The Future Of European Public Transport: Hydrogen Vs. Battery Buses
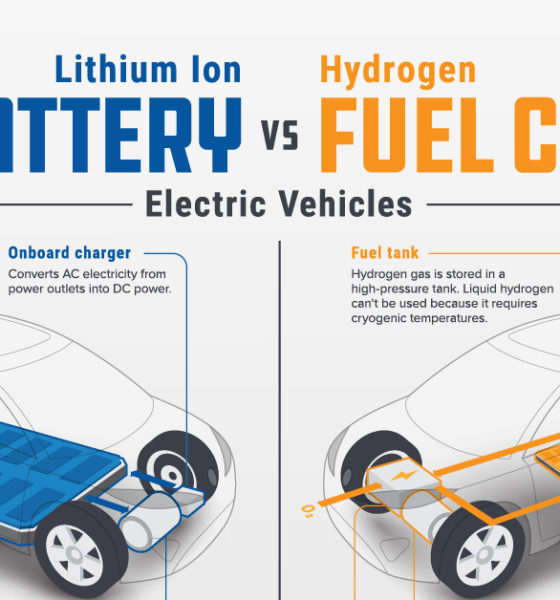
Table of Contents
Battery-Electric Buses: The Current Frontrunner
Advantages of Battery-Electric Buses:
Battery-electric buses currently represent a significant step forward in sustainable European public transport. Their advantages are numerous:
- Lower upfront cost: Compared to hydrogen buses, the initial investment for battery-electric buses is considerably lower, making them a more accessible option for many cities and municipalities. This lower cost of entry is a major factor driving their current market dominance.
- Established charging infrastructure: Many European cities already possess a degree of charging infrastructure, making the integration of battery-electric buses relatively straightforward. This existing infrastructure reduces the initial investment needed for deployment.
- Reduced noise pollution: Battery-electric buses operate significantly quieter than their diesel counterparts, contributing to a more pleasant urban environment and improved quality of life for residents. This is a key benefit for city centers.
- Well-established technology: Battery-electric bus technology is mature and well-understood, offering proven reliability and reduced operational risks. This maturity translates to easier maintenance and readily available parts.
- Lower maintenance costs (potentially): While long-term data is still being collected, initial indications suggest that battery-electric buses may offer lower maintenance costs than hydrogen buses, although this remains a subject of ongoing investigation.
- Growing battery technology advancements: Continuous advancements in battery technology are leading to increased range, longer lifespan, and faster charging times, addressing some of the initial limitations of this technology. This ongoing innovation ensures that battery-electric buses will continue to improve.
Disadvantages of Battery-Electric Buses:
Despite their advantages, battery-electric buses also present challenges:
- Limited range: Compared to hydrogen buses, battery-electric buses have a significantly shorter range, limiting their suitability for longer routes and requiring more frequent charging stops.
- Environmental impact of battery production: The mining and processing of raw materials for battery production have significant environmental consequences, including carbon emissions and habitat destruction. Sustainable sourcing and recycling programs are crucial to mitigate these impacts.
- Charging infrastructure expansion: Significant expansion of charging infrastructure is needed in many European cities to support widespread adoption of battery-electric buses. This requires substantial investment and planning.
- Battery lifespan and replacement costs: Battery lifespan is a key factor affecting the overall cost-effectiveness of battery-electric buses. Replacement costs can be substantial, requiring careful consideration in long-term planning.
- Grid capacity upgrades: The increased demand for electricity from widespread battery-electric bus charging may necessitate upgrades to existing power grids, adding further cost and complexity.
Hydrogen Buses: A Potential Game Changer
Advantages of Hydrogen Buses:
Hydrogen fuel cell buses offer a compelling alternative to battery-electric buses, with several key advantages:
- Longer range: Hydrogen buses boast a significantly longer range than battery-electric buses, making them ideal for longer routes and reducing the frequency of refueling stops.
- Faster refueling times: Refueling a hydrogen bus takes only a few minutes, compared to the longer charging times required for battery-electric buses. This faster turnaround time is crucial for maintaining efficient public transport schedules.
- Zero tailpipe emissions: Hydrogen fuel cell buses produce only water vapor as a byproduct, resulting in zero tailpipe emissions and significantly reduced air pollution. This is a crucial element in improving air quality in European cities.
- Potential for greater energy independence: The production of green hydrogen, using renewable energy sources like solar and wind power, offers the potential for greater energy independence and reduced reliance on fossil fuels. This aspect is especially important for European energy security.
- Adaptable to existing bus depots (potentially): In some cases, existing bus depots can be adapted for hydrogen refueling with relatively minimal modifications, reducing the upfront infrastructure investment. However, this is highly dependent on the specific depot and its infrastructure.
Disadvantages of Hydrogen Buses:
Despite their promise, hydrogen buses also face challenges:
- High initial investment costs: The upfront costs for both the buses themselves and the necessary refueling infrastructure are significantly higher than for battery-electric buses. This is a major barrier to widespread adoption.
- Limited hydrogen refueling infrastructure: Currently, the infrastructure for hydrogen refueling is extremely limited across Europe, hindering the widespread deployment of hydrogen buses. Significant investment is needed to build this crucial infrastructure.
- Energy-intensive hydrogen production: The production of hydrogen can be energy-intensive, particularly if not sourced from renewable energy sources. The environmental impact of hydrogen production must be carefully considered.
- Safety concerns: Safety concerns associated with the storage and handling of hydrogen require stringent safety protocols and regulations to ensure safe operation.
- Lower energy efficiency (potentially): While constantly improving, the energy efficiency of hydrogen fuel cells may currently be lower than that of battery-electric systems, affecting overall operational efficiency.
Comparing Infrastructure Needs: A Key Differentiator
Battery-Electric Infrastructure:
Widespread adoption of battery-electric buses requires a substantial investment in charging infrastructure, including:
- Extensive charging stations: A network of strategically located high-power charging stations is needed to support the operational needs of battery-electric bus fleets.
- Grid upgrades: In many areas, upgrades to existing electricity grids will be necessary to handle the increased demand from numerous charging stations.
- Smart charging management systems: Intelligent charging management systems are needed to optimize energy consumption and minimize strain on the electricity grid.
Hydrogen Infrastructure:
Deploying hydrogen buses demands a different type of infrastructure investment:
- Widespread hydrogen production facilities: The production of green hydrogen requires significant investment in renewable energy-powered electrolysis plants.
- Specialized refueling stations: A network of specialized hydrogen refueling stations is needed, requiring significant investment and specialized equipment.
- Robust safety protocols: Stringent safety protocols and regulations are crucial to mitigate the risks associated with hydrogen storage and handling.
The Role of Government Policy:
Substantial government investment and supportive policies are essential for the successful deployment of both battery-electric and hydrogen bus technologies. Incentives, subsidies, and regulatory frameworks are critical for stimulating innovation and encouraging private sector investment.
Environmental Impact: A Holistic View
Lifecycle Emissions:
A comprehensive assessment of the environmental impact of both battery-electric and hydrogen buses requires considering their lifecycle emissions. This includes:
- Manufacturing emissions: The emissions associated with the production of buses, batteries, and hydrogen fuel cells must be factored into the analysis.
- Operational emissions: The emissions during the operational phase, including electricity consumption for charging and hydrogen production, must be assessed.
- End-of-life disposal: The environmental impact of disposing of batteries and bus components at the end of their lifespan must be taken into account.
Green Hydrogen's Potential:
The use of renewable energy sources (like solar and wind) to produce green hydrogen significantly reduces the overall environmental impact of hydrogen buses. This is a crucial aspect in determining the long-term sustainability of hydrogen fuel cell technology.
Conclusion:
Both battery-electric and hydrogen buses offer significant advantages for sustainable European public transport. The optimal choice depends on various factors, including existing infrastructure, available renewable energy resources, and the specific needs of each city or region. While battery-electric buses currently hold a market advantage due to lower costs and more readily available infrastructure, hydrogen buses offer compelling long-term possibilities, particularly for longer routes and areas with less developed electrical grids. Further investment in research, development, and supportive policies are crucial for advancing both technologies and ensuring a greener future for European public transport. To learn more about the future of sustainable transportation and make informed decisions for your community, continue researching the best options for European public transport systems.

Featured Posts
-
 Should The Wolves Trade For Julius Randle A Thorough Analysis
May 07, 2025
Should The Wolves Trade For Julius Randle A Thorough Analysis
May 07, 2025 -
 Forza Horizon 5 On Ps 5 Release Date Time And Everything You Need To Know
May 07, 2025
Forza Horizon 5 On Ps 5 Release Date Time And Everything You Need To Know
May 07, 2025 -
 Julius Randles Redemption A Timberwolves Success Story
May 07, 2025
Julius Randles Redemption A Timberwolves Success Story
May 07, 2025 -
 April 16 2025 Lotto Results Winning Numbers Announced
May 07, 2025
April 16 2025 Lotto Results Winning Numbers Announced
May 07, 2025 -
 Knicks Vs Cavaliers Game Prediction Breaking Down The Odds
May 07, 2025
Knicks Vs Cavaliers Game Prediction Breaking Down The Odds
May 07, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 76
May 08, 2025
76
May 08, 2025 -
 The Night Inter Milan Defeated Barcelona In The Champions League Final
May 08, 2025
The Night Inter Milan Defeated Barcelona In The Champions League Final
May 08, 2025 -
 2 0 76
May 08, 2025
2 0 76
May 08, 2025 -
 Champions League Final Inter Milans Triumph Against Barcelona
May 08, 2025
Champions League Final Inter Milans Triumph Against Barcelona
May 08, 2025 -
 76 2 0
May 08, 2025
76 2 0
May 08, 2025
