Uncertainty Rises: Inflation And Unemployment Risks Elevate Economic Concerns
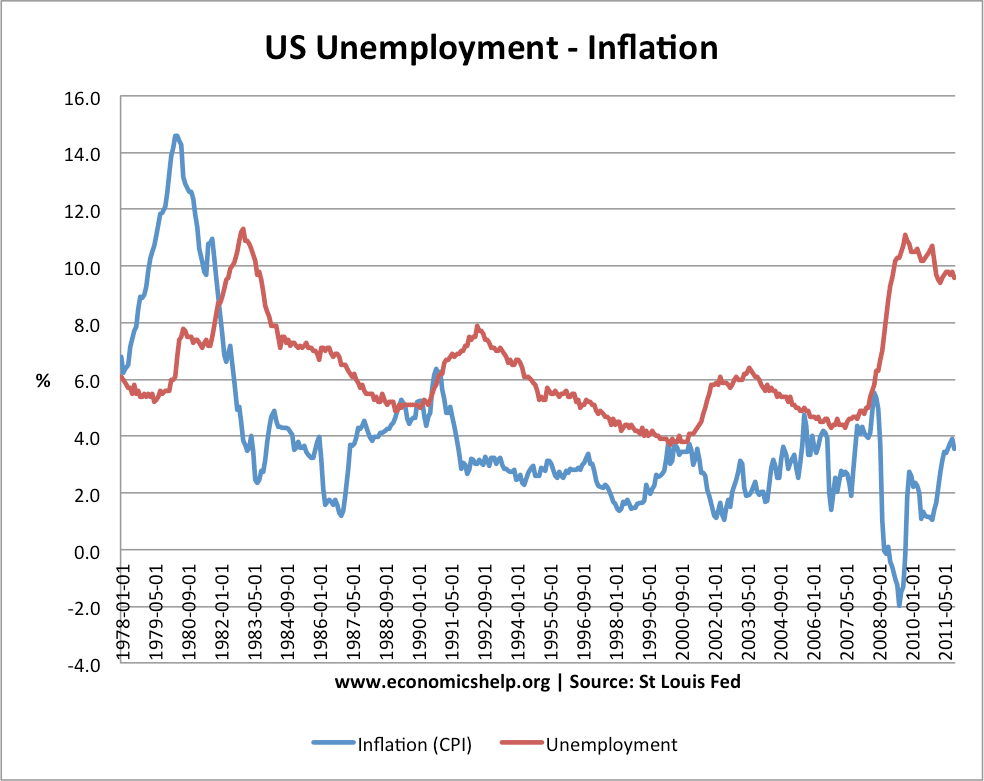
Table of Contents
Soaring Inflation: Eroding Purchasing Power and Stifling Growth
High inflation is a significant threat to economic stability, eroding purchasing power and stifling economic growth. Understanding its mechanics is crucial to addressing its impact.
Understanding the Inflationary Spiral
Inflation, a general increase in the price level of goods and services in an economy over a period of time, can stem from various sources. Demand-pull inflation arises when aggregate demand outpaces aggregate supply, driving up prices. Cost-push inflation, on the other hand, occurs when production costs increase, leading businesses to raise prices to maintain profitability.
- CPI (Consumer Price Index): Measures the average change in prices paid by urban consumers for a basket of consumer goods and services. A rising CPI indicates increasing inflation.
- PPI (Producer Price Index): Measures the average change in selling prices received by domestic producers for their output. A rising PPI often precedes increases in CPI.
- Examples of Rising Prices: Currently, we see significant price increases in energy (fuel, electricity), food staples (grain, meat, dairy), and housing, impacting household budgets dramatically. This reduction in real income directly affects consumer spending, creating a negative feedback loop.
The Impact on Businesses and Investment
High inflation significantly impacts businesses and investment decisions.
- Increased Production Costs: Businesses face higher costs for raw materials, energy, and labor, squeezing profit margins.
- Reduced Consumer Demand: As purchasing power declines, consumers reduce spending, impacting business revenue and potentially leading to job losses.
- Uncertainty in Planning and Investment: The unpredictable nature of high inflation makes it difficult for businesses to plan long-term investments and expansion strategies. Uncertainty surrounding future prices and costs creates hesitancy.
Government Responses to Inflation
Governments employ various strategies to combat inflation, primarily through monetary and fiscal policies.
- Interest Rate Hikes: Central banks raise interest rates to make borrowing more expensive, thus reducing demand and cooling down the economy. This, however, can have negative consequences on business investment and employment.
- Fiscal Policy Adjustments: Governments can implement fiscal measures like reducing government spending or increasing taxes to curb aggregate demand. This can be politically challenging and may negatively impact social programs and economic growth.
- Effectiveness and Trade-offs: The effectiveness of these policies depends on various factors, including the severity and cause of inflation. Often, there are trade-offs; for example, higher interest rates may control inflation but at the cost of higher unemployment.
Rising Unemployment: A Looming Shadow over Economic Stability
Alongside inflation, rising unemployment poses a severe threat to economic stability and social well-being.
Factors Contributing to Unemployment Increases
Several factors contribute to rising unemployment rates.
- Automation and Technological Advancements: Automation and technological advancements displace workers in various sectors, leading to job losses and requiring workforce retraining and adaptation.
- Economic Slowdowns and Recessions: Economic downturns significantly reduce business activity, leading to layoffs and increased unemployment.
- Global Events and Supply Chain Disruptions: Global events like pandemics or geopolitical conflicts can disrupt supply chains, impacting production and leading to job losses.
The Human Cost of Unemployment
Unemployment carries a heavy human cost, impacting individuals, families, and society as a whole.
- Poverty and Reduced Social Mobility: Job loss can lead to poverty, hindering social mobility and creating long-term economic hardship for individuals and their families.
- Mental Health Challenges: Unemployment is associated with increased stress, anxiety, and depression, impacting mental health significantly.
- Strain on Social Safety Nets: Increased unemployment strains social safety nets, such as unemployment benefits and social assistance programs.
Government Initiatives to Combat Unemployment
Governments implement various programs to mitigate unemployment.
- Job Training and Retraining Initiatives: These programs help workers acquire new skills to adapt to changing job market demands.
- Unemployment Benefits: These provide temporary financial assistance to unemployed individuals, helping them meet basic needs while seeking new employment.
- Infrastructure Investments: Government investments in infrastructure projects create jobs and stimulate economic growth. The effectiveness of these programs varies, and often depends on their design and implementation.
The Interplay Between Inflation and Unemployment: The Phillips Curve Revisited
The relationship between inflation and unemployment is complex and has been a central topic in macroeconomic analysis for decades, often visualized through the Phillips Curve.
Understanding the Trade-off
The Phillips curve traditionally suggests an inverse relationship between inflation and unemployment: low unemployment is associated with high inflation, and vice-versa. However, the curve's predictive power has limitations, especially in scenarios of stagflation.
- Stagflation: This is a period of slow economic growth, high unemployment, and high inflation—a situation that defies the traditional Phillips curve relationship.
- Historical Context: The Phillips curve's relevance has been challenged by historical events where high inflation and high unemployment occurred simultaneously.
- Limitations of the Curve: The curve simplifies a complex reality and doesn't always accurately predict economic outcomes.
Navigating the Complex Relationship
Policymakers face a significant challenge in balancing inflation control with maintaining employment levels.
- Difficulties in Implementing Effective Policies: The optimal mix of monetary and fiscal policies is highly context-dependent and often involves difficult trade-offs.
- Potential for Unintended Consequences: Policy interventions can have unintended consequences, exacerbating existing economic problems or creating new ones.
Conclusion
The intertwined risks of high inflation and rising unemployment present significant challenges to global economic stability. Understanding the causes, consequences, and interplay between these two economic forces is crucial for individuals, businesses, and policymakers. Staying informed about economic trends and indicators is vital. Seek professional financial advice to mitigate personal economic risks associated with inflation and unemployment. Continue monitoring key economic indicators like CPI and PPI, and explore resources from reputable financial institutions and government agencies for further reading on inflation and unemployment risks. Proactive planning and informed decision-making are key to navigating the uncertainties of the current economic climate.

Featured Posts
-
 Sustainable Urban Development In India Exploring Cool Materials For Heat Mitigation
May 30, 2025
Sustainable Urban Development In India Exploring Cool Materials For Heat Mitigation
May 30, 2025 -
 Schliessung Der Schwangerschaftsberatungsstellen Des Drk In Crivitz Und Sternberg
May 30, 2025
Schliessung Der Schwangerschaftsberatungsstellen Des Drk In Crivitz Und Sternberg
May 30, 2025 -
 Out Of State Registrations Maryland Residents And The Drain On Virginias Revenue
May 30, 2025
Out Of State Registrations Maryland Residents And The Drain On Virginias Revenue
May 30, 2025 -
 La Poderosa Frase Para Marcelo Rios El Ex Numero 3 Del Mundo Y Su Legado
May 30, 2025
La Poderosa Frase Para Marcelo Rios El Ex Numero 3 Del Mundo Y Su Legado
May 30, 2025 -
 Bts Jin Promises Fans A Swift Return Following Coldplay Seoul Show
May 30, 2025
Bts Jin Promises Fans A Swift Return Following Coldplay Seoul Show
May 30, 2025
