The Impact Of Cost And Stigma On Mental Health Claim Rates
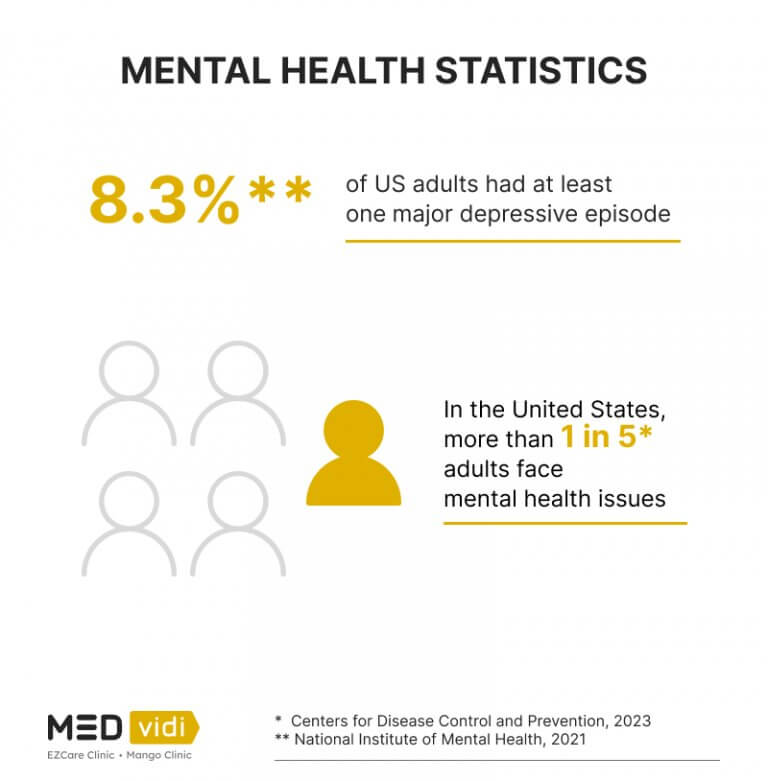
Table of Contents
The High Cost of Mental Healthcare and its Impact on Claim Rates
The financial burden of mental healthcare is a major contributor to low claim rates. Many individuals face significant affordability barriers and gaps in insurance coverage, ultimately deterring them from seeking professional help.
Affordability Barriers
High out-of-pocket expenses are a significant deterrent to accessing mental healthcare. Many individuals lack adequate health insurance coverage, leaving them with substantial costs.
- High deductibles, copays, and limited network providers: These factors significantly restrict access to care, making treatment unaffordable for many. Finding an in-network therapist or psychiatrist can be challenging, especially in rural areas.
- Costly treatments: Effective treatments like therapy (including Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) and Dialectical Behavior Therapy (DBT)), medication management, and specialized programs are often expensive. The cumulative cost of these services can quickly become prohibitive.
- Lack of affordable options: The absence of affordable mental health services forces many to forgo necessary care, leading to worsening conditions and potentially higher healthcare costs in the long run. This particularly impacts low-income individuals and families.
Underinsurance and Gaps in Coverage
Even with health insurance, many plans provide insufficient coverage for mental health treatment. This results in substantial financial burdens for individuals seeking care.
- Limited session allowances per year: Insurance companies may limit the number of therapy sessions covered annually, forcing patients to either pay out-of-pocket for additional sessions or discontinue treatment prematurely.
- Restrictions on specific types of therapy or medication: Some plans may only cover certain types of therapy or medications, excluding more effective or personalized treatments. This lack of flexibility can hinder treatment effectiveness.
- Lack of coverage for preventative mental healthcare: Many plans don't cover preventative mental healthcare services, such as regular check-ups or stress management programs. This proactive approach could significantly reduce the need for more intensive and costly treatment later.
The Financial Impact on Claim Rates
The high cost of care directly correlates with lower mental health claim rates. Individuals often prioritize other essential expenses over mental healthcare, leading to delayed or forgone treatment.
- Delayed or avoided care: Individuals may delay or avoid seeking help until their condition worsens, leading to more severe symptoms and increased healthcare costs in the long run.
- Increased severity of illness: Delaying treatment can result in a more severe mental health condition, requiring more extensive and expensive treatment interventions.
- Financial strain as a deterrent: The financial strain associated with mental healthcare is a significant barrier to seeking proactive care, preventing many individuals from prioritizing their mental well-being.
The Role of Stigma in Reducing Mental Health Claim Rates
Stigma, both social and self-imposed, significantly contributes to low mental health claim rates. The fear of judgment and negative consequences prevents many from seeking help.
Social Stigma and Fear of Judgment
The pervasive social stigma surrounding mental illness deters many individuals from seeking professional help. They fear judgment from family, friends, employers, or the wider community.
- Concerns about confidentiality and potential discrimination: Individuals worry about their mental health information being disclosed and the potential for discrimination in employment, housing, or social interactions.
- Fear of negative consequences: The fear of negative consequences on relationships, employment prospects, or social standing prevents many from seeking help.
- Lack of open conversations: A lack of open and honest conversations about mental health in society exacerbates the stigma and perpetuates the silence surrounding mental health issues.
Self-Stigma and Internalized Negative Beliefs
Individuals may internalize societal stigma, leading to feelings of shame, guilt, or inadequacy that prevent them from acknowledging their need for help.
- Self-blame and self-doubt: Self-blame and self-doubt hinder help-seeking behaviors, preventing individuals from seeking the support they need.
- Belief that mental illness is a personal weakness: Many believe mental illness is a personal weakness or character flaw, preventing them from seeking assistance.
- Reluctance to admit vulnerability: A reluctance to admit vulnerability or seek professional assistance contributes to the delay or avoidance of treatment.
The Impact of Stigma on Claim Rates
The combination of social and self-stigma directly contributes to low mental health claim rates. Many individuals choose to suffer in silence rather than seek professional help.
- Delayed or avoided professional support: Individuals may delay or avoid seeking professional support, leading to a worsening of their condition.
- Self-treatment and ineffective coping mechanisms: They may attempt self-treatment or rely on less effective coping mechanisms, which may not adequately address the underlying issues.
- Worsening mental health conditions: This lack of intervention can lead to worsening mental health conditions and potentially higher healthcare costs in the long run.
Strategies to Increase Mental Health Claim Rates
Increasing mental health claim rates requires a multi-pronged approach addressing both cost and stigma. Effective strategies include improving insurance coverage, addressing stigma, and increasing access to affordable care.
Improving Insurance Coverage
Expanding access to affordable mental healthcare through comprehensive insurance coverage is paramount.
- Increased parity laws: Mandating equal coverage for mental and physical healthcare is crucial to ensure equitable access to care.
- Government subsidies: Expanding access to affordable mental health care through government subsidies can help alleviate the financial burden for many individuals.
- Broader coverage: Insurance plans need to broaden their coverage to include a wider range of mental health services, including preventative care, various therapy types, and medications.
Addressing the Stigma Through Public Awareness Campaigns
Public awareness campaigns play a vital role in reducing stigma and encouraging help-seeking behaviors.
- Promoting open conversations: Open and honest conversations about mental health are crucial to destigmatize mental illness and foster a culture of support.
- Sharing personal stories: Sharing personal stories of recovery can help reduce shame and foster empathy, encouraging others to seek help.
- Highlighting effective treatments: Highlighting the availability and effectiveness of various treatments can encourage individuals to seek professional help.
Investing in Accessible and Affordable Mental Healthcare
Increasing the availability of accessible and affordable mental healthcare services is essential.
- Expanding access to community-based centers: Expanding access to community-based mental health centers can increase the availability of services in underserved areas.
- Training more mental health professionals: Training more mental health professionals can address the shortage of providers and improve access to care.
- Utilizing technology: Utilizing technology, such as telehealth, can help bridge geographical barriers to care and increase access for individuals in remote areas.
Conclusion
The low mental health claim rates reflect a complex interplay of high costs and persistent stigma. Addressing both these challenges is crucial to improving access to care and promoting better mental health outcomes. By improving insurance coverage, reducing stigma through education, and increasing access to affordable mental healthcare, we can significantly impact mental health claim rates. Let's work together to break down these barriers and prioritize mental healthcare – improving mental health claim rates is a vital step towards a healthier and more supportive society.

Featured Posts
-
 Rome Une Ingerence Francaise Dans L Election Papale
May 03, 2025
Rome Une Ingerence Francaise Dans L Election Papale
May 03, 2025 -
 The Future Of Reform Uk Five Potential Pitfalls
May 03, 2025
The Future Of Reform Uk Five Potential Pitfalls
May 03, 2025 -
 Israil Parlamentosu Nda Esir Yakinlari Ve Guevenlik Guecleri Arasindaki Gerginlik
May 03, 2025
Israil Parlamentosu Nda Esir Yakinlari Ve Guevenlik Guecleri Arasindaki Gerginlik
May 03, 2025 -
 Maines Post Election Audit Pilot Transparency And Accountability
May 03, 2025
Maines Post Election Audit Pilot Transparency And Accountability
May 03, 2025 -
 Joseph La Nouvelle Serie De Tf 1 Vaut Elle Le Detour
May 03, 2025
Joseph La Nouvelle Serie De Tf 1 Vaut Elle Le Detour
May 03, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Zakharova Prokommentirovala Otnosheniya Emmanuelya I Brizhit Makron
May 03, 2025
Zakharova Prokommentirovala Otnosheniya Emmanuelya I Brizhit Makron
May 03, 2025 -
 Un Echange Muscle Sardou Reproche A Macron
May 03, 2025
Un Echange Muscle Sardou Reproche A Macron
May 03, 2025 -
 La Visite De Trump Au Vatican Un Echange Houleux Avec Macron
May 03, 2025
La Visite De Trump Au Vatican Un Echange Houleux Avec Macron
May 03, 2025 -
 Macron Face A La Critique De Sardou Les Coulisses D Un Diner
May 03, 2025
Macron Face A La Critique De Sardou Les Coulisses D Un Diner
May 03, 2025 -
 Le Vatican Terrain De Tensions L Incident Trump Macron
May 03, 2025
Le Vatican Terrain De Tensions L Incident Trump Macron
May 03, 2025
