U.S. GDP Falls 0.2%: Impact Of Reduced Spending And Tariffs
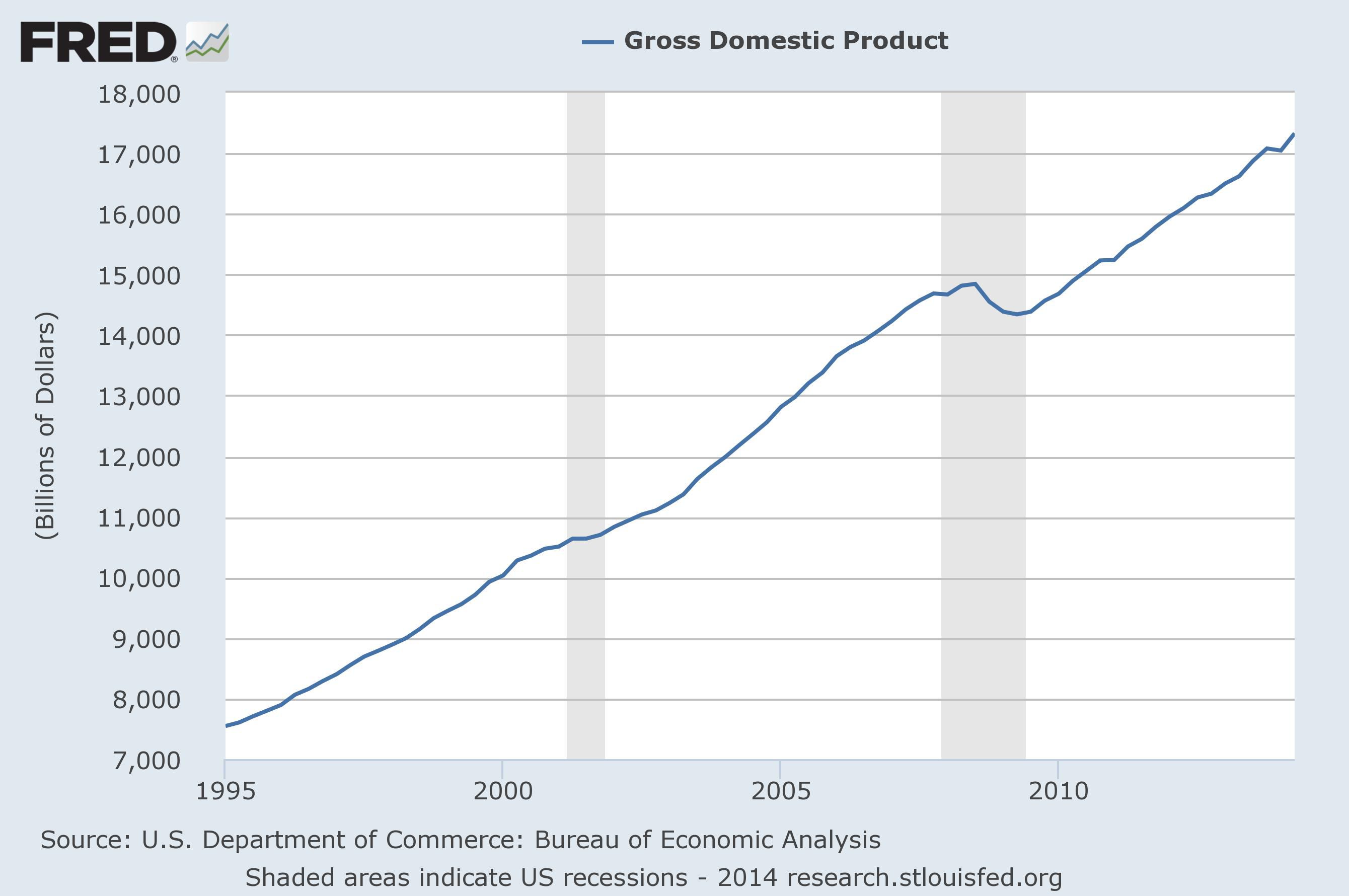
Table of Contents
Reduced Consumer Spending: A Major Contributor to GDP Decline
Weakening Consumer Confidence
Several factors have contributed to a decline in consumer confidence, leading to reduced spending. Inflation, persistently high interest rates, and lingering uncertainty about the future economic outlook have all played a role. Consumers are tightening their belts, leading to decreased spending across various sectors.
- Reduced spending on durable goods: Purchases of large appliances, vehicles, and furniture have significantly decreased.
- Lower retail sales: Data shows a notable downturn in retail sales across multiple categories, reflecting decreased consumer purchasing power.
- Increased savings rates: Many consumers are prioritizing saving rather than spending, further impacting GDP growth.
According to the Bureau of Economic Analysis, consumer spending, which accounts for roughly 70% of U.S. GDP, experienced a notable contraction during the relevant period. This decline directly translates to a significant drop in overall economic output.
Impact on Various Economic Sectors
The ripple effects of reduced consumer spending are felt across numerous sectors. Industries heavily reliant on consumer demand are experiencing substantial slowdowns.
- Manufacturing: Reduced demand for consumer goods has led to decreased production and potential job losses in the manufacturing sector.
- Retail and hospitality: These industries are particularly vulnerable, with reduced foot traffic and lower sales impacting businesses of all sizes.
- Service industries: Even service sectors, such as entertainment and recreation, are experiencing a slowdown as consumers cut back on discretionary spending.
The decrease in consumer confidence is reflected in various economic indicators, such as the Consumer Sentiment Index, which has shown a consistent decline in recent months, indicating a pessimistic outlook among consumers regarding the economy.
Government Policies and Consumer Spending
Government policies, both fiscal and monetary, play a crucial role in influencing consumer spending and economic growth. Stimulus packages and adjustments to interest rates can impact consumer behavior and overall economic activity.
- Tax cuts: Targeted tax cuts could potentially boost disposable income and encourage consumer spending.
- Interest rate adjustments: Lowering interest rates can make borrowing more attractive, stimulating investment and consumption.
- Direct financial assistance: Programs providing direct financial assistance to households can help bolster consumer spending.
However, the effectiveness of these interventions depends on various factors, including the overall economic climate and the specific design of the policies. The impact of recent government interventions on consumer spending requires ongoing assessment.
The Impact of Tariffs on U.S. GDP
Trade Wars and Economic Slowdown
The imposition of tariffs has disrupted global trade and significantly impacted U.S. businesses. These tariffs increase the cost of imported goods, leading to higher prices for consumers and decreased competitiveness for U.S. businesses.
- Increased import prices: Tariffs on goods from specific countries directly lead to increased prices for consumers.
- Reduced export competitiveness: Retaliatory tariffs from other countries make U.S. exports more expensive in foreign markets.
- Disruption of supply chains: Tariffs can complicate and increase costs within already-complex global supply chains.
Data from the U.S. Census Bureau reveals a significant decline in trade volumes following the imposition of certain tariffs, illustrating their negative impact on economic activity.
Supply Chain Disruptions and Inflation
Tariffs contribute significantly to supply chain disruptions, exacerbating inflationary pressures. Increased import costs are passed down the chain, leading to higher production costs and ultimately, higher prices for consumers.
- Increased production costs: Businesses face higher input costs due to tariffs, forcing them to raise prices or cut production.
- Reduced consumer purchasing power: Higher prices erode consumer purchasing power, leading to a further decrease in consumer spending.
- Wage stagnation: The combined effects of inflation and reduced consumer spending can lead to wage stagnation, further hindering economic growth.
The link between tariffs, supply chain disruptions, and inflation is evident in rising consumer prices across various sectors.
Retaliatory Tariffs and Their Consequences
Retaliatory tariffs imposed by other countries in response to U.S. tariffs have further damaged the U.S. economy. These countermeasures decrease demand for U.S. exports, hurting American businesses and workers.
- Reduced U.S. exports: Retaliatory tariffs lead to a decline in the demand for U.S. goods in foreign markets.
- Job losses in export-oriented sectors: Industries relying heavily on exports are particularly vulnerable to these retaliatory measures.
- Increased trade tensions: Escalating trade conflicts create uncertainty and hinder overall economic growth.
Statistics showing the decline in U.S. exports to countries that have imposed retaliatory tariffs highlight the detrimental effects of these trade disputes.
Other Contributing Factors to the GDP Decline (Optional)
While reduced consumer spending and tariffs are the primary drivers of the recent GDP decline, other factors also contributed. Global economic uncertainty, geopolitical instability, and unforeseen events like natural disasters can all impact economic growth. However, their relative contribution to the 0.2% drop is significantly less than the impact of reduced consumer spending and tariffs.
Conclusion: Understanding and Addressing the U.S. GDP Decline
The 0.2% drop in U.S. GDP underscores the significant impact of reduced consumer spending and tariffs on the U.S. economy. These intertwined factors have created a challenging environment for businesses and consumers alike. The future trajectory of the U.S. economy depends on addressing these underlying issues. Possible scenarios include further contraction if these trends persist, or a potential recovery depending on policy responses and shifts in consumer confidence. Understanding the interplay between consumer spending, tariffs, and overall economic growth is crucial for informed decision-making. Stay updated on the latest developments regarding the U.S. GDP and its key influencing factors. The ongoing impact of reduced spending and tariffs on the U.S. GDP requires close monitoring and proactive strategies to mitigate further negative consequences.

Featured Posts
-
 Orange County Friday May 23rd Scores And Player Stats
May 31, 2025
Orange County Friday May 23rd Scores And Player Stats
May 31, 2025 -
 Zverevs Indian Wells Loss A Griekspoor Masterclass
May 31, 2025
Zverevs Indian Wells Loss A Griekspoor Masterclass
May 31, 2025 -
 Miley Cyrus Syytetaeaen Edelleen Bruno Marsin Musiikin Kopioinnista
May 31, 2025
Miley Cyrus Syytetaeaen Edelleen Bruno Marsin Musiikin Kopioinnista
May 31, 2025 -
 Creating Voice Assistants Made Easy Open Ais 2024 Announcement
May 31, 2025
Creating Voice Assistants Made Easy Open Ais 2024 Announcement
May 31, 2025 -
 Up To 30 Off Your Luxurious Spring Hotel Awaits
May 31, 2025
Up To 30 Off Your Luxurious Spring Hotel Awaits
May 31, 2025
