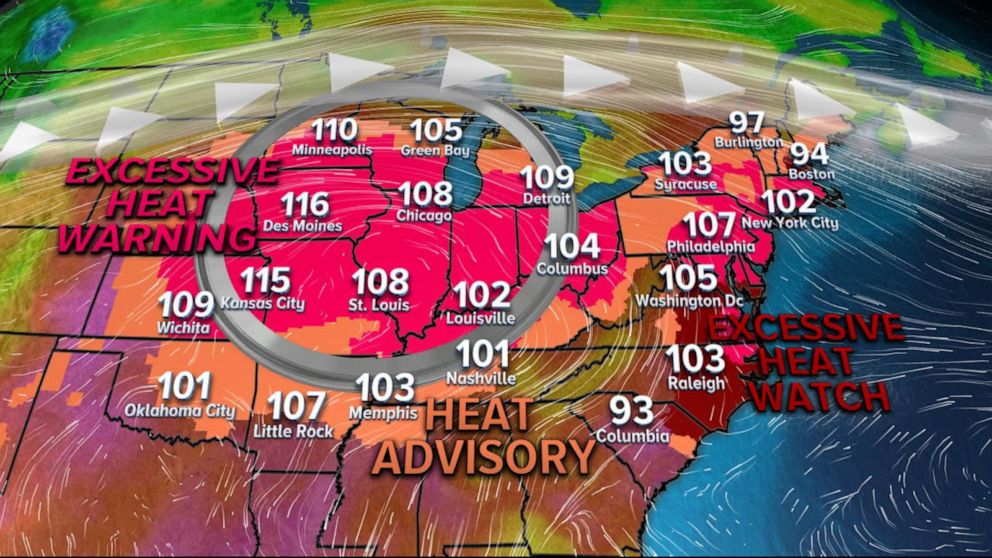
Table of Contents
Improved Forecasting and Warning Systems
Advancements in meteorological technology and data analysis have significantly improved weather forecasting accuracy, potentially leading to more precise and targeted excessive heat warnings. This doesn't necessarily mean fewer extreme heat events, but rather a more refined approach to alerting the public.
-
Enhanced weather models provide more precise predictions of temperature extremes: Sophisticated computer models now incorporate higher-resolution data, leading to better predictions of both the intensity and geographic reach of heat waves. This allows for more accurate heat index forecasting, a crucial factor in determining the actual danger posed by high temperatures.
-
Improved communication infrastructure allows for faster dissemination of warnings: Modern communication technologies, including social media, mobile alerts, and targeted email campaigns, ensure that excessive heat warnings reach a wider audience more quickly than ever before. This rapid dissemination is crucial for timely protective action.
-
Better understanding of heat’s impact enables more effective targeting of vulnerable populations: With a deeper understanding of social vulnerability and the disproportionate impact of extreme heat on the elderly, children, and those with chronic illnesses, warnings can be tailored to reach those most at risk. This targeted approach improves the effectiveness of early warning systems.
However, improvements in warning systems might lead to a perceived decline in warnings, even if the actual number of extreme heat events remains constant or increases. More precise warnings might focus alerts on smaller, more specifically affected areas, reducing the overall number of broad region-wide alerts.
Changes in Climate Patterns (or Lack Thereof)
The decline in excessive heat warnings might, in part, reflect actual changes in climate patterns, or it might not. Analyzing long-term temperature data is crucial to determine whether extreme heat events are genuinely decreasing in frequency and intensity.
-
Analysis of long-term temperature data to determine if extreme heat events are genuinely decreasing: Decades of temperature records must be analyzed to identify true trends, accounting for natural climate variability. A decrease in excessive heat warnings might simply be a statistical fluctuation, not a long-term change.
-
Discussion of potential confounding factors, such as urban heat island effects and microclimates: Urban areas tend to experience higher temperatures than surrounding rural areas due to the urban heat island effect. Changes in urban development or land use can influence local temperature readings and heat wave intensity. Microclimates, localized variations in temperature, also play a role.
-
Examination of regional variations in heat wave frequency and intensity: Climate change impacts vary regionally. Some areas might experience a decrease in extreme heat while others see an increase. Analyzing regional trends is crucial for understanding the global picture.
The lack of a clear, widespread decrease in extreme heat events, despite potential regional variations, suggests a continuing need for robust excessive heat warnings, even with climate change considerations.
Underreporting and Systemic Issues
The possibility that the decline in excessive heat warnings is due to underreporting or systemic issues within warning systems cannot be ignored.
-
Discussion of potential biases in data collection or reporting: Inconsistent data collection methods across regions can lead to inaccuracies in assessing the true frequency of heat waves. Similarly, reporting biases can influence the overall picture.
-
Exploration of resource limitations that might hinder the issuance of warnings, especially in underserved communities: Resource constraints, particularly in underserved communities, can limit the capacity to issue and disseminate timely excessive heat warnings effectively.
-
Analysis of the impact of political or economic pressures on warning systems: Political or economic pressures might influence the issuance of warnings, potentially leading to underreporting or downplaying the severity of extreme heat events.
The Impact on Public Health
Regardless of the cause of the decline in excessive heat warnings, the human consequences are significant. A decrease in warnings, whether due to improvements in accuracy or systemic issues, results in greater risks for the public.
-
Increased risk of heatstroke and other heat-related illnesses: Fewer warnings leave individuals unprepared, increasing the risk of heatstroke, heat exhaustion, and other heat-related illnesses.
-
Higher mortality rates, particularly among vulnerable populations (elderly, children, chronically ill): Vulnerable populations are disproportionately affected by extreme heat, and a decline in warnings exacerbates this risk, leading to higher mortality rates.
-
Strain on healthcare resources during heat waves: An increase in heat-related illnesses places a significant strain on healthcare systems, potentially overwhelming resources during peak heat events.
Conclusion
The apparent decline in excessive heat warnings presents a complex issue with multifaceted causes and significant implications. While improvements in forecasting and warning systems play a role, it's crucial to consider the possibility of unchanging or even worsening extreme heat events masked by underreporting or systemic shortcomings. Understanding the true reasons behind this trend is paramount to safeguarding public health. Further research and investment in improved data collection, resource allocation, and public awareness campaigns regarding excessive heat warnings are urgently needed to ensure the safety and well-being of communities facing increasingly frequent and intense heat waves. Let's work together to understand and address the complexities surrounding excessive heat warnings and protect vulnerable populations from the devastating effects of extreme heat.

Featured Posts
-
 Olly Alexanders Electrifying 3 Olympia Theatre Performance Photos Inside
May 30, 2025
Olly Alexanders Electrifying 3 Olympia Theatre Performance Photos Inside
May 30, 2025 -
 Paddy Pimblett Predicts The Winner Of Jones Vs Aspinall Ufc Heavyweight Title Fight
May 30, 2025
Paddy Pimblett Predicts The Winner Of Jones Vs Aspinall Ufc Heavyweight Title Fight
May 30, 2025 -
 Experience Bioluminescent Waves Spring And Fall In So Cal
May 30, 2025
Experience Bioluminescent Waves Spring And Fall In So Cal
May 30, 2025 -
 James Arthur Announces 2026 Uk Tour Dates Manchester And Beyond
May 30, 2025
James Arthur Announces 2026 Uk Tour Dates Manchester And Beyond
May 30, 2025 -
 Astronomers Discover Unprecedented Pulsing Object In Space
May 30, 2025
Astronomers Discover Unprecedented Pulsing Object In Space
May 30, 2025
