Why Interdisciplinary And Transdisciplinary Approaches Matter: A Comprehensive Guide
Table of Contents
Enhanced Problem-Solving Capabilities
Combining different perspectives leads to more comprehensive and innovative solutions. The power of interdisciplinary and transdisciplinary approaches lies in their ability to leverage a wider range of expertise and tools. This collaborative approach offers several key advantages:
- Wider range of expertise and tools available: Researchers and practitioners gain access to a broader toolkit, including diverse methodologies, analytical frameworks, and technological resources. This allows for a more nuanced understanding of complex problems.
- Identification of blind spots and biases within individual disciplines: By bringing together different perspectives, it becomes easier to identify inherent biases and limitations within individual disciplines, leading to more robust and objective analyses.
- Development of more creative and holistic solutions: The fusion of diverse viewpoints often sparks creative solutions that would not emerge from a single discipline's perspective. This holistic approach leads to more effective and sustainable outcomes.
- Improved critical thinking and problem-solving skills: The process of navigating differing perspectives and integrating multiple datasets enhances critical thinking and problem-solving capabilities within each participating discipline.
For example, consider urban planning. A transdisciplinary approach might integrate ecological expertise (assessing environmental impact), sociological insights (understanding community needs), and economic analysis (evaluating cost-effectiveness) to create truly sustainable and equitable urban developments, far surpassing what a solely architectural or engineering approach could achieve.
Fostering Collaboration and Knowledge Integration
Effective communication and collaboration are paramount to successful interdisciplinary and transdisciplinary approaches. These approaches necessitate breaking down the traditional disciplinary silos that often hinder progress.
- Breaking down disciplinary silos and fostering mutual understanding: Collaboration fosters mutual understanding and respect between different disciplines, leading to a richer intellectual exchange.
- Building stronger networks and collaborations: These approaches naturally lead to the development of stronger research networks and collaborations, extending beyond individual institutions and geographical boundaries.
- Facilitating knowledge exchange and transfer between fields: The sharing of knowledge and methodologies across disciplines accelerates innovation and progress.
- Promoting a more integrated and holistic understanding of complex systems: By integrating diverse perspectives, these methods allow for a more comprehensive understanding of complex systems and their interconnectedness.
For instance, a successful interdisciplinary research project on climate change might involve climatologists, ecologists, economists, and social scientists working together to develop integrated mitigation and adaptation strategies. The collaborative efforts involved in such projects create a powerful synergy, yielding more comprehensive and impactful results than individual disciplinary efforts could achieve.
Addressing Complex Challenges Effectively
The true power of interdisciplinary and transdisciplinary approaches shines through in their application to real-world problems. These approaches are essential for tackling some of the world's most pressing issues:
- Climate change mitigation and adaptation strategies: Developing effective climate solutions requires input from across scientific disciplines and social sciences to understand the diverse impacts and develop integrated responses.
- Public health initiatives and pandemic response: Combating global health crises requires the expertise of epidemiologists, virologists, healthcare professionals, social scientists, and public policy experts to effectively manage outbreaks and create resilient healthcare systems.
- Sustainable development goals and global challenges: Achieving the UN Sustainable Development Goals demands a transdisciplinary approach, encompassing ecological, economic, social, and political perspectives to achieve integrated and sustainable progress.
- Technological innovation and societal impact: The ethical and societal implications of technological advancements necessitate collaboration between technologists, ethicists, social scientists, and policymakers to ensure responsible innovation and equitable outcomes.
Overcoming Limitations of Single-Discipline Approaches
Single-discipline approaches often fall short when dealing with complex, multifaceted problems. The narrow focus of a single discipline can lead to incomplete or even flawed solutions.
- Narrow perspectives can lead to incomplete solutions: A limited viewpoint might overlook crucial factors or interactions contributing to the problem.
- Lack of integration can hinder progress: Working in isolation prevents the synthesis of knowledge and methods needed for truly innovative solutions.
- Disciplinary biases can affect results: Each discipline has inherent biases and assumptions which, if unchecked, can lead to skewed or inaccurate results.
For example, attempting to solve traffic congestion solely through engineering solutions (e.g., building more roads) might overlook sociological factors (e.g., commuting patterns, urban sprawl) and economic constraints, ultimately failing to address the root causes of the problem.
Conclusion
In summary, embracing interdisciplinary and transdisciplinary approaches offers significant benefits: enhanced problem-solving capabilities, fostering collaboration and knowledge integration, and more effective tackling of complex challenges. The limitations of single-discipline approaches are overcome by the rich tapestry of perspectives and collaborative efforts inherent in these integrated strategies. We must reiterate the importance of these approaches in research, practice, and education. Embrace the power of interdisciplinary and transdisciplinary approaches to drive innovation and create positive change. By fostering collaboration and integrating diverse perspectives, we can overcome complex challenges and build a more sustainable and equitable future. Let's actively promote and implement these vital methodologies in our own work and advocate for their wider adoption within our communities and institutions.

Featured Posts
-
 Alleged Kelowna Bear Spray Victims Detail Halloween Night Attack
May 19, 2025
Alleged Kelowna Bear Spray Victims Detail Halloween Night Attack
May 19, 2025 -
 Gazzeli Cocuklar Cadirda Kuran Oegreniyor Ezber Teknikleri Ve Oenemli Noktalar
May 19, 2025
Gazzeli Cocuklar Cadirda Kuran Oegreniyor Ezber Teknikleri Ve Oenemli Noktalar
May 19, 2025 -
 Orlando City Falls To Philadelphia Union In Season Opener
May 19, 2025
Orlando City Falls To Philadelphia Union In Season Opener
May 19, 2025 -
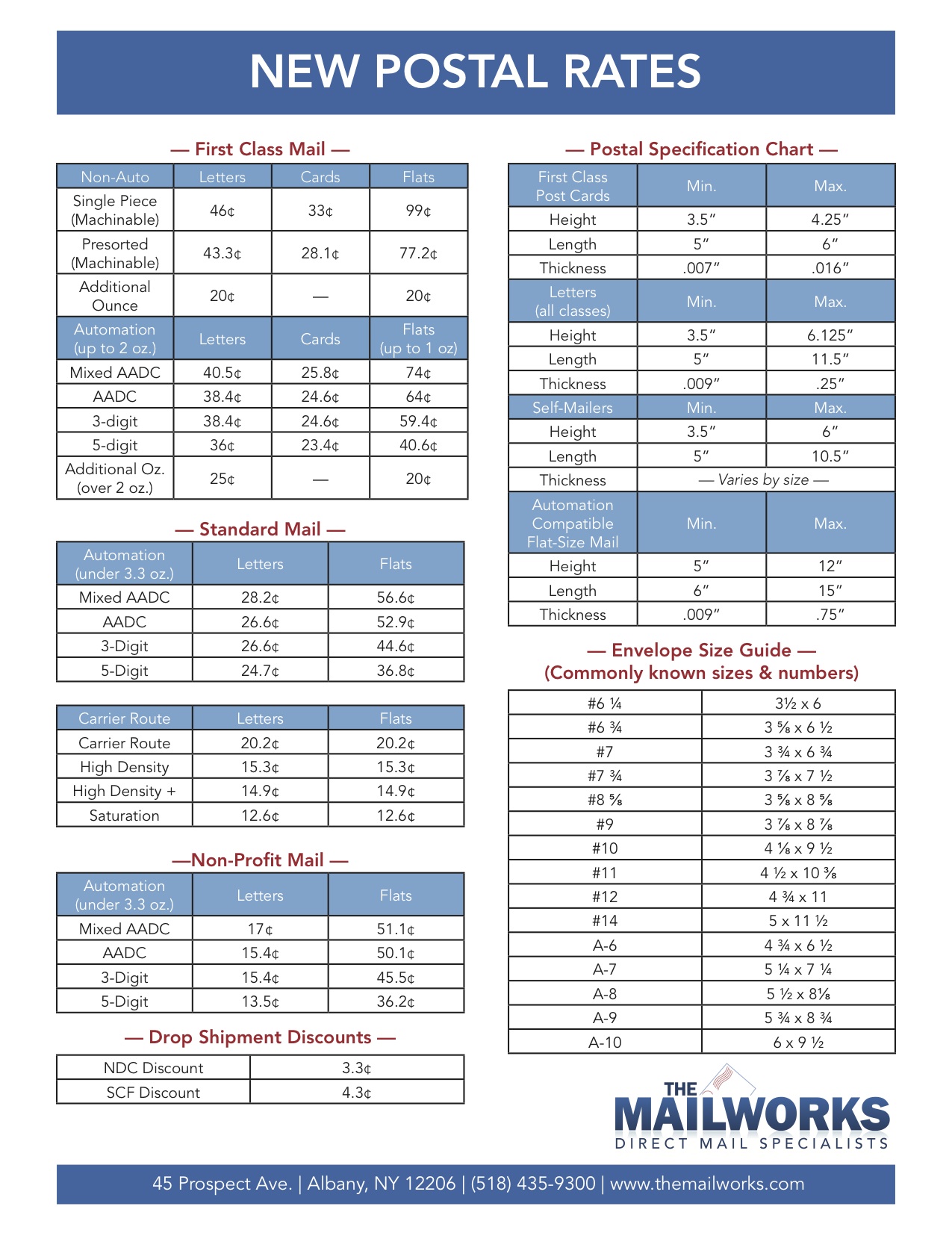 Royal Mail Price Hikes Full List Of Exact Stamp Price Increases From April 7th
May 19, 2025
Royal Mail Price Hikes Full List Of Exact Stamp Price Increases From April 7th
May 19, 2025 -
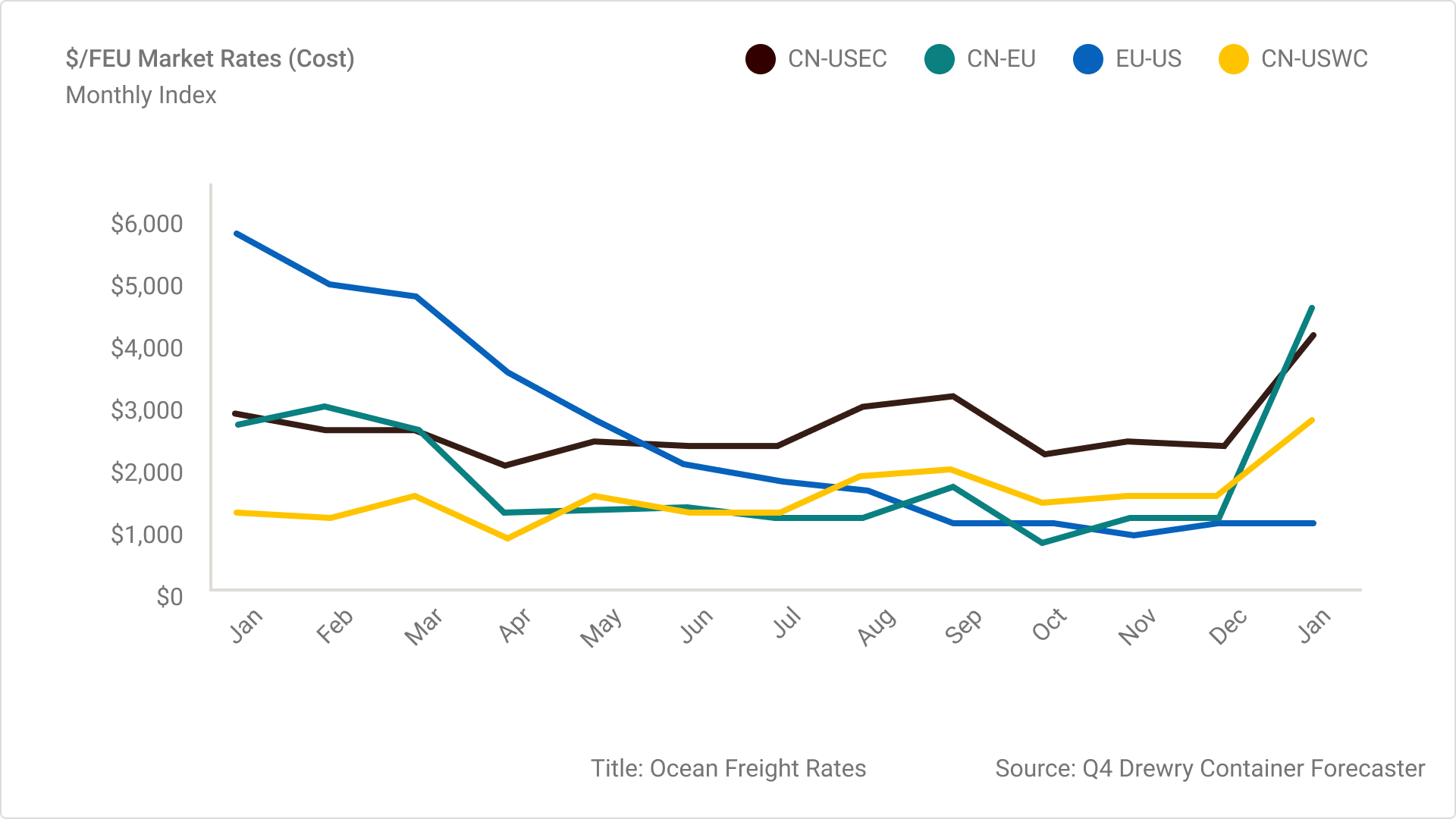 Payden And Rygel Analyzing China To Us Container Shipping Trends
May 19, 2025
Payden And Rygel Analyzing China To Us Container Shipping Trends
May 19, 2025
