The Undervalued Asset: How Middle Managers Benefit Companies And Employees
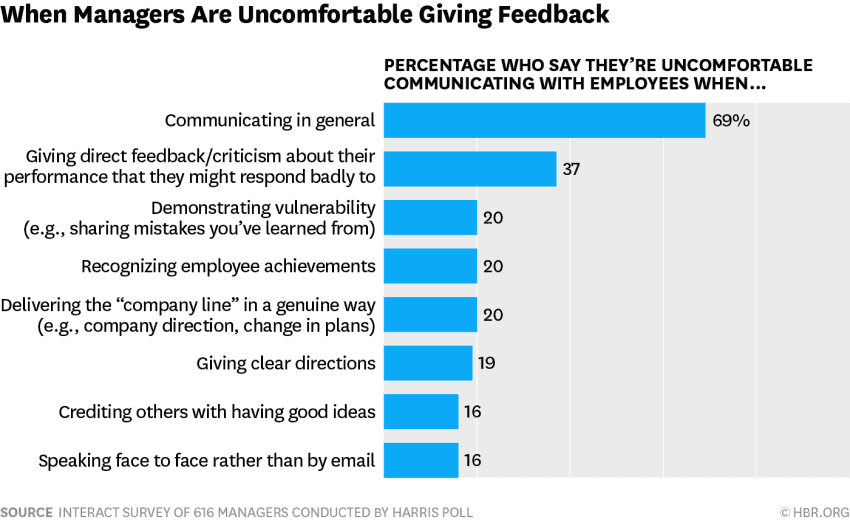
Table of Contents
Bridging the Gap: How Middle Managers Facilitate Communication and Collaboration
Middle managers play a crucial role in ensuring effective communication and collaboration throughout an organization. They act as the vital link between upper management and frontline employees, facilitating a two-way flow of information.
Improved Communication Flow
Middle managers translate complex strategic goals from upper management into actionable tasks for their teams. This ensures everyone understands their role in achieving overarching objectives. Conversely, they effectively relay employee feedback, concerns, and suggestions to upper management, providing valuable insights and preventing potential issues from escalating.
- Example: A middle manager might break down a large-scale project into smaller, manageable tasks for individual team members, providing clear guidelines and expectations.
- Example: A middle manager might identify recurring complaints about a specific process from their team and bring it to the attention of senior leadership, leading to process improvements.
Enhanced Collaboration and Teamwork
Middle managers are instrumental in fostering a collaborative and supportive work environment. They facilitate team meetings, resolve conflicts, and actively promote a positive team dynamic. This nurturing environment improves overall team performance and morale.
- Example: Middle managers can organize team-building activities to strengthen relationships and improve communication among team members.
- Example: They can mediate disagreements, providing fair and constructive solutions that benefit the entire team. This demonstrates strong leadership and conflict resolution skills.
Driving Efficiency and Productivity: The Operational Expertise of Middle Managers
Middle managers possess deep operational expertise, allowing them to significantly enhance efficiency and productivity within their teams. Their understanding of daily operations allows for effective process improvement and performance monitoring.
Streamlining Processes and Workflow
By closely monitoring workflows, middle managers identify bottlenecks and inefficiencies. They then implement improvements, such as optimizing processes, introducing new technologies, and providing necessary training, resulting in significant gains in productivity.
- Example: A middle manager might identify a redundant step in a workflow and eliminate it, saving time and resources.
- Example: They might introduce project management software to improve team coordination and task tracking.
Performance Monitoring and Improvement
Middle managers are responsible for tracking team performance against established goals. They provide regular feedback, address performance issues, and implement corrective actions, ensuring consistent high performance within their teams.
- Example: Setting SMART (Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, Time-bound) goals for team members and regularly monitoring progress.
- Example: Identifying underperforming employees and providing them with support and training to help them improve.
Empowering Employees and Fostering Development: The Human Capital Impact of Middle Managers
Middle managers play a crucial role in developing and motivating their teams. Their leadership directly impacts employee engagement and retention.
Employee Training and Development
Middle managers are key to employee growth. They provide mentorship, coaching, and identify opportunities for skill development, ultimately contributing to a more skilled and engaged workforce.
- Example: Providing regular feedback and coaching sessions to help employees improve their skills and performance.
- Example: Identifying training needs and arranging relevant training opportunities for team members.
Employee Motivation and Engagement
By creating a positive and supportive work environment, middle managers boost employee morale and engagement. This includes recognizing and rewarding achievements and fostering an inclusive culture.
- Example: Recognizing and celebrating team successes and individual contributions.
- Example: Promoting open communication and ensuring that all team members feel valued and respected.
Strategic Thinking and Problem Solving: The Value of Middle Management Insight
Middle managers are not just operational executors; they are strategic thinkers who contribute significantly to the overall success of the organization.
Identifying and Addressing Challenges
Middle managers are often the first to identify potential problems or roadblocks within their teams or departments. Their proximity to day-to-day operations allows them to proactively address these issues before they escalate into larger problems.
Contributing to Strategic Planning
Their hands-on experience and deep understanding of operational realities provide invaluable input during strategic planning processes. Middle managers can offer realistic assessments of the feasibility and potential impact of strategic initiatives.
Adaptability and Innovation
Middle managers are on the front lines of change, constantly adapting to new challenges and implementing innovative solutions to improve efficiency and effectiveness. This adaptability is crucial in today's dynamic business environment.
Conclusion: Rethinking the Value of Middle Managers – An Untapped Resource
Middle managers are far more than simply a layer of management; they are essential drivers of communication, efficiency, employee development, and strategic thinking. Their undervaluation represents a significant missed opportunity for organizations. To unlock the full potential of your company, you must invest in your middle managers, provide them with the resources and support they need, and empower them to lead and innovate. Recognize the value of your middle managers, empower your middle management team, and invest in their development. By doing so, you will not only enhance your company's performance but also foster a more engaged and productive workforce.

Featured Posts
-
 Ftcs Antitrust Case Against Meta A Defensive Shift
May 18, 2025
Ftcs Antitrust Case Against Meta A Defensive Shift
May 18, 2025 -
 Sydney Crown Property Acquired By Air Trunk Billionaire Second Luxurious Investment
May 18, 2025
Sydney Crown Property Acquired By Air Trunk Billionaire Second Luxurious Investment
May 18, 2025 -
 The Zuckerberg Trump Dynamic Impact On Tech And Society
May 18, 2025
The Zuckerberg Trump Dynamic Impact On Tech And Society
May 18, 2025 -
 Meta Faces Ftc Defense In Antitrust Case
May 18, 2025
Meta Faces Ftc Defense In Antitrust Case
May 18, 2025 -
 Unlocking Potential The Value Of Middle Managers In Todays Workplace
May 18, 2025
Unlocking Potential The Value Of Middle Managers In Todays Workplace
May 18, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Analyzing Michael Confortos Early Season Performance And Improvement
May 18, 2025
Analyzing Michael Confortos Early Season Performance And Improvement
May 18, 2025 -
 Dodgers Beat Mariners 6 4 Confortos First Home Run For La
May 18, 2025
Dodgers Beat Mariners 6 4 Confortos First Home Run For La
May 18, 2025 -
 Confortos Spring Training Struggles A Look At His Recovery
May 18, 2025
Confortos Spring Training Struggles A Look At His Recovery
May 18, 2025 -
 Confortos Dodgers Debut Can He Follow Hernandezs Lead
May 18, 2025
Confortos Dodgers Debut Can He Follow Hernandezs Lead
May 18, 2025 -
 Michael Confortos Hot Streak Continues In Dodgers Victory Over Mariners
May 18, 2025
Michael Confortos Hot Streak Continues In Dodgers Victory Over Mariners
May 18, 2025
