What Is A Conclave? A Detailed Explanation Of The Papal Election Process

Table of Contents
The History and Evolution of Papal Conclaves
Papal elections haven't always been conducted within the confines of a conclave. Early methods were often tumultuous, marked by political maneuvering and even violence. From the chaotic early elections, where the process was far less structured, the need for a more organized system became apparent. The conclave system, as we know it, gradually emerged over centuries, evolving from informal gatherings to the highly regulated process seen today. Key historical changes included the introduction of formal rules concerning secrecy and the establishment of clear eligibility criteria for electors.
- Early methods of papal election: Often involved open voting and intense lobbying by powerful factions, sometimes leading to protracted disputes and even bloodshed.
- The introduction of the conclave system: Aimed to reduce external influence and promote a more focused and prayerful election process. This was a crucial step towards greater order and fairness.
- Key reforms throughout history: These reforms aimed to minimize external pressures, improve the fairness of the process, and ensure the secrecy of deliberations. Notable examples include the introduction of strict rules on communication with the outside world during the conclave.
- Examples of historically significant conclaves: The conclave of 1268, which lasted nearly three years, and the conclave of 1455, which saw intense political maneuvering, illustrate the challenges and complexities of the process throughout history. Studying these historical examples provides valuable context for understanding the modern-day conclave.
The Participants: Cardinals and Electors
The conclave's participants are the Cardinals, senior members of the Catholic clergy. Only Cardinals under the age of 80 are eligible to participate as electors in a papal conclave. The process of selecting Cardinals is a complex one, with the Pope consulting with various Church officials to nominate individuals based on their theological expertise, leadership qualities, and reputation for holiness. The number of electors fluctuates slightly depending on the number of Cardinals under 80. The College of Cardinals, the body of all Cardinals, plays a vital role in the Church's governance and in the selection of the Pope.
- Cardinal eligibility requirements: Must be under 80 years old at the time of the conclave.
- The College of Cardinals' composition: A diverse group of Cardinals from around the world, reflecting the global reach of the Catholic Church.
- The role of the Cardinal Dean: The most senior Cardinal presides over the conclave proceedings.
- The number of electors in a typical conclave: This varies, depending on how many cardinals under 80 are living at the time of a papal election.
The Conclave Process: Steps and Procedures
The conclave is a meticulously planned and highly secretive event. The process begins with the death or resignation of the Pope. Cardinals from around the world then gather in Rome. The pre-conclave period involves various liturgical and administrative preparations. The Cardinals then enter the Sistine Chapel, where they are effectively secluded from the outside world. The voting process, known as "scrutiny," takes place daily until a two-thirds majority is reached. The iconic "fumata bianca" (white smoke) signals the election of a new Pope, while "fumata nera" (black smoke) indicates that no agreement has been reached. Secrecy is paramount throughout the entire conclave.
- Pre-conclave preparations: Include liturgical ceremonies and administrative arrangements for the seamless transition.
- The seclusion of the Cardinals: They are confined to the Vatican City to ensure the integrity and secrecy of the process, eliminating outside influence.
- The voting process (scrutiny): A detailed procedure ensuring fairness and anonymity in the ballots.
- Interpretation of smoke signals: The visual signals offer a public indication of the conclave's progress.
- Maintenance of secrecy: Stringent rules are in place to prevent any leaks of information to the outside world during the process.
The Election of the Pope: Criteria and Considerations
The election is valid only when a candidate receives a two-thirds majority vote of the eligible electors. Cardinals consider various factors when casting their votes, including theological views, administrative abilities, pastoral experience, and global perspective. They seek a candidate who can effectively lead the Church in the modern world. Once a candidate reaches the required votes, the election is declared, the new Pope's name is announced ("Habemus Papam!"), and the process of papal inauguration begins.
- The two-thirds majority rule: Ensures a strong consensus and minimizes the chance of a narrow and potentially divisive election.
- Factors influencing Cardinal votes: Consideration of theological alignment, administrative capabilities, and global perspectives are key factors.
- Announcing the new Pope (Habemus Papam!): The announcement is a highly anticipated moment, both for the Church and the world.
- The Papal Inauguration: A formal ceremony marking the commencement of the new Pope's pontificate.
Conclusion: Understanding the Significance of the Conclave
The conclave is a crucial event, demonstrating the Catholic Church's unique process for electing its supreme leader. Its history reveals a fascinating evolution from chaotic beginnings to a highly regulated and secretive process. The solemnity and secrecy surrounding the conclave highlight the gravity of electing a new Pope, a figure who will guide billions of Catholics worldwide. Learn more about the intricacies of the conclave and the fascinating history of papal elections by exploring [link to relevant resource, e.g., the Vatican website]. Understanding the conclave provides deeper insights into the governance and traditions of the Catholic Church.

Featured Posts
-
 El Papel Esencial De La Terapia En La Vida De Simone Biles
May 07, 2025
El Papel Esencial De La Terapia En La Vida De Simone Biles
May 07, 2025 -
 Office365 Data Breach Millions Stolen Suspect Arrested
May 07, 2025
Office365 Data Breach Millions Stolen Suspect Arrested
May 07, 2025 -
 Celebrities Light Up The Met Gala Red Carpet
May 07, 2025
Celebrities Light Up The Met Gala Red Carpet
May 07, 2025 -
 Watch Dallas Wings Vs Las Vegas Aces Wnba Preseason Live Online
May 07, 2025
Watch Dallas Wings Vs Las Vegas Aces Wnba Preseason Live Online
May 07, 2025 -
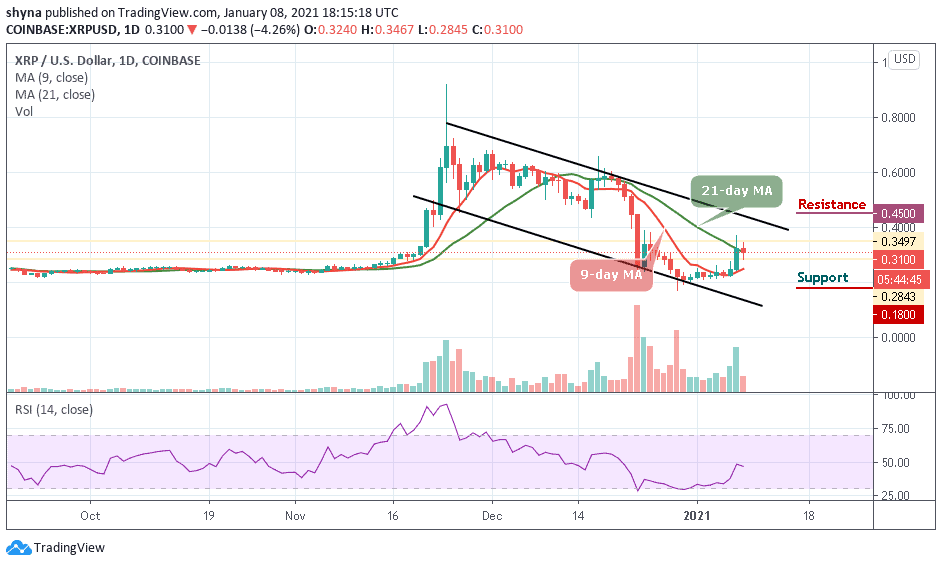 Analyzing Ripples Xrp Potential To Reach 3 40
May 07, 2025
Analyzing Ripples Xrp Potential To Reach 3 40
May 07, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 The Rogue One Recut What The Andor Director Almost Revealed
May 08, 2025
The Rogue One Recut What The Andor Director Almost Revealed
May 08, 2025 -
 Revealing Too Much Andor Director And The Rogue One Recut
May 08, 2025
Revealing Too Much Andor Director And The Rogue One Recut
May 08, 2025 -
 A Rogue One Stars Unconventional View Of A Popular Character
May 08, 2025
A Rogue One Stars Unconventional View Of A Popular Character
May 08, 2025 -
 Andor Season 2 Will It Surpass The First Season Diego Luna Weighs In
May 08, 2025
Andor Season 2 Will It Surpass The First Season Diego Luna Weighs In
May 08, 2025 -
 Directors Near Miss Unveiling The Rogue One Recut
May 08, 2025
Directors Near Miss Unveiling The Rogue One Recut
May 08, 2025
