The End Of A Desegregation Order: A Look At The Justice Department's Decision And Its Potential Impact
Table of Contents
Background of the Desegregation Order
Historical Context:
The Little Rock School District's desegregation order stems from the landmark 1954 Brown v. Board of Education Supreme Court decision, which declared state laws establishing separate public schools for black and white students to be unconstitutional. However, the implementation of Brown v. Board faced significant resistance, particularly in the South. Little Rock, Arkansas, became a focal point of this resistance, culminating in the infamous 1957 crisis at Central High School. The subsequent desegregation order aimed to rectify decades of legally mandated segregation and create a more integrated school system. This involved busing, redrawing school boundaries, and implementing affirmative action programs.
Initial Impact and Effectiveness:
The initial impact of the desegregation order in Little Rock was mixed. While it led to some integration, significant resistance persisted, resulting in protracted legal battles and ongoing challenges to full desegregation. Early data showed a slow but steady increase in the number of African American students attending previously all-white schools. However, achievement gaps between white and Black students remained, highlighting the limitations of simply integrating schools without addressing systemic inequalities in funding and resources.
- Specific examples of improvements: Increased opportunities for Black students to access advanced courses and extracurricular activities.
- Specific examples of challenges: Continued residential segregation leading to de facto segregation in schools, despite legal efforts.
- Key figures: The role of the NAACP Legal Defense and Educational Fund in advocating for desegregation in Little Rock is critical.
The Justice Department's Decision to End the Order
Rationale and Justification:
The Justice Department's decision to end the desegregation order cited the district's substantial progress towards integration, arguing that the current level of racial balance and the absence of intentional segregation justify the termination. They pointed to increased diversity in schools and a reduction in racial disparities, though critics dispute the extent of this progress.
Legal Basis:
The decision rests on the legal principle that desegregation orders are not permanent and should be terminated once the goals of eliminating state-sponsored segregation have been substantially achieved. This legal framework is based on a series of Supreme Court cases which emphasize the need for ongoing monitoring and the potential for termination when substantial progress has been demonstrated.
- Key arguments supporting the decision: Significant racial balance in schools, elimination of overt discriminatory practices.
- Counterarguments: Persistence of achievement gaps, ongoing residential segregation leading to de facto segregation, insufficient attention to historical inequities.
- Statements from involved parties: The Justice Department issued a press release outlining their reasoning. The Little Rock School District responded with a statement, while community groups expressed varied opinions, reflecting differing perspectives on the issue.
Potential Impact and Consequences
Educational Outcomes:
Ending the desegregation order raises concerns about the potential for a resurgence of racial segregation and the widening of achievement gaps. Without active measures to maintain integration and address systemic inequities, there is a risk that schools will become more racially isolated, limiting opportunities for students of color.
Social and Community Impact:
The decision's impact extends beyond the educational sphere. It could exacerbate existing racial tensions within the community, potentially leading to increased social division. The possibility of re-segregation may also affect property values and residential patterns.
Legal Challenges and Future Litigation:
Given the significant concerns surrounding the decision, legal challenges are likely. Civil rights organizations may argue that the district has not achieved unitary status and that the termination of the order is premature. This could lead to protracted legal battles and further uncertainty for the school district.
- Predictions of future enrollment patterns: Increased racial segregation in certain schools is a possibility.
- Potential for increased racial disparities: Funding disparities could worsen if there's a lack of proactive measures to address historical inequities.
- Expert opinions: Educational experts and civil rights advocates have expressed serious concerns about the potential negative consequences of ending the order.
Conclusion: The End of a Desegregation Order: Looking Ahead
The Justice Department's decision to end the desegregation order for the Little Rock School District carries profound implications for educational equity and racial justice. While the department claims substantial progress has been made, critics point to persistent achievement gaps and the risk of re-segregation. The potential consequences of lifting desegregation orders highlight the ongoing need for vigilance and proactive measures to ensure equitable access to quality education for all students. Understanding the implications of the end of this desegregation order is crucial for ensuring equitable educational opportunities for all children. Stay informed about similar cases and advocate for policies promoting desegregation and educational justice. Contact your elected officials and support organizations working to combat educational inequality and promote racial justice. The fight for true educational equity continues.
Featured Posts
-
 Ai Driven Podcast Creation From Repetitive Scatological Texts To Engaging Audio
May 03, 2025
Ai Driven Podcast Creation From Repetitive Scatological Texts To Engaging Audio
May 03, 2025 -
 Play Station Network Kullanici Girisi Ve Sorun Giderme
May 03, 2025
Play Station Network Kullanici Girisi Ve Sorun Giderme
May 03, 2025 -
 Bo J Slashes Economic Growth Forecast Trade War Takes Toll
May 03, 2025
Bo J Slashes Economic Growth Forecast Trade War Takes Toll
May 03, 2025 -
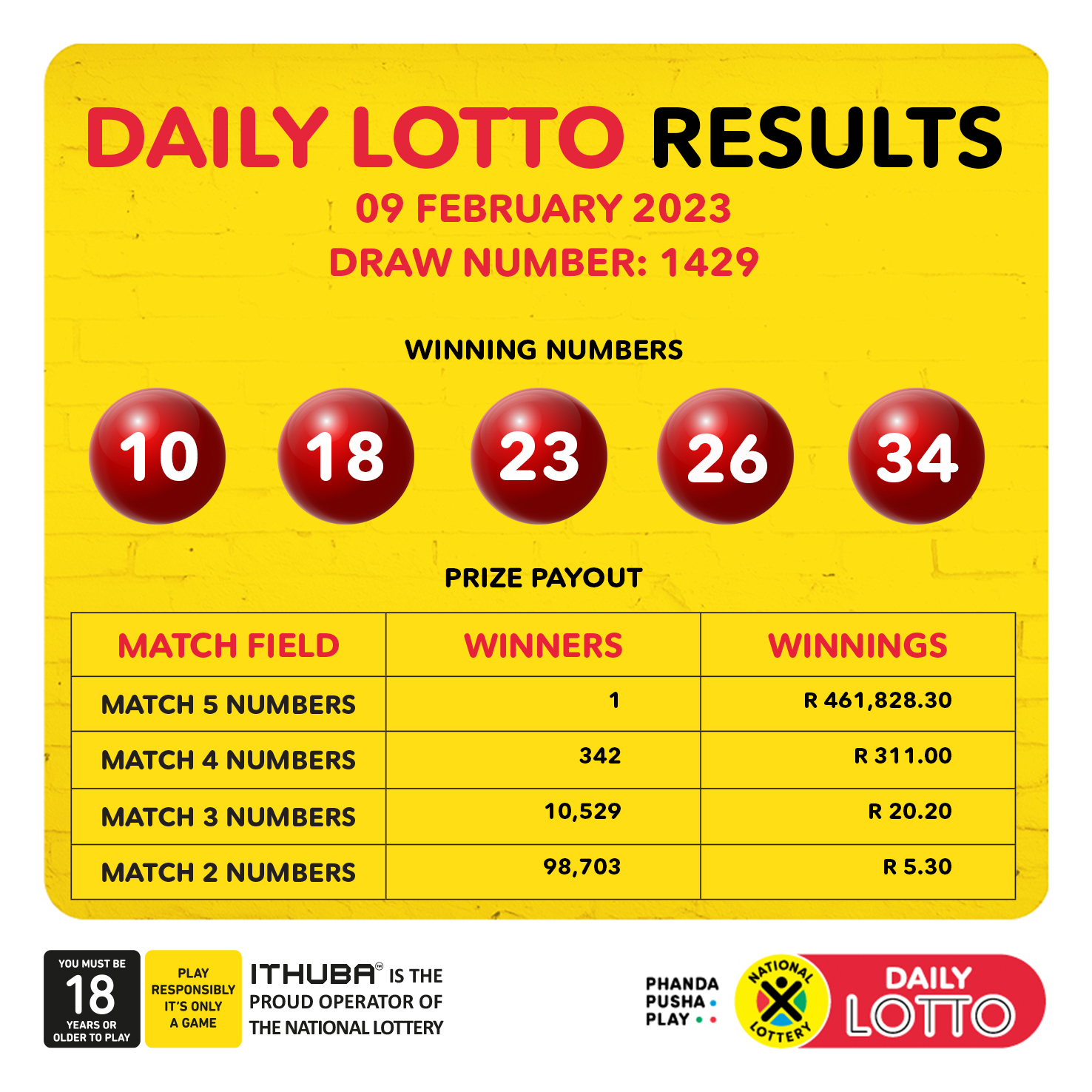 Check Your Tickets Latest Lotto Lotto Plus 1 And Lotto Plus 2 Numbers
May 03, 2025
Check Your Tickets Latest Lotto Lotto Plus 1 And Lotto Plus 2 Numbers
May 03, 2025 -
 The End Of A Chapter School Desegregation Order And Its Legacy
May 03, 2025
The End Of A Chapter School Desegregation Order And Its Legacy
May 03, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Dari Sampah Menjadi Harta Manfaat Cangkang Telur Bagi Pertanian Dan Peternakan
May 04, 2025
Dari Sampah Menjadi Harta Manfaat Cangkang Telur Bagi Pertanian Dan Peternakan
May 04, 2025 -
 Raya Promotion Free Hpc Ev Charging On Shell Recharge East Coast
May 04, 2025
Raya Promotion Free Hpc Ev Charging On Shell Recharge East Coast
May 04, 2025 -
 Daur Ulang Cangkang Telur Pupuk Alami Dan Sumber Kalsium Untuk Tanaman Dan Hewan
May 04, 2025
Daur Ulang Cangkang Telur Pupuk Alami Dan Sumber Kalsium Untuk Tanaman Dan Hewan
May 04, 2025 -
 Enjoy 100 Rebate On Shell Recharge Hpc Ev Chargers This Raya East Coast
May 04, 2025
Enjoy 100 Rebate On Shell Recharge Hpc Ev Chargers This Raya East Coast
May 04, 2025 -
 T 1
May 04, 2025
T 1
May 04, 2025
