The Geopolitics Of Greenland: Assessing The Long-Term Effects Of Trump's Actions

Table of Contents
Trump's Attempted Purchase and its Global Implications
Trump's 2019 suggestion to purchase Greenland sparked immediate and widespread international reaction. The geopolitics of Greenland were thrust into the global spotlight, raising questions about US foreign policy and the future of Arctic governance.
The immediate reaction from Denmark and the international community.
- Denmark: The Danish government, which oversees Greenland's foreign affairs, swiftly and firmly rejected the proposal, deeming it absurd and unrealistic. Prime Minister Mette Frederiksen stated that Greenland was not for sale.
- International Community: The international community largely echoed Denmark's response. Many saw the proposal as a sign of disrespect for Greenland's self-governance and a disregard for established international norms. The incident highlighted the complexities of sovereignty and self-determination in the Arctic.
- Legal and Practical Impossibilities: The sheer impracticality of such a purchase was evident. Greenland, while a constituent country within the Kingdom of Denmark, possesses significant autonomy and its own government. A forced sale would have been a major violation of international law and principles of self-determination.
- Impact on US-Denmark Relations: Trump's actions strained the historically strong relationship between the US and Denmark. The incident exposed underlying tensions and differing perspectives on Arctic governance and resource management.
The strategic significance of Greenland's location and resources.
Greenland's strategic importance stems from its location and resources. Its vast Arctic territory offers significant geopolitical advantages:
- Resource Extraction: Greenland possesses substantial reserves of rare earth minerals, crucial for modern technologies, and potential oil and gas reserves. Control over these resources is a major driver of international interest.
- Military Implications: Greenland's geographic position commands key Arctic shipping routes, making it strategically important for military operations and surveillance. Control over these routes is vital for maintaining power projection in the Arctic.
- Climate Change Research: Greenland's massive ice sheet is a critical indicator of climate change. Access to research facilities and monitoring capabilities in Greenland provides valuable insights into global climate patterns.
Shifting Power Dynamics in the Arctic
Trump's actions, while ultimately unsuccessful in their intended aim, accelerated the already burgeoning competition for influence in the Arctic. The geopolitics of Greenland are intrinsically linked to the broader dynamics of Arctic power.
Increased competition between global powers in the Arctic region.
The Arctic is experiencing a renewed "great game," with nations like Russia and China increasingly assertive in the region:
- Russia: Russia has significantly invested in its Arctic military infrastructure, asserting its claims to Arctic resources and navigational routes.
- China: China has also expressed a strong interest in the Arctic, framing its involvement as part of its "Polar Silk Road" initiative, aiming to enhance trade and resource access.
- Militarization Concerns: The increased presence of global powers in the Arctic raises concerns about potential militarization and the risk of conflict over resources and territorial claims.
The role of Greenlandic self-determination in the geopolitical landscape.
Greenland's growing autonomy is a significant factor in the geopolitics of Greenland:
- Greenland's Strategic Interests: Greenland aims to balance its relationship with external powers while pursuing its own economic and environmental priorities. It seeks to leverage its strategic position for greater economic and political independence.
- Foreign Policy Autonomy: Greenland is increasingly asserting its own foreign policy independence, engaging in bilateral agreements and international collaborations separate from Denmark.
- Economic Diversification: Greenland seeks to diversify its economy, reducing reliance on traditional sectors like fishing and promoting sustainable development in areas like renewable energy and tourism.
Long-Term Economic and Environmental Consequences
The increased international attention on Greenland brings both economic opportunities and environmental risks. The geopolitics of Greenland are inextricably linked to its environmental future.
The potential impact of increased resource extraction on Greenland's environment.
The exploitation of Greenland's resources poses significant environmental challenges:
- Mining and Oil Exploration Risks: Mining operations and oil exploration carry risks of pollution, habitat destruction, and disruption to delicate Arctic ecosystems.
- Unique Ecosystem Threats: Greenland's unique biodiversity and fragile ecosystems are vulnerable to the impacts of resource extraction and climate change.
- Sustainable Development Needs: Balancing economic development with environmental protection is crucial for ensuring the long-term well-being of Greenland's environment and people.
The economic benefits and drawbacks of increased foreign investment.
Foreign investment presents both opportunities and risks for Greenland's economy:
- Economic Growth Potential: Increased investment can stimulate economic growth, creating jobs and improving infrastructure.
- Economic Exploitation Risks: There's a risk that foreign investment could lead to economic exploitation, leaving Greenland dependent on external actors.
- Balanced Economic Development: Greenland needs to ensure that economic development benefits its people equitably and sustainably, avoiding dependency and promoting local ownership.
Conclusion: The Enduring Legacy of Trump's Greenland Gambit
Trump's attempted purchase of Greenland, though ultimately unsuccessful, had a lasting impact on the geopolitics of Greenland. It dramatically increased international attention on the region, highlighting its strategic importance and accelerating the competition for influence among global powers. The incident underscored Greenland's growing self-determination and the need for balanced economic and environmental management. Key takeaways include the heightened geopolitical tensions in the Arctic, the focus on Greenland's resources, and the imperative for sustainable development.
Understanding the geopolitics of Greenland requires ongoing attention. Continue exploring this critical region and its evolving relationship with global powers, considering the complex interplay of environmental concerns, economic opportunities, and Greenland's own path to self-determination. The future of Greenland's geopolitics depends on informed decisions that prioritize its unique identity and the sustainability of its environment.

Featured Posts
-
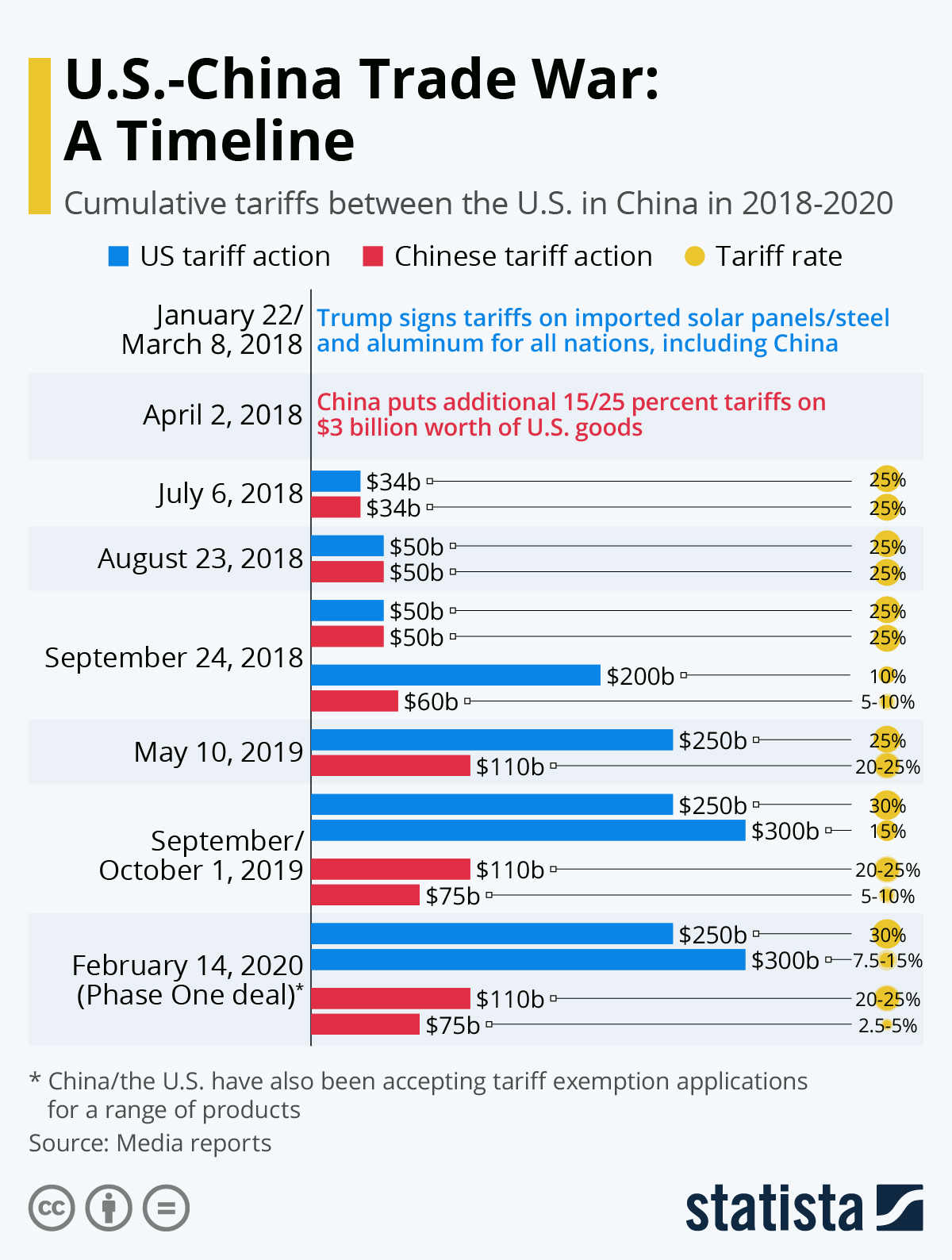 The Impact Of Trade Wars On Chinese Goods Focusing On The Example Of Bubble Blasters
May 09, 2025
The Impact Of Trade Wars On Chinese Goods Focusing On The Example Of Bubble Blasters
May 09, 2025 -
 Bert Kreischers Wife On His Netflix Jokes A Candid Look At Their Marriage
May 09, 2025
Bert Kreischers Wife On His Netflix Jokes A Candid Look At Their Marriage
May 09, 2025 -
 Expensive Babysitting Costs Lead To Higher Daycare Fees A Case Study
May 09, 2025
Expensive Babysitting Costs Lead To Higher Daycare Fees A Case Study
May 09, 2025 -
 Stock Market Today Sensex And Niftys Sharp Rise Ultra Tech Cement Dip
May 09, 2025
Stock Market Today Sensex And Niftys Sharp Rise Ultra Tech Cement Dip
May 09, 2025 -
 Tien Giang Xu Ly Nghiem Vu Bao Mau Bao Hanh Tre Em
May 09, 2025
Tien Giang Xu Ly Nghiem Vu Bao Mau Bao Hanh Tre Em
May 09, 2025
