Transferred And Archived: Managing Your Data Lifecycle
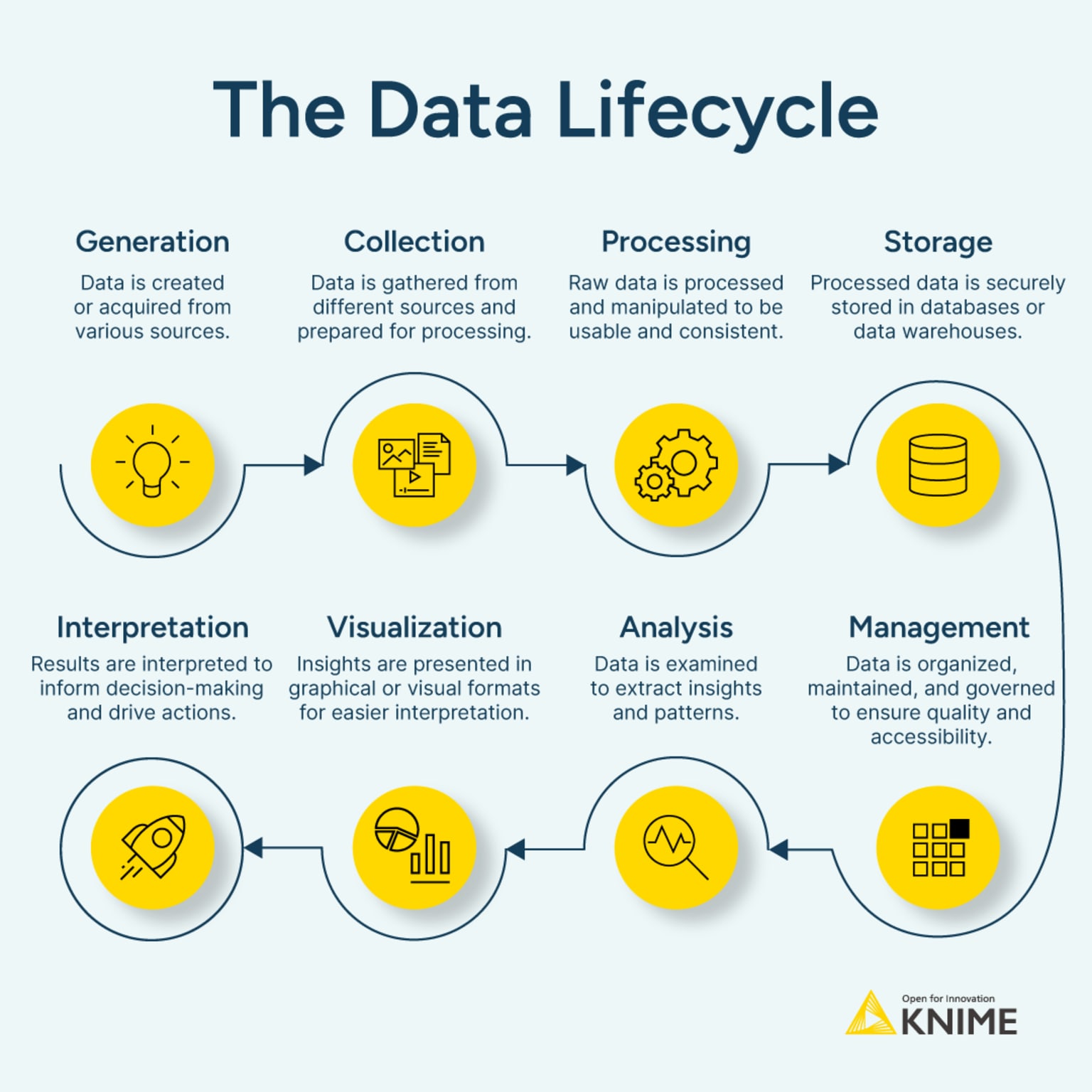
Table of Contents
Understanding the Data Lifecycle Stages
A comprehensive understanding of the data lifecycle is the cornerstone of effective data management. This lifecycle typically comprises five key stages: creation, storage, use, archiving, and deletion. Careful planning for each stage is crucial for efficient information lifecycle management.
- Creation: Data is generated from various sources, including databases, applications, sensors, and user interactions. Understanding the origin and nature of your data is the first step towards effective management.
- Storage: Active data, frequently accessed for business operations, resides in primary storage systems such as databases, servers, and cloud storage. This stage requires careful consideration of storage capacity, performance, and security.
- Use: Data is accessed and utilized for various business functions, from reporting and analytics to decision-making and operational processes. Efficient data access is critical for productivity and profitability.
- Archiving: Less frequently accessed data is moved to secondary storage, often referred to as "cold storage." This frees up space in primary storage and reduces costs. Effective data retention policies dictate which data should be archived and for how long. This stage is closely tied to data governance principles.
- Deletion: The final stage involves the secure and compliant disposal of data that is no longer needed. This requires adhering to strict data privacy regulations and implementing secure data deletion methods to prevent data breaches.
Effective Data Transfer Strategies
Moving data between different storage locations or systems is a crucial aspect of data lifecycle management. Effective data transfer strategies are essential for maintaining data integrity and ensuring business continuity. Several methods exist, each with its own advantages and disadvantages:
- Cloud Migration: Migrating data to cloud storage platforms like AWS, Azure, or GCP offers scalability, cost-effectiveness, and increased accessibility. However, careful planning is required to ensure a seamless and secure migration, including considerations for data security and compliance. This often utilizes specialized data migration tools.
- Data Replication: Creating copies of data across multiple locations ensures data redundancy and high availability. This is crucial for business continuity in case of primary system failures. Data synchronization tools are instrumental in maintaining consistency across replicated datasets.
- Database Transfers: Moving data between different database systems requires specialized tools and expertise. This process must ensure data integrity and minimize downtime. Considerations include schema mapping, data transformation, and testing. The security of the secure data transfer process is paramount.
Optimal Data Archiving Techniques
Choosing the right archiving method is critical for cost-effectiveness, data accessibility, and compliance. Several options exist:
- Cloud Archiving: Cloud providers offer cost-effective long-term storage solutions, often utilizing object storage. This is an ideal option for large volumes of infrequently accessed data.
- Tape Archiving: Magnetic tape remains a cost-effective solution for archiving massive datasets that are rarely accessed. However, access times are significantly slower compared to other methods.
- Disk Archiving: Disk-based archiving provides faster access times than tape but can be more expensive for large volumes of data. This is a suitable option for data requiring more frequent retrieval. This often involves robust data warehousing solutions.
Data Security and Compliance in Archiving
Data security and compliance are paramount throughout the archiving process. Best practices include:
- Data Encryption: Encrypting data both in transit and at rest protects sensitive information from unauthorized access.
- Access Control: Implementing robust access control mechanisms ensures that only authorized personnel can access archived data. This aligns with principles of data governance.
- Compliance Regulations: Adhering to relevant regulations, such as GDPR and CCPA, is crucial for avoiding penalties and maintaining customer trust. This includes implementing measures for data loss prevention. Meeting regulatory compliance is non-negotiable.
Conclusion
Effective data lifecycle management, encompassing efficient data transfer and archiving techniques, is vital for organizations of all sizes. Careful planning, robust security measures, and strict adherence to compliance regulations are essential at each stage. A well-defined strategy yields significant benefits, including cost savings, improved operational efficiency, enhanced data accessibility, and minimized compliance risks. Implement a robust data lifecycle management strategy today to optimize your organization's data handling processes and drive sustainable business growth. Learn more about best practices for [link to relevant resource/service on data lifecycle management]. Don't let inefficient data lifecycle management hinder your business growth – take control of your data today.

Featured Posts
-
 Lotto Results Your Guide To Lotto Lotto Plus 1 And Lotto Plus 2
May 08, 2025
Lotto Results Your Guide To Lotto Lotto Plus 1 And Lotto Plus 2
May 08, 2025 -
 One Cryptocurrency Surviving The Trade War
May 08, 2025
One Cryptocurrency Surviving The Trade War
May 08, 2025 -
 Gary Neville Predicts Psg Vs Arsenal A Tense Encounter
May 08, 2025
Gary Neville Predicts Psg Vs Arsenal A Tense Encounter
May 08, 2025 -
 Arsenal Ps Zh Istoriya Protivostoyaniy V Evrokubkakh
May 08, 2025
Arsenal Ps Zh Istoriya Protivostoyaniy V Evrokubkakh
May 08, 2025 -
 Sms Dolandiriciligi Sikayetlerinde Artis Son Dakika Gelismeleri
May 08, 2025
Sms Dolandiriciligi Sikayetlerinde Artis Son Dakika Gelismeleri
May 08, 2025
