The Global Artworld 1850-1950: A Critical Art Review

Table of Contents
The Rise of Modernism and its Diverse Expressions
The late 19th and early 20th centuries saw the rise of modern art movements that fundamentally redefined artistic expression. This period of artistic innovation was characterized by a rejection of academic traditions and an exploration of new forms, styles, and subjects. Global art trends emerged, influenced by both internal artistic developments and external socio-political factors.
- Impressionism and its influence: Impressionists like Monet, Renoir, and Degas revolutionized painting with their focus on capturing fleeting moments and the effects of light. Their innovative techniques, emphasizing visible brushstrokes and capturing momentary impressions, had a global impact, inspiring artists worldwide.
- Example: Monet's Impression, soleil levant (Impression, Sunrise) is considered the quintessential Impressionist work, giving the movement its name.
- Post-Impressionism: Artists like Van Gogh, Cézanne, and Gauguin moved beyond Impressionism's focus on light and explored more subjective and expressive approaches. Van Gogh's emotionally charged brushwork and Gauguin's exploration of symbolic color laid the groundwork for later movements like Expressionism.
- Example: Van Gogh's The Starry Night exemplifies his expressive style and use of impasto.
- Early Modernism beyond Europe: Modern art wasn't confined to Europe. Latin American modernism, for example, developed unique styles reflecting local culture and political realities. Similarly, Japanese art movements, while influenced by Western art, retained distinctive characteristics. The exchange of ideas through global trade and colonial encounters significantly shaped these developments.
- Example: The Mexican Muralist movement, featuring artists like Diego Rivera and José Clemente Orozco, combined European artistic techniques with distinctly Mexican themes.
- Keywords: Latin American modernism, Japanese art movements, global art trends
The Impact of Industrialization and Technological Advancements
The Industrial Revolution profoundly impacted art. New technologies and the mass production of goods altered artistic practices and the very definition of art itself.
- Photography's impact on painting: The invention of photography challenged traditional artistic representation. Painters no longer needed to solely focus on realistic depictions, freeing them to explore more subjective and abstract forms.
- Example: Many Impressionists used photography as a tool to capture scenes quickly and accurately, influencing their compositions.
- New artistic mediums: The rise of new materials and techniques, including film and collage, broadened the scope of artistic expression. Artists experimented with these new mediums, pushing boundaries and creating novel forms of art.
- Example: Cubism, with its fragmentation of forms and perspectives, utilized collage as a key technique.
- The rise of mass production and its effects on art: Mass production led to the increased accessibility of art, raising questions about originality, authenticity, and the concept of "art for the masses." The shift from handcrafted objects to mass-produced goods impacted artistic production significantly.
- Example: The proliferation of posters and printed images, facilitated by lithography and other printing techniques, brought art to a wider audience.
- Keywords: industrial revolution art, photography's influence, new artistic mediums
Cultural Exchange and Artistic Cross-Pollination
The Global Artworld 1850-1950 was characterized by significant artistic globalization and cross-cultural influences. The exchange of artistic ideas and styles transcended geographical boundaries.
- The impact of colonialism and trade: Colonialism and global trade networks facilitated the exchange of artistic ideas and styles. Artistic motifs and techniques traveled across continents, leading to a blending of styles and influences.
- Example: The influence of Japanese woodblock prints on Impressionist artists like Monet and Degas is well-documented.
- Examples of cross-cultural influences: Many artistic movements show evidence of cross-cultural influences. The exchange of ideas wasn't always a one-way street; rather, it involved reciprocal interaction and adaptation.
- Example: The development of Art Nouveau, with its organic forms and decorative style, drew inspiration from various global sources.
- The rise of international exhibitions: International exhibitions, such as the World's Fairs, played a critical role in disseminating artistic ideas and styles globally. These events brought together artists and art from various nations, fostering artistic exchange and cross-pollination.
- Example: The Paris Salons played a major role in shaping artistic trends and showcasing the work of international artists.
- Keywords: global art exchange, cross-cultural influences, artistic globalization
The Seeds of Postmodernism
By the mid-20th century, the seeds of postmodernism were being sown. The art world was grappling with new ideas and challenges that laid the groundwork for the artistic movements of the latter half of the century.
- Dadaism and Surrealism: Dadaism, with its anti-art stance and rejection of logic, and Surrealism, with its exploration of the unconscious mind, challenged traditional artistic conventions. These movements laid the groundwork for later conceptual and performance art.
- Example: Dadaist artists like Marcel Duchamp challenged the very definition of art with his readymades.
- Early conceptual art: Early forms of conceptual art, which prioritized the idea behind an artwork over its physical manifestation, began to emerge during this period. This represented a significant shift in artistic focus and practice.
- Example: The work of Marcel Duchamp and Kasimir Malevich foreshadowed later developments in conceptual art.
- The impact of World War I and II: The devastating World Wars profoundly impacted artistic sensibilities. The horrors of war led to a questioning of traditional values and a search for new forms of expression.
- Example: The existential concerns of many artists are reflected in the works produced after the wars.
- Keywords: early postmodernism, precursors to postmodern art, avant-garde movements
Conclusion: Understanding the Legacy of the Global Artworld 1850-1950
The Global Artworld 1850-1950 represents a period of immense change and artistic innovation. The rise of modernism, the impact of industrialization, and the intensification of global cultural exchange irrevocably altered the course of art history. Understanding this era is crucial to appreciating the complexities and diversity of contemporary art. The movements and artists discussed here continue to resonate today, shaping artistic practice and inspiring new generations of artists.
Key Takeaways: This period saw the emergence of major artistic movements like Impressionism, Post-Impressionism, and early forms of modernism beyond Europe, coupled with the profound impact of technological advancements and global cultural exchange. The seeds of Postmodernism were also sown during this time, challenging traditional artistic conventions.
Call to Action: Deepen your understanding of the "Global Artworld 1850-1950" by exploring online resources from museums like the Metropolitan Museum of Art or the Museum of Modern Art. Delve into the biographies of the artists mentioned, and further research the individual art movements discussed. By engaging with these resources, you can gain a richer appreciation for this pivotal era in art history.

Featured Posts
-
 Sinners Post Ban Return Includes Hamburg Tournament
May 19, 2025
Sinners Post Ban Return Includes Hamburg Tournament
May 19, 2025 -
 College Admissions Balancing Merit And Diversity In A Changing World
May 19, 2025
College Admissions Balancing Merit And Diversity In A Changing World
May 19, 2025 -
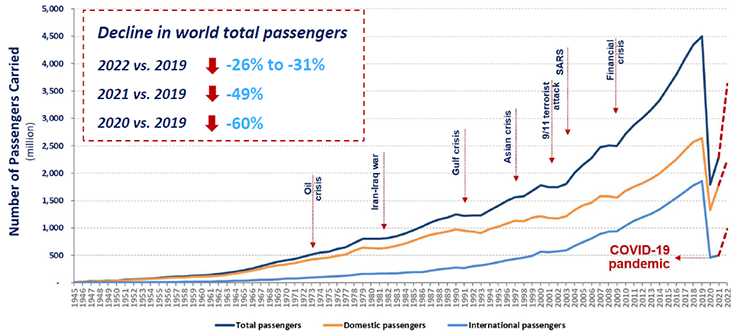 Early 2025 Air Passenger Numbers A Sharp Decline In Maastricht
May 19, 2025
Early 2025 Air Passenger Numbers A Sharp Decline In Maastricht
May 19, 2025 -
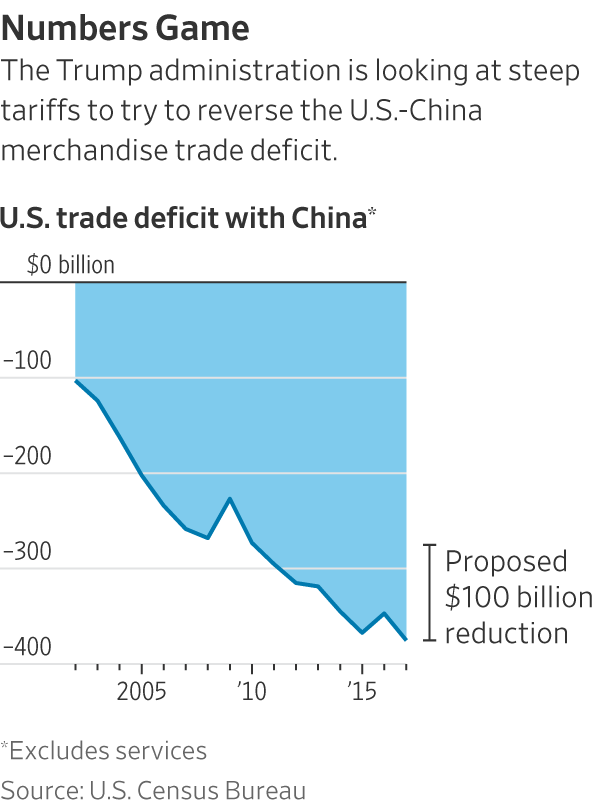 Analysts Forecast Trump Era 30 China Tariffs To Extend To Late 2025
May 19, 2025
Analysts Forecast Trump Era 30 China Tariffs To Extend To Late 2025
May 19, 2025 -
 Clemsons Spring Football Practice Distractions And Expectations
May 19, 2025
Clemsons Spring Football Practice Distractions And Expectations
May 19, 2025
