The Rising Cost Of Groceries: Outpacing Inflation For Three Straight Months

Table of Contents
Factors Contributing to the Rising Cost of Groceries
Several interconnected factors contribute to the current surge in grocery prices. Understanding these elements is crucial to addressing the issue effectively.
Increased Energy Prices
Higher energy costs significantly impact the entire food system, from farm to table. This translates directly into higher grocery prices.
- Increased fuel costs for farming equipment: Farmers rely heavily on machinery, and the rising price of diesel fuel directly increases their operating costs.
- Transportation of goods: Getting food from farms to processing plants and finally to grocery stores requires significant energy. Increased fuel costs inflate these transportation expenses.
- Energy used in processing plants: Food processing is energy-intensive. Higher electricity and gas prices lead to higher production costs, ultimately passed on to consumers. For example, the price of diesel fuel, crucial for transporting produce, has increased by 25% in the last year, impacting the cost of fresh fruits and vegetables.
Supply Chain Disruptions
Ongoing supply chain issues continue to plague the food industry, limiting availability and driving up costs.
- Labor shortages: A lack of workers in various stages of the food supply chain, from farming to trucking, slows down the process and increases costs.
- Port congestion: Delays in unloading cargo at ports contribute to shortages and price increases, especially for imported food items.
- Weather-related disruptions to harvests: Extreme weather events can significantly impact crop yields, reducing supply and increasing prices. A recent report indicates that supply chain bottlenecks have contributed to a 15% increase in the price of certain imported goods.
Climate Change and Extreme Weather
Climate change and increasingly frequent extreme weather events are significantly impacting agricultural production.
- Droughts: Prolonged droughts reduce crop yields, leading to shortages and price hikes. The recent drought in California, for example, significantly impacted the price of almonds and other agricultural products.
- Floods: Heavy rainfall and flooding damage crops and disrupt transportation, further affecting supply and prices.
- Heatwaves: Extreme heat can severely damage crops, reducing yields and driving up prices.
Increased Demand and Inflation
Increased consumer demand, fueled partly by post-pandemic spending patterns, combined with general inflation, has further contributed to the rising cost of groceries.
- Post-pandemic spending patterns: Changes in consumer behavior, such as increased dining at home, have put more pressure on grocery stores.
- Global inflation impacting input costs: Inflation affects the cost of everything involved in producing and transporting food, from fertilizer to packaging. Grocery inflation currently sits at 10%, significantly higher than overall inflation, which stands at 7%.
Impact on Consumers and the Economy
The rising cost of groceries has significant repercussions for both consumers and the broader economy.
Financial Strain on Households
The escalating grocery bills place a considerable financial burden on many families.
- Reduced discretionary spending: Higher grocery costs force families to cut back on other expenses, impacting the overall economy.
- Food insecurity concerns: For low and middle-income families, the increasing grocery prices are a serious threat, leading to increased food insecurity. "It's getting harder and harder to make ends meet," says Sarah Miller, a single mother of two. "I'm constantly having to make difficult choices about what to buy."
Economic Ripple Effects
The rising cost of groceries creates wider economic consequences.
- Increased consumer price index (CPI): Higher grocery prices contribute to a higher overall CPI, potentially leading to further interest rate hikes.
- Potential for reduced consumer spending in other sectors: As families spend more on groceries, they have less money to spend on other goods and services, slowing economic growth. A recent study suggests a direct correlation between rising food prices and reduced consumer confidence. (Illustrative chart/graph would be inserted here)
Strategies for Managing Rising Grocery Costs
There are strategies both individuals and governments can employ to mitigate the impact of rising grocery costs.
Smart Shopping Techniques
Consumers can implement various smart shopping strategies to save money on groceries.
- Meal planning: Careful planning ensures you buy only what you need, reducing waste and saving money.
- Using coupons and loyalty programs: Take advantage of discounts and special offers to lower your grocery bill.
- Comparing prices: Shop around and compare prices between different stores and brands to find the best deals.
- Buying in bulk (when appropriate): Purchasing larger quantities can sometimes save money, but only if you can use it before it spoils.
- Choosing store brands: Generic or store brands often offer significant savings compared to name brands.
Government Interventions
Governments can play a crucial role in addressing the rising cost of groceries.
- Subsidies: Government subsidies can help reduce the cost of essential food items for consumers.
- Food assistance programs: Expanding access to food banks and other assistance programs can help vulnerable populations.
- Price controls (if applicable): In extreme cases, temporary price controls may be considered to prevent excessive price gouging.
Conclusion: The Rising Cost of Groceries: Finding Solutions and Strategies
The rising cost of groceries is a complex issue driven by a combination of increased energy prices, supply chain disruptions, climate change, and general inflation. This surge in prices significantly impacts consumers, leading to financial strain and reduced spending in other sectors. Smart shopping techniques, along with potential government interventions, are crucial in mitigating this challenge. Understanding the factors driving the rising cost of groceries is crucial for implementing effective strategies to manage your budget. Stay informed about price changes and employ the smart shopping techniques discussed to navigate this challenging economic climate.

Featured Posts
-
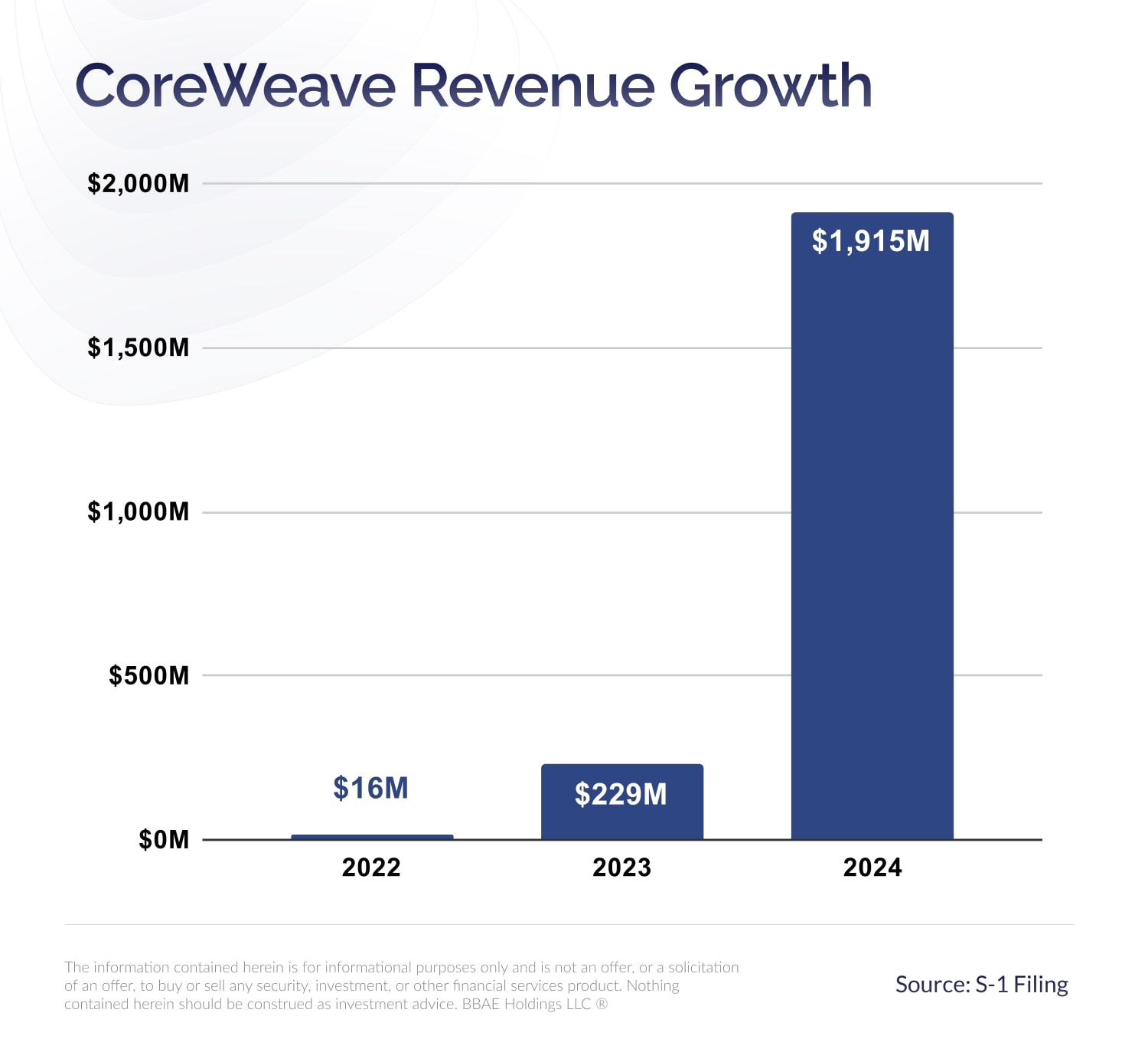 Why Did Core Weave Crwv Stock Price Increase Significantly On Thursday
May 22, 2025
Why Did Core Weave Crwv Stock Price Increase Significantly On Thursday
May 22, 2025 -
 Peppa Pigs Mums Stylish London Gender Reveal Party
May 22, 2025
Peppa Pigs Mums Stylish London Gender Reveal Party
May 22, 2025 -
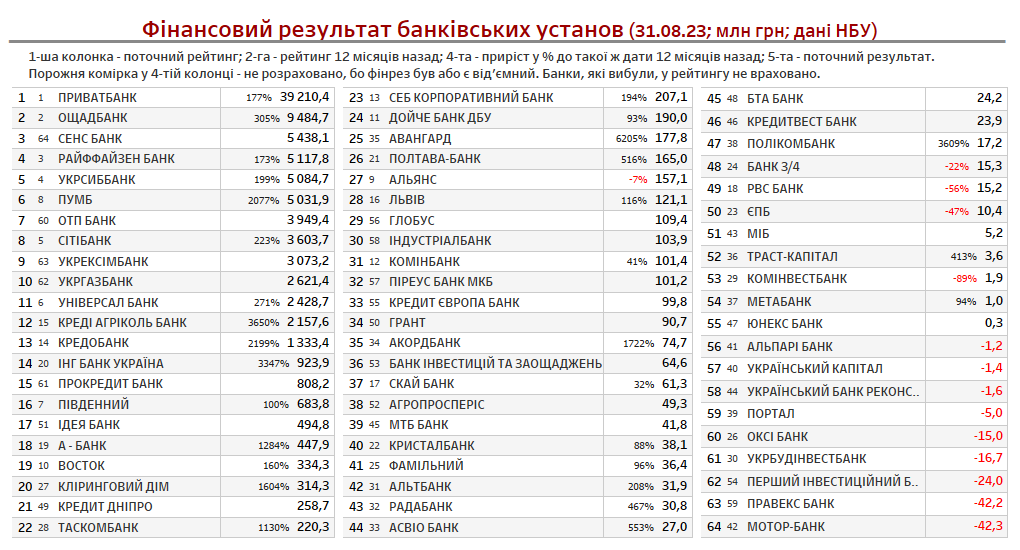 Reyting Finansovikh Kompaniy Ukrayini 2024 Credit Kasa Finako Ukrfinzhitlo Atlana Ta Credit Plus Lidiruyut Za Dokhodami
May 22, 2025
Reyting Finansovikh Kompaniy Ukrayini 2024 Credit Kasa Finako Ukrfinzhitlo Atlana Ta Credit Plus Lidiruyut Za Dokhodami
May 22, 2025 -
 Rising Grocery Costs A Third Month Of Outpacing Inflation
May 22, 2025
Rising Grocery Costs A Third Month Of Outpacing Inflation
May 22, 2025 -
 Les Grands Fusains De Boulemane Discussion Au Book Club Le Matin
May 22, 2025
Les Grands Fusains De Boulemane Discussion Au Book Club Le Matin
May 22, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Route 581 Closure Box Truck Crash Causes Major Delays
May 22, 2025
Route 581 Closure Box Truck Crash Causes Major Delays
May 22, 2025 -
 Used Car Dealership Fire Extensive Damage Reported
May 22, 2025
Used Car Dealership Fire Extensive Damage Reported
May 22, 2025 -
 Firefighters Respond To Major Used Car Lot Fire
May 22, 2025
Firefighters Respond To Major Used Car Lot Fire
May 22, 2025 -
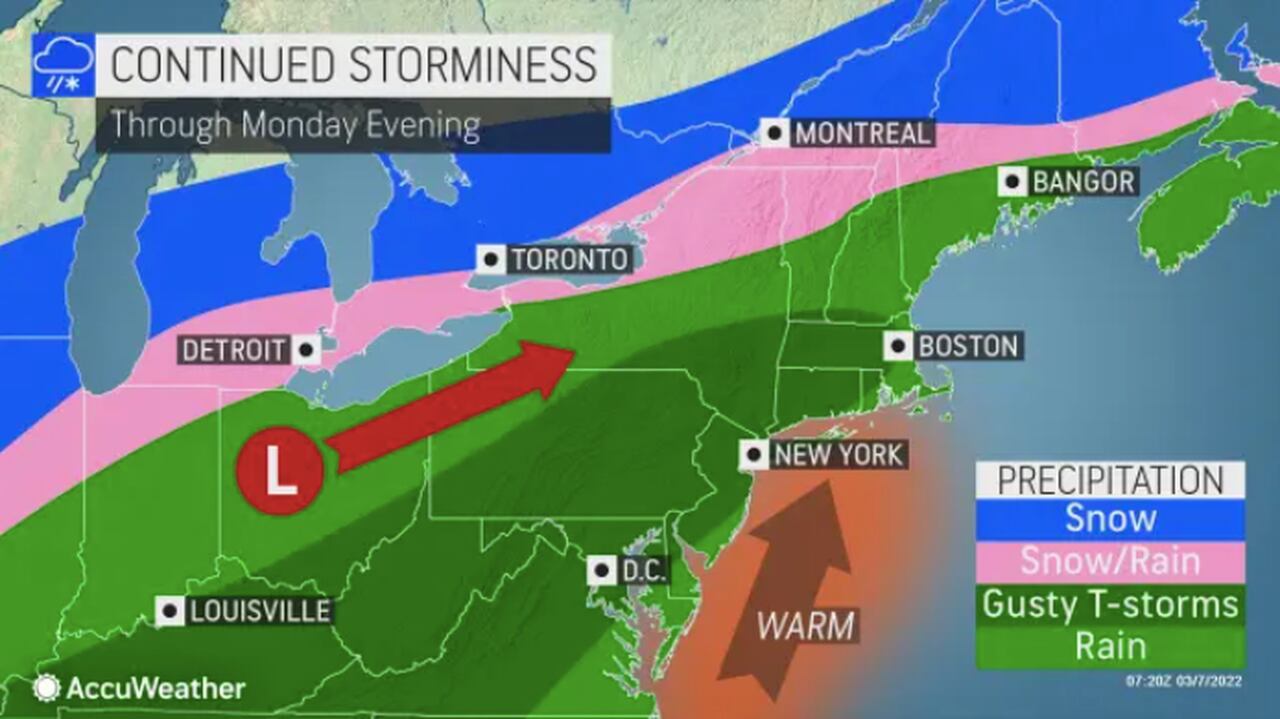 Pennsylvania Severe Thunderstorm Warning And Watch Information
May 22, 2025
Pennsylvania Severe Thunderstorm Warning And Watch Information
May 22, 2025 -
 Shooting In Lancaster County Police Release Update On Investigation
May 22, 2025
Shooting In Lancaster County Police Release Update On Investigation
May 22, 2025
