US Ban On Foreign Officials: Retaliation For Social Media Censorship

Table of Contents
The Rationale Behind US Sanctions for Social Media Censorship
The US government's justification for these sanctions rests on two primary pillars: protecting fundamental human rights and countering foreign influence and disinformation.
Protecting Free Speech and Human Rights
The core argument centers on safeguarding fundamental human rights, specifically freedom of expression, as enshrined in international declarations like the Universal Declaration of Human Rights and the International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights. Social media censorship, often employed by authoritarian regimes, directly violates these rights, silencing dissent and suppressing critical voices.
- Examples of human rights violations linked to social media censorship: The arbitrary detention of journalists and activists for online posts, the widespread blocking of websites and social media platforms, and the use of sophisticated surveillance technologies to monitor online activity.
- Detailed explanation: The ethical and moral imperative to defend freedom of expression is paramount. These sanctions represent a commitment to upholding universal human rights principles and holding perpetrators of these violations accountable. The US aims to signal that such actions will not be tolerated within the international community.
Countering Foreign Influence and Disinformation
Social media censorship is frequently used to manipulate public opinion and spread disinformation, impacting US national security interests. By controlling the information flow, authoritarian regimes can create a biased narrative, both domestically and internationally.
- Examples of foreign governments using social media censorship: State-sponsored campaigns to suppress narratives critical of government policies, the coordinated spread of propaganda and misinformation, and the silencing of opposition voices during elections or periods of social unrest. The role of social media in geopolitical conflicts is increasingly significant, making control over online narratives a key element of power projection.
- Detailed explanation: The manipulation of social media for disinformation campaigns undermines democratic processes both within the targeted countries and potentially within the US itself. Social media censorship is thus linked to broader concerns about foreign interference in democratic processes and the integrity of elections.
The Effectiveness of US Sanctions as a Deterrent
Assessing the effectiveness of US sanctions as a deterrent requires a nuanced analysis of both successes and failures.
Case Studies of Successful and Unsuccessful Sanctions
The impact of sanctions varies significantly depending on the specific context.
- Examples of countries where sanctions led to changes in censorship policies: While direct causal links are difficult to definitively establish, some instances suggest a correlation between sanctions and a subsequent easing of censorship or improved access to information. Further research is needed to establish causal relationships.
- Examples where they had little to no effect: In other cases, sanctions have proven ineffective due to the targeted country's economic resilience, its ability to find alternative sources of support, or the entrenched nature of the authoritarian regime. Sanctions may also be circumvented through sophisticated methods.
- Detailed explanation: Factors influencing effectiveness include the level of international cooperation (multilateral sanctions tend to be more effective), the economic strength of the targeted country, the nature of the regime (more authoritarian regimes are less susceptible), and the presence of alternative support networks.
Unintended Consequences and Limitations
While intending to promote free speech, sanctions can have unintended consequences.
- Potential for harming ordinary citizens: Sanctions can inadvertently harm ordinary citizens through economic hardship, limiting access to essential goods and services.
- The risk of escalating tensions: Sanctions may trigger retaliatory measures from the targeted government, escalating tensions and potentially harming diplomatic relations.
- The possibility of sanctions being circumvented: Authoritarian regimes may find ways to circumvent sanctions, rendering them ineffective in achieving their stated goals.
- Detailed explanation: The complex interplay between economic pressure and political change necessitates careful consideration of the potential unintended consequences. A nuanced approach is necessary to balance the goals of promoting human rights and avoiding further harm.
The Broader Implications for International Relations and the Fight Against Digital Authoritarianism
Addressing social media censorship requires a multi-faceted approach, going beyond unilateral sanctions.
The Role of International Cooperation
International collaboration is crucial in tackling the global challenge of social media censorship.
- Mention relevant international organizations and initiatives: The UN Human Rights Council, the Organization for Security and Co-operation in Europe (OSCE), and various NGOs actively working on digital rights and freedom of expression are key players.
- Detailed explanation: Multilateral approaches, involving coordinated action by multiple countries and international organizations, are likely to be more effective than unilateral sanctions. This would require a unified international stance against digital authoritarianism.
The Future of Digital Freedom in an Increasingly Connected World
The future of digital freedom faces significant challenges.
- Discuss emerging trends in digital censorship and counter-strategies: The development of sophisticated censorship technologies and the increasing use of artificial intelligence for surveillance necessitate the development of innovative counter-strategies.
- Consider the role of technology companies: Technology companies have a crucial role to play in protecting user data and promoting free speech online. However, their role is often controversial due to ethical and commercial concerns.
- Detailed explanation: The fight for digital freedom requires a long-term commitment, combining international cooperation, technological innovation, and strong advocacy for human rights. A multi-pronged approach is required to address the multifaceted nature of this global issue.
Conclusion
US sanctions targeting social media censorship aim to protect human rights and counter foreign influence. While their effectiveness varies, they highlight the growing concern over digital authoritarianism. The limitations of sanctions emphasize the need for international cooperation and a holistic approach involving governments, international organizations, and technology companies to safeguard digital freedom. Staying informed about the ongoing developments surrounding US sanctions on social media censorship, advocating for human rights, and promoting freedom of expression worldwide are crucial steps in this ongoing struggle. Further research into "US sanctions on social media censorship," "digital authoritarianism," and "international human rights law" will provide a deeper understanding of this critical issue.

Featured Posts
-
 French Far Left Seizes On Killing To Reignite Islamophobia Discussion
May 31, 2025
French Far Left Seizes On Killing To Reignite Islamophobia Discussion
May 31, 2025 -
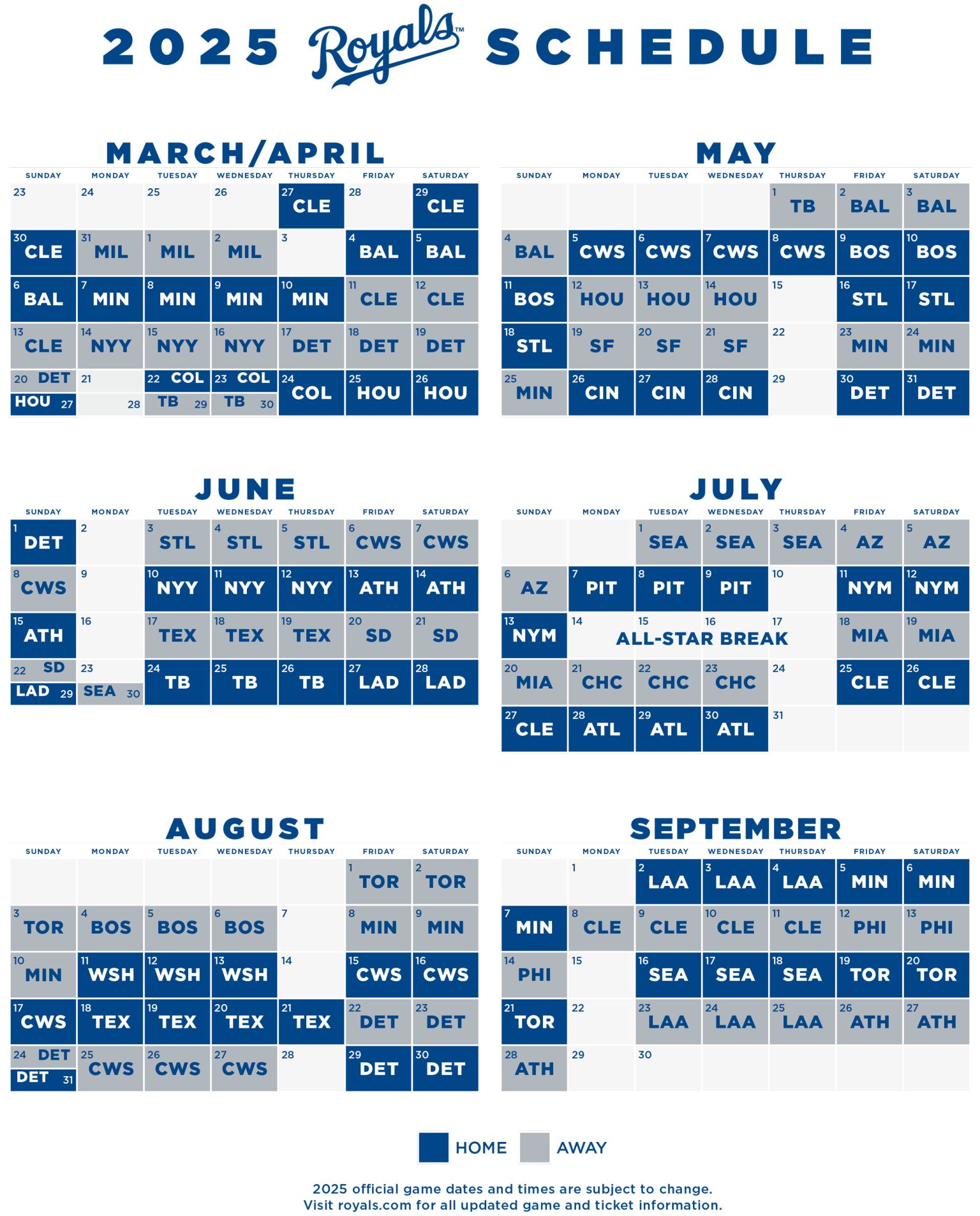 Full Kansas City Royals Game Schedule Kctv 5 And Cbs Broadcast Details
May 31, 2025
Full Kansas City Royals Game Schedule Kctv 5 And Cbs Broadcast Details
May 31, 2025 -
 Defining Your Good Life Personal Values And Intentional Living
May 31, 2025
Defining Your Good Life Personal Values And Intentional Living
May 31, 2025 -
 Creating Your Good Life A Holistic Approach
May 31, 2025
Creating Your Good Life A Holistic Approach
May 31, 2025 -
 Shelton Through To Munich Semis After Darderi Victory
May 31, 2025
Shelton Through To Munich Semis After Darderi Victory
May 31, 2025
