The Impact Of Wildfires: Driving Record Levels Of Global Forest Loss
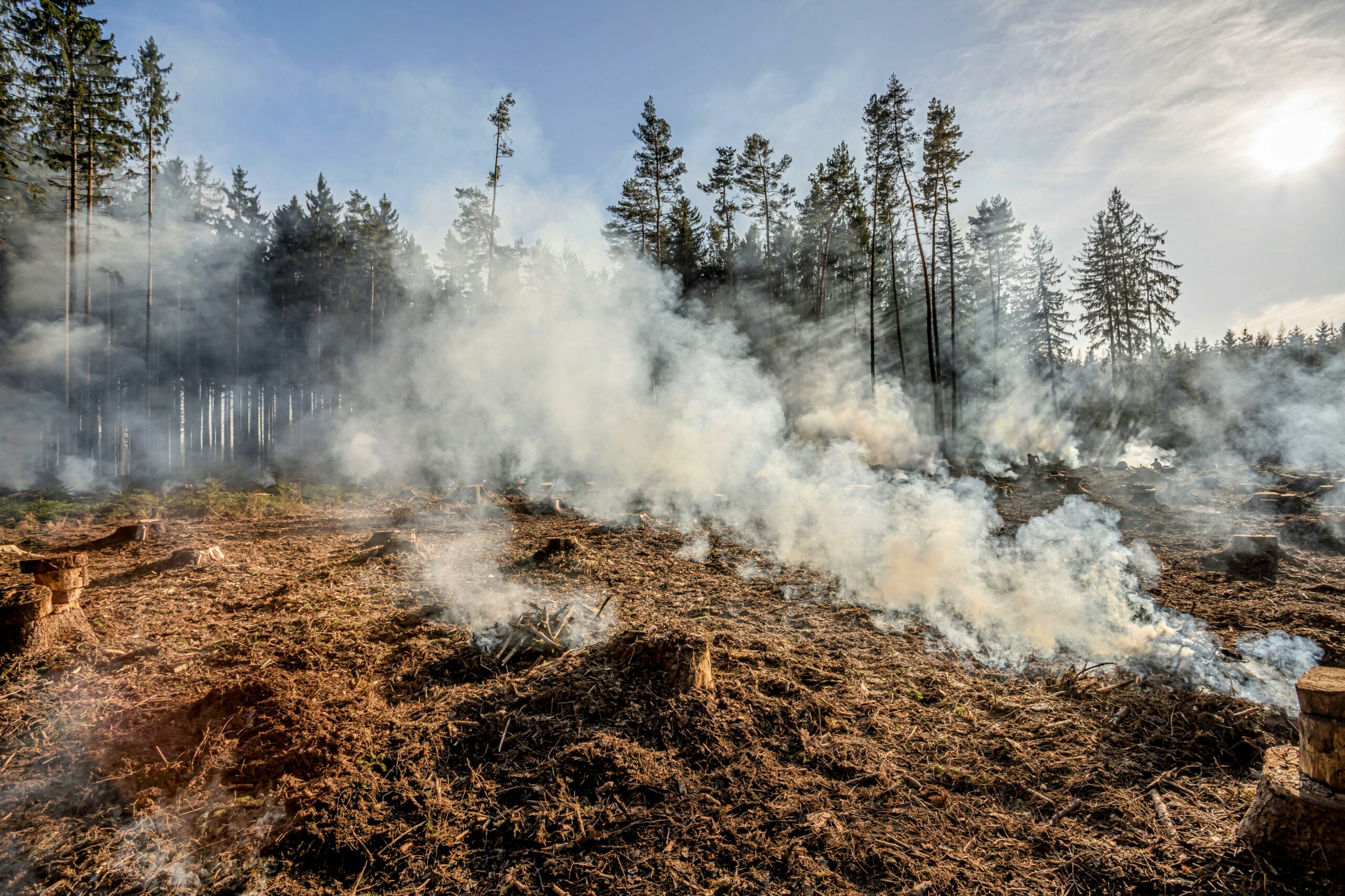

Table of Contents
The Devastating Scale of Wildfire-Induced Forest Loss
The scale of forest loss due to wildfires is alarming and continues to escalate. Global statistics paint a grim picture, revealing a dramatic increase in burned areas compared to previous decades. According to the Global Forest Watch, [insert relevant data and source here, e.g., "an estimated X million hectares of forest were lost to wildfires in 2023, a Y% increase compared to the average of the previous decade." ], showcasing the severity of the situation.
- Specific examples of regions most impacted: The Amazon rainforest, Siberian forests, and the forests of California have experienced particularly devastating wildfires in recent years, resulting in significant habitat loss and biodiversity decline. Australia's bushfires in 2019-2020 also caused unprecedented damage.
- Types of forests affected: Both boreal forests (like those in Canada and Russia), temperate forests (like those in California and the Mediterranean), and tropical forests (like the Amazon) are increasingly vulnerable to intense and widespread wildfires.
- Quantify the loss: [Insert data on hectares or acres lost, citing sources]. This vast loss has profound long-term implications for the planet's ecosystems and climate.
The long-term implications of this loss are significant. Reduced carbon sequestration capacity exacerbates climate change, contributing to a vicious cycle of increased wildfire risk. The destruction of habitats leads to biodiversity loss, threatening countless plant and animal species. The impact of wildfires on global forest ecosystems is a critical concern for the future of our planet.
Contributing Factors to Increased Wildfire Severity and Frequency
The increased severity and frequency of wildfires are driven by a complex interplay of factors, primarily climate change and human activities.
Climate Change
Rising global temperatures, prolonged droughts, and altered precipitation patterns are creating ideal conditions for wildfires to ignite and spread rapidly.
- Increased frequency of heatwaves: More frequent and intense heatwaves dry out vegetation, turning forests into tinderboxes.
- Drier vegetation acting as fuel: Extended periods of drought leave forests vulnerable to even the smallest spark.
- Stronger winds spreading fires more rapidly: Climate change can also lead to more intense and unpredictable weather patterns, making wildfires harder to control.
Human Activities
Human actions significantly contribute to the increased wildfire risk.
- Deforestation and land-use change: The clearing of forests for agriculture, urbanization, and resource extraction reduces the natural barriers to wildfire spread.
- Suppression of natural fire regimes: In many regions, fire suppression policies have inadvertently led to the build-up of flammable underbrush, creating conditions for larger and more intense wildfires.
- Arson and accidental ignitions: Human negligence, through activities such as discarding cigarettes or improperly using equipment, remains a significant source of wildfire ignition.
These human activities are intrinsically linked to climate change, creating a dangerous feedback loop: deforestation contributes to greenhouse gas emissions, further exacerbating climate change and increasing the likelihood of wildfires.
The Ecological and Economic Consequences of Wildfire-Driven Forest Loss
The consequences of wildfire-driven forest loss are far-reaching, impacting both the environment and the economy.
Biodiversity Loss
Habitat destruction caused by wildfires leads to the loss of plant and animal species, some of which may face extinction.
- Impact on endangered species: Many endangered species rely on specific forest habitats, making them extremely vulnerable to wildfire impacts.
- Disruption of ecological processes: Wildfires disrupt crucial ecological processes, such as nutrient cycling and seed dispersal, harming overall ecosystem health.
- Loss of genetic diversity: The destruction of entire forest stands results in a significant loss of genetic diversity, reducing the resilience of remaining populations.
Economic Impacts
The economic costs associated with wildfires are staggering and extend far beyond the immediate damage.
- Cost of firefighting efforts: Suppression of large wildfires requires substantial financial resources and personnel.
- Economic losses in tourism and related industries: Wildfires can devastate tourism-dependent economies, impacting hotels, restaurants, and recreational activities.
- Displacement of communities: Wildfires often force people to evacuate their homes, leading to significant economic hardship and disruption.
The long-term economic consequences of reduced forest resources, including timber and non-timber forest products, are equally significant.
Mitigation and Adaptation Strategies to Combat Wildfire Impacts
Combating the impact of wildfires requires a multi-pronged approach focusing on prevention, mitigation, and climate change mitigation.
Prevention and Mitigation
Strategies to reduce wildfire risk include:
- Improved forest management practices: Controlled burns, thinning of dense vegetation, and the creation of firebreaks can help prevent the spread of wildfires.
- Early warning systems and rapid response: Investing in advanced technology and improving communication networks can facilitate quicker responses to wildfires.
- Public awareness campaigns: Educating the public about wildfire prevention and safe practices is crucial in reducing human-caused ignitions.
Climate Change Mitigation
Addressing climate change is paramount in reducing the severity and frequency of wildfires.
- Reducing greenhouse gas emissions: Transitioning to renewable energy sources, improving energy efficiency, and adopting sustainable land use practices are critical steps.
- Transitioning to renewable energy sources: Shifting away from fossil fuels towards cleaner energy sources is vital in mitigating climate change.
- Supporting international climate agreements: International cooperation and the implementation of effective climate policies are essential to tackle global warming.
The interconnectedness of climate action and wildfire prevention cannot be overstated. Addressing climate change is not merely an environmental issue; it is an essential element of a comprehensive strategy to reduce the devastating impact of wildfires.
Conclusion
The significant scale of forest loss due to wildfires, driven by climate change and human activities, poses a severe threat to global ecosystems and economies. The resulting ecological damage, including biodiversity loss, and the economic consequences, including the costs of firefighting and economic disruption, underscore the urgency of the situation. Effective mitigation and adaptation strategies, including improved forest management, early warning systems, and, critically, climate change mitigation, are crucial for protecting our forests from further wildfire-induced destruction. Understanding the devastating impact of wildfires is crucial for safeguarding our planet's forests. Let's work together to combat the escalating threat and protect our invaluable forest ecosystems through wildfire prevention, forest conservation, and climate change mitigation.

Featured Posts
-
 Today Show Host Dylan Dreyer A Look At Her Near Career Setback
May 23, 2025
Today Show Host Dylan Dreyer A Look At Her Near Career Setback
May 23, 2025 -
 Curran Anticipates A Difficult Bd Rollout
May 23, 2025
Curran Anticipates A Difficult Bd Rollout
May 23, 2025 -
 Freepoint Eco Systems And Ing Partner On Project Finance Initiative
May 23, 2025
Freepoint Eco Systems And Ing Partner On Project Finance Initiative
May 23, 2025 -
 Big Rig Rock Report 3 12 X101 5 Radio Show Recap
May 23, 2025
Big Rig Rock Report 3 12 X101 5 Radio Show Recap
May 23, 2025 -
 Nisan Ayinda Hangi Burclar Zengin Olacak 2024 Tahmini
May 23, 2025
Nisan Ayinda Hangi Burclar Zengin Olacak 2024 Tahmini
May 23, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Commencement Speaker A World Famous Amphibian At University Of Maryland
May 23, 2025
Commencement Speaker A World Famous Amphibian At University Of Maryland
May 23, 2025 -
 Renowned Amphibian To Give Commencement Speech University Of Maryland
May 23, 2025
Renowned Amphibian To Give Commencement Speech University Of Maryland
May 23, 2025 -
 Kermits Words Of Wisdom University Of Maryland Commencement Speech Analysis
May 23, 2025
Kermits Words Of Wisdom University Of Maryland Commencement Speech Analysis
May 23, 2025 -
 University Of Maryland Graduation Kermit The Frogs Inspiring Speech
May 23, 2025
University Of Maryland Graduation Kermit The Frogs Inspiring Speech
May 23, 2025 -
 University Of Maryland Commencement A Celebrated Amphibian To Speak
May 23, 2025
University Of Maryland Commencement A Celebrated Amphibian To Speak
May 23, 2025
