WTO Accession: Navigating The Privilege Dilemma
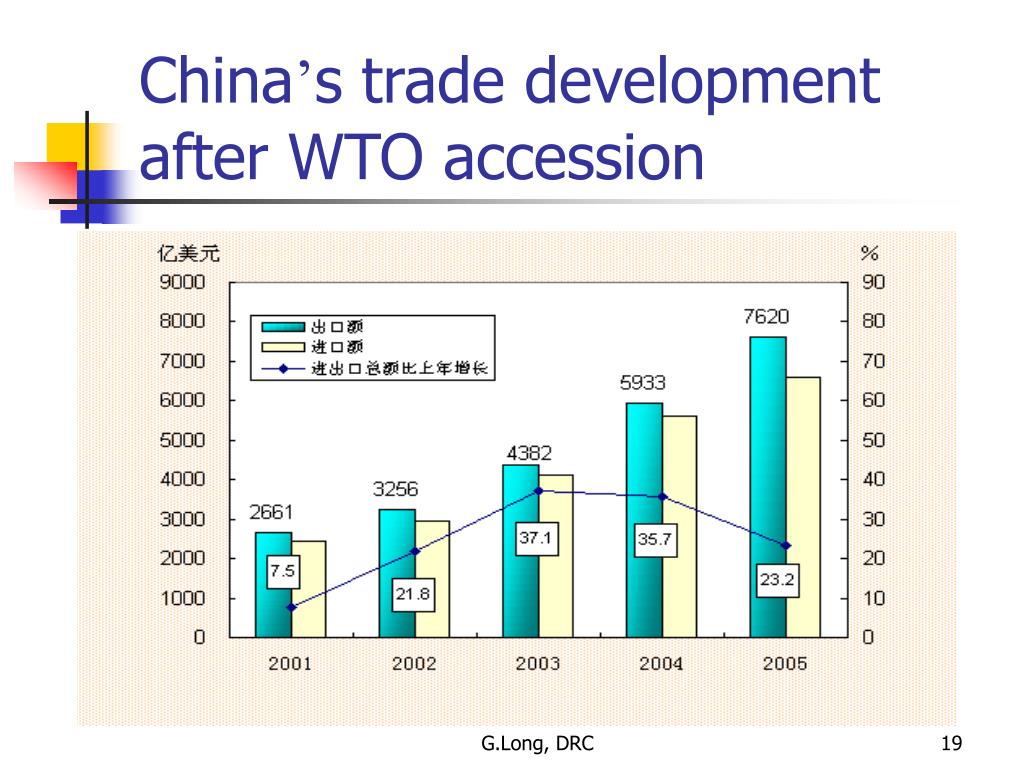
Table of Contents
Economic Benefits and Opportunities of WTO Accession
WTO accession unlocks a wealth of economic opportunities for participating nations. The advantages extend far beyond simply gaining access to new markets; they touch upon fundamental aspects of economic development and growth.
Increased Market Access
WTO membership significantly expands market access by reducing or eliminating trade barriers such as tariffs and quotas. This translates to:
- Increased export opportunities: Businesses gain access to a vastly larger customer base, enabling them to expand their operations and boost revenue.
- Access to larger consumer bases: Companies can reach consumers in countries previously inaccessible due to high tariffs or non-tariff barriers.
- Diversification of markets: Reducing reliance on a single or few markets mitigates risk and promotes economic stability.
For example, China's WTO accession in 2001 led to a dramatic surge in its exports, significantly contributing to its economic growth. Similar successes have been observed in other countries that have undergone successful WTO accession processes.
Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) Attraction
WTO accession enhances a nation's attractiveness to foreign investors by:
- Improving investor confidence: The transparent and predictable regulatory environment fostered by WTO agreements encourages greater foreign investment.
- Streamlining regulations: The process of WTO accession often necessitates regulatory reforms, creating a more business-friendly climate.
- Increased transparency: WTO membership promotes transparency in trade policies and regulations, reducing uncertainty for investors.
The WTO's dispute settlement mechanism further protects investor rights, offering a reliable platform for resolving trade-related disputes.
Technological Advancement and Knowledge Transfer
WTO accession acts as a catalyst for technological advancement and knowledge transfer. The increased competition resulting from global market access pushes companies to innovate and improve efficiency. Furthermore:
- Increased competition leading to efficiency gains: Companies are incentivized to adopt more efficient production methods to remain competitive.
- Access to global best practices: Exposure to international standards and practices facilitates the adoption of best-in-class technologies and management techniques.
- Technology spillover effects: Knowledge and technology transfer occurs through foreign investment, joint ventures, and cross-border collaborations.
Challenges and Obligations of WTO Accession
While the potential rewards of WTO accession are substantial, it is crucial to acknowledge the significant challenges and obligations involved.
Regulatory Reform and Domestic Adjustments
Meeting WTO standards requires substantial internal reforms, often necessitating changes in various sectors:
- Intellectual property rights: Harmonizing intellectual property laws with international standards can be complex and costly.
- Sanitary and phytosanitary regulations: Implementing stringent food safety and animal health regulations requires significant investment.
- Competition policy: Establishing and enforcing effective competition laws is crucial to prevent anti-competitive practices.
These reforms can lead to short-term costs and disruptions, requiring careful planning and management.
Trade-offs and Policy Compromises
WTO accession necessitates balancing national interests with WTO obligations. This often involves difficult trade-offs, such as:
- Protecting sensitive industries: Governments may need to make concessions on tariffs or other trade barriers to gain access to larger markets.
- Addressing social concerns: Balancing economic liberalization with social and environmental considerations requires careful policy design.
The negotiation process itself can be challenging, requiring skillful diplomacy and compromise.
Dispute Settlement and Compliance
The WTO's dispute settlement system plays a crucial role in enforcing trade rules. However:
- Potential risks of trade disputes: Non-compliance with WTO rules can lead to trade disputes, which can be costly and time-consuming.
- Importance of adhering to WTO rules: Strict adherence to WTO rules is essential to avoid disputes and maintain a positive trading relationship with other members.
- Implications of non-compliance: Non-compliance can lead to retaliatory measures from other WTO members, negatively impacting a nation's economy.
Strategies for Successful WTO Accession
Successful WTO accession requires careful planning, effective negotiation, and ongoing adaptation.
Thorough Preparation and Strategic Planning
A well-defined national strategy is essential for successful WTO accession. This includes:
- Needs assessment: Identifying the country's strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats in relation to WTO membership.
- Capacity building: Developing the necessary expertise and institutional capacity to implement WTO commitments.
- Stakeholder consultation: Engaging with relevant stakeholders (businesses, civil society, government agencies) to ensure broad support for the accession process.
- Clear objectives: Defining clear and achievable goals for the accession process.
Effective Negotiation and Diplomacy
Successful WTO accession relies heavily on effective negotiation and diplomacy:
- Building alliances: Seeking support from other WTO members to facilitate the accession process.
- Anticipating challenges: Identifying potential obstacles and developing strategies to overcome them.
- Flexible approach: Being prepared to make concessions and compromises to achieve a mutually beneficial agreement.
Post-Accession Implementation and Monitoring
Effective implementation of WTO commitments is crucial after WTO accession. This requires:
- Ongoing monitoring: Continuously monitoring the impact of WTO commitments on the national economy.
- Capacity building: Continuously enhancing the capacity to implement and enforce WTO rules.
- Adaptation to changing global trade dynamics: Adapting to changes in the global trading environment and adjusting policies accordingly.
Navigating the Path to Successful WTO Accession
WTO accession presents a complex "privilege dilemma," offering substantial economic benefits but demanding significant internal reforms and policy adjustments. Successful integration requires thorough preparation, strategic planning, effective negotiation, and ongoing adaptation to changing global trade dynamics. Understanding the intricacies of WTO accession and its implications is crucial for any nation seeking to participate in the global trading system. Understand the complexities of WTO accession and navigate the privilege dilemma effectively by exploring further resources on [link to relevant resource].

Featured Posts
-
 Who Is Dina Exploring Isabela Merceds Character In The Last Of Us Season 2
May 07, 2025
Who Is Dina Exploring Isabela Merceds Character In The Last Of Us Season 2
May 07, 2025 -
 Cavaliers Playoff Chances Evaluating Threats Beyond The Celtics
May 07, 2025
Cavaliers Playoff Chances Evaluating Threats Beyond The Celtics
May 07, 2025 -
 Cavs Playoffs Tickets Round 2 On Sale Tuesday
May 07, 2025
Cavs Playoffs Tickets Round 2 On Sale Tuesday
May 07, 2025 -
 Ralph Macchios 38 Year Marriage Avoiding Hollywoods Spotlight
May 07, 2025
Ralph Macchios 38 Year Marriage Avoiding Hollywoods Spotlight
May 07, 2025 -
 14 0 Blowout Mariners First Inning Power Overwhelms Marlins
May 07, 2025
14 0 Blowout Mariners First Inning Power Overwhelms Marlins
May 07, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 A Whistle For Krypto Supermans Summer Special
May 08, 2025
A Whistle For Krypto Supermans Summer Special
May 08, 2025 -
 Latest News F4 Elden Ring Possum And Superman
May 08, 2025
Latest News F4 Elden Ring Possum And Superman
May 08, 2025 -
 Unforgettable Tales Exploring The Best Krypto Stories
May 08, 2025
Unforgettable Tales Exploring The Best Krypto Stories
May 08, 2025 -
 Darkseids Legion Attacks Dcs Superman July 2025 Solicits Revealed
May 08, 2025
Darkseids Legion Attacks Dcs Superman July 2025 Solicits Revealed
May 08, 2025 -
 Dont Miss It Superman And Krypto Next Week
May 08, 2025
Dont Miss It Superman And Krypto Next Week
May 08, 2025
