Unveiling The Wonder Of Animals: A Comprehensive Guide To The Animal Kingdom

Table of Contents
H2: Classifying the Animal Kingdom: A Look at Taxonomy
Understanding the Animal Kingdom begins with taxonomy, the science of classifying organisms. This involves organizing animals into hierarchical groups based on shared characteristics. The broadest categories are phyla, representing major evolutionary branches.
H3: The Major Phyla:
The Animal Kingdom encompasses a vast array of phyla, each with unique characteristics. Some of the most important include:
- Chordata: Animals possessing a notochord (a flexible rod supporting the body) at some point in their development. Examples include mammals, birds, reptiles, amphibians, and fish. [Link to Chordata information]
- Arthropoda: The largest phylum, characterized by segmented bodies, exoskeletons, and jointed appendages. This includes insects, arachnids (spiders, scorpions), crustaceans (crabs, lobsters), and myriapods (centipedes, millipedes). [Link to Arthropoda information]
- Mollusca: Soft-bodied animals, often with a shell. Examples include snails, slugs, clams, oysters, and octopuses. [Link to Mollusca information]
- Nematoda: Roundworms, found in various environments, many of which are parasitic. [Link to Nematoda information]
- Cnidaria: Aquatic animals with radial symmetry, including jellyfish, corals, and sea anemones. [Link to Cnidaria information]
H3: Evolutionary Relationships:
Understanding the evolutionary relationships within the Animal Kingdom is crucial. Phylogenetic trees visually represent these relationships, showing how different groups are related through common ancestry. Key evolutionary milestones, such as the development of multicellularity, bilateral symmetry, and segmented bodies, shaped the diversity we see today. The study of comparative anatomy, genetics, and embryology helps scientists reconstruct the evolutionary history of animals, revealing the fascinating connections between seemingly disparate species.
H2: Animal Habitats and Adaptations
Animals have conquered nearly every habitat on Earth, from the highest mountain peaks to the deepest ocean trenches. Their remarkable survival is a testament to their incredible adaptability.
H3: Terrestrial Habitats:
Terrestrial habitats, such as forests, deserts, and grasslands, present unique challenges. Animals have evolved diverse adaptations to thrive in these environments. For example:
- Camouflage: A chameleon changing color to blend with its surroundings.
- Hibernation: Bears sleeping through the winter to conserve energy.
- Water conservation: Camels storing water in their humps.
(Include relevant images here)
H3: Aquatic Habitats:
Aquatic animals face different challenges, including buoyancy, water pressure, and oxygen availability. Adaptations include:
- Gills: For extracting oxygen from water.
- Streamlined bodies: For efficient movement through water.
- Echolocation: Used by whales and dolphins to navigate and hunt.
The impact of pollution and climate change on aquatic animals is a serious concern, threatening the delicate balance of these ecosystems.
H3: Aerial Habitats:
Animals that have conquered the skies have evolved remarkable adaptations for flight, including:
- Wings: For generating lift and propulsion.
- Lightweight bones: Reducing weight for efficient flight.
- Powerful muscles: For generating the force needed for flight.
Aerial life presents challenges such as wind currents and the need for efficient energy use.
H2: Animal Behavior and Communication
Animal behavior is incredibly diverse and fascinating, shaped by evolution and environmental pressures.
H3: Social Behavior:
Animals exhibit a wide range of social structures:
- Solitary: Animals living alone, such as tigers.
- Social groups: Animals living in herds, flocks, or packs, such as elephants or wolves.
- Hierarchies: Animals with dominance structures, such as chimpanzees.
Animal communication is essential for social interactions and survival. Methods include pheromones, vocalizations, and body language.
H3: Foraging and Predation:
Animals employ diverse foraging strategies to obtain food, while predators have evolved sophisticated techniques to capture prey. Camouflage, mimicry, and other defensive mechanisms are crucial for survival. The predator-prey relationship drives co-evolution, where both predator and prey constantly adapt to each other.
H3: Reproduction and Life Cycles:
Animals employ diverse reproductive strategies, including sexual and asexual reproduction. Life cycles vary greatly, with some involving complete metamorphosis (e.g., butterflies) and others direct development (e.g., reptiles). Parental care varies extensively, ranging from no parental involvement to extensive investment in offspring.
H2: Conservation of the Animal Kingdom
The Animal Kingdom faces numerous threats, demanding urgent conservation efforts.
H3: Threats to Animal Populations:
Major threats to animal populations include:
- Habitat loss: Destruction and fragmentation of habitats due to deforestation, urbanization, and agriculture.
- Climate change: Altering habitats and disrupting ecosystems.
- Pollution: Contaminating environments and harming animals.
- Poaching: Illegal hunting and trade of wildlife.
Many species are endangered or threatened, highlighting the urgent need for conservation.
H3: Conservation Efforts:
Conservation strategies include:
- Protected areas: Establishing national parks and reserves to safeguard habitats.
- Captive breeding programs: Breeding endangered species in captivity to increase their numbers.
- Anti-poaching initiatives: Combating illegal wildlife trade.
Governments, organizations, and individuals play a crucial role in conservation. Supporting these efforts is vital for preserving the Animal Kingdom's biodiversity.
3. Conclusion:
This exploration of the Animal Kingdom has revealed its incredible diversity, complex adaptations, and fascinating behaviors. We have examined its classification, diverse habitats, intricate communication, and the pressing need for conservation. From the microscopic to the majestic, the animal kingdom is a testament to the power of evolution and the interconnectedness of life on Earth. Delve deeper into the wonders of the animal kingdom by exploring further resources, supporting conservation efforts, and appreciating the incredible biodiversity around us. Protecting this precious resource is not just essential for the animals themselves but for the health and well-being of our planet and future generations. The future of the animal kingdom depends on our collective action.

Featured Posts
-
 Cassie Announces Pregnancy Third Baby On The Way
May 13, 2025
Cassie Announces Pregnancy Third Baby On The Way
May 13, 2025 -
 The Impact Of Algorithmic Standards And Migration On The Post Quantum Cryptography Market 2030 Forecast
May 13, 2025
The Impact Of Algorithmic Standards And Migration On The Post Quantum Cryptography Market 2030 Forecast
May 13, 2025 -
 Pregnant Cassie And Husband Alex Fine Shine At Mob Land Premiere
May 13, 2025
Pregnant Cassie And Husband Alex Fine Shine At Mob Land Premiere
May 13, 2025 -
 Your Weekly Dose Of Efl Highlights Action And Analysis
May 13, 2025
Your Weekly Dose Of Efl Highlights Action And Analysis
May 13, 2025 -
 11 10 Defeat Dodgers Comeback Bid Falls Short
May 13, 2025
11 10 Defeat Dodgers Comeback Bid Falls Short
May 13, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Coinsilium Group Limited Forzas Gibraltar Launch Highlights
May 13, 2025
Coinsilium Group Limited Forzas Gibraltar Launch Highlights
May 13, 2025 -
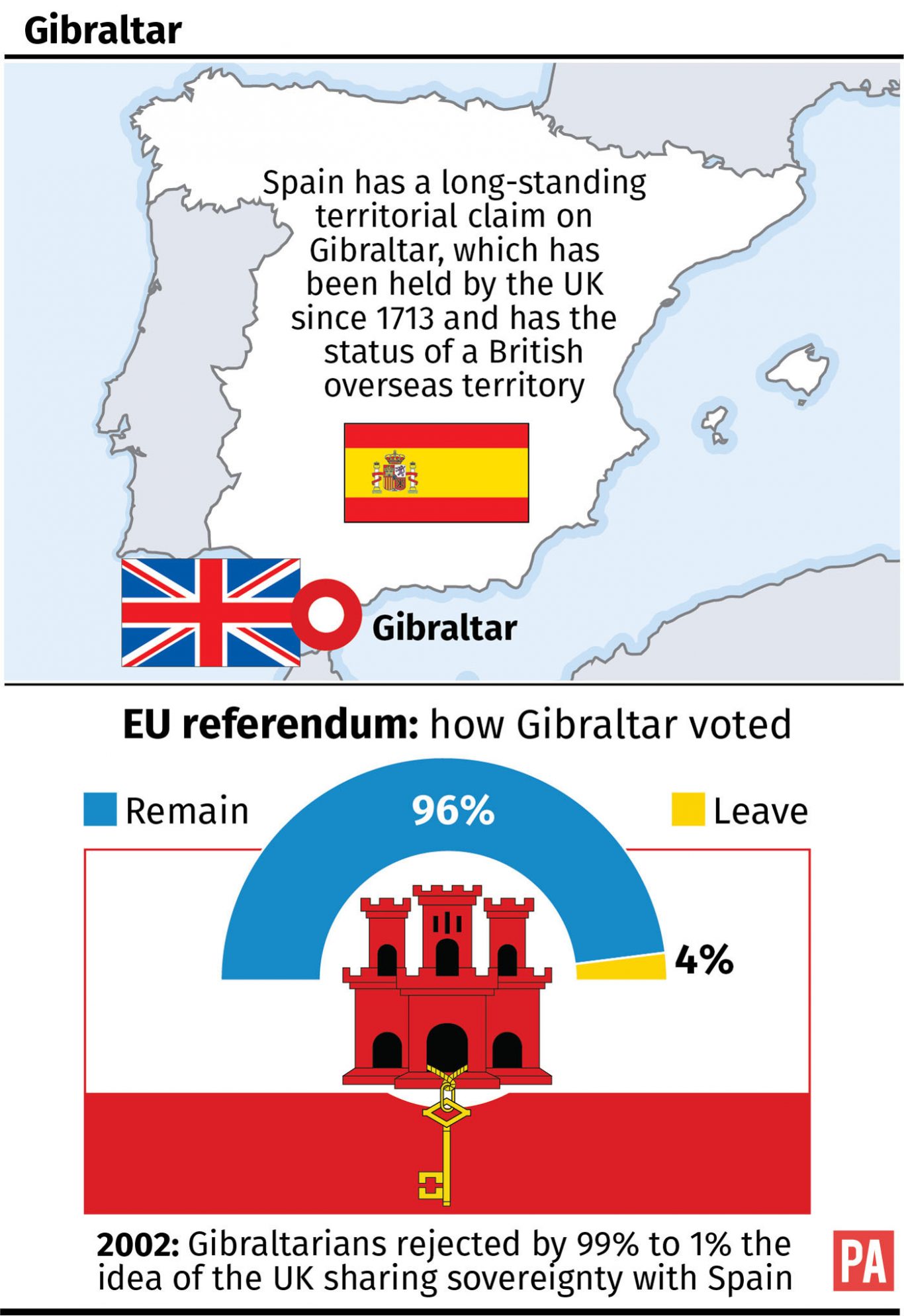 Brexits Gibraltar Problem Ongoing Negotiations And Uncertain Future
May 13, 2025
Brexits Gibraltar Problem Ongoing Negotiations And Uncertain Future
May 13, 2025 -
 Megalos Kataklysmos Mesogeioy Nea Dedomena Gia Tin Plimmyra
May 13, 2025
Megalos Kataklysmos Mesogeioy Nea Dedomena Gia Tin Plimmyra
May 13, 2025 -
 Un Accord Post Brexit Pour Gibraltar Perspectives Et Defis
May 13, 2025
Un Accord Post Brexit Pour Gibraltar Perspectives Et Defis
May 13, 2025 -
 Gibraltar And Brexit Unfinished Business And Stalled Talks
May 13, 2025
Gibraltar And Brexit Unfinished Business And Stalled Talks
May 13, 2025
