A Look Back: The History And Significance Of Independence Day

Table of Contents
The Road to Independence: Colonial Grievances and the Revolutionary War
The American Revolution, the crucible from which Independence Day emerged, wasn't a spontaneous eruption but the culmination of simmering discontent. Years of escalating tensions between Great Britain and its thirteen American colonies fueled the flames of rebellion. Taxation without representation, a cornerstone of colonial grievances, became a rallying cry. Acts like the Stamp Act and the Townshend Acts, imposing taxes on various goods and services without colonial consent, ignited widespread protests and boycotts. The Boston Tea Party, a dramatic act of defiance in 1773, further exacerbated the already strained relationship.
- Key figures involved: George Washington, the commander of the Continental Army, Thomas Jefferson, the principal author of the Declaration of Independence, and Benjamin Franklin, a key diplomat and statesman, played crucial roles.
- Major battles and their significance: Battles such as Lexington and Concord, Bunker Hill, Saratoga (a turning point securing French alliance), and Yorktown (the decisive victory) shaped the course of the Revolutionary War.
- The impact of Enlightenment ideals: Enlightenment thinkers like John Locke profoundly influenced the colonists' desire for self-governance and natural rights, providing the philosophical framework for their rebellion against British rule. Their belief in liberty and self-determination fueled the fight for independence. The ideals of liberty, equality, and the pursuit of happiness found a powerful voice in the burgeoning movement for freedom.
The Declaration of Independence: A Pivotal Document
The Declaration of Independence, adopted by the Continental Congress on July 4, 1776, stands as a landmark document in human history. Drafted primarily by Thomas Jefferson, it eloquently articulated the colonists' grievances against King George III and declared their intention to establish an independent nation.
- Key phrases and their meaning: The phrase "all men are created equal," enshrined in the Declaration, remains a powerful ideal, though its full realization continues to be a work in progress. The assertion of "life, liberty, and the pursuit of happiness" as unalienable rights profoundly influenced subsequent movements for human rights and social justice worldwide.
- The philosophical underpinnings of the document: The Declaration's philosophical underpinnings are firmly rooted in Enlightenment ideals of natural rights, popular sovereignty, and the right to revolution. It provided a moral and philosophical justification for the rebellion.
- The impact of the Declaration: The Declaration of Independence not only served as a declaration of war but also a powerful statement of the colonists’ aspirations for a free and self-governing society. It profoundly shaped the course of the war and laid the foundation for the future American nation.
Securing Independence: The War and its Aftermath
The Revolutionary War, a protracted and arduous struggle, eventually resulted in the American victory. While the initial years saw setbacks for the Continental Army, key turning points, such as the Battle of Saratoga, secured crucial foreign alliances, particularly with France.
- Key battles and their outcomes: Significant battles, including those mentioned previously, determined the trajectory of the war, gradually tilting the balance of power in favor of the American colonists.
- The role of foreign alliances: The alliance with France provided essential military and financial support, proving indispensable to the American victory.
- The challenges faced by the newly independent nation: The newly independent nation faced immense challenges in the post-war period, including establishing a stable government, addressing economic instability, and defining its relationship with Native American tribes. The Treaty of Paris, signed in 1783, formally recognized American independence, marking the end of the war and the birth of a new nation. Nation-building was a complex process, fraught with internal disagreements and external pressures.
The Evolution of Independence Day Celebrations
Independence Day celebrations have evolved significantly since the first commemorations. Early celebrations were often more subdued affairs, focused on civic gatherings and readings of the Declaration.
- Early celebrations and their significance: The earliest celebrations featured parades, church services, and public readings of the Declaration. These commemorations were important in fostering a sense of shared national identity and purpose.
- The development of traditional customs: Over time, fireworks displays, parades, barbecues, and family gatherings became ingrained traditions associated with Independence Day. Patriotic music and displays of national symbols further cemented these customs.
- How celebrations have evolved: Modern Independence Day celebrations reflect the changing social and political landscape. While traditional customs persist, celebrations also incorporate broader themes of diversity, inclusion, and reflection on the ongoing struggle for equality and justice.
Conclusion
Independence Day stands as a testament to the courage and determination of those who fought for freedom and self-governance. From the colonial grievances that sparked the American Revolution to the signing of the Declaration of Independence and the ultimate victory in the war, the events leading up to and following July 4, 1776, shaped the identity of the United States and continue to resonate throughout the world. This Independence Day, let's remember the struggles and triumphs that led to our freedom, and continue to celebrate the spirit of Independence Day with pride and reflection. Let us honor the sacrifices made and reaffirm our commitment to the ideals of liberty and justice for all, ensuring that the spirit of Independence Day lives on for generations to come. Celebrate this Independence Day with thoughtful remembrance and renewed dedication to the principles upon which our nation was founded.

Featured Posts
-
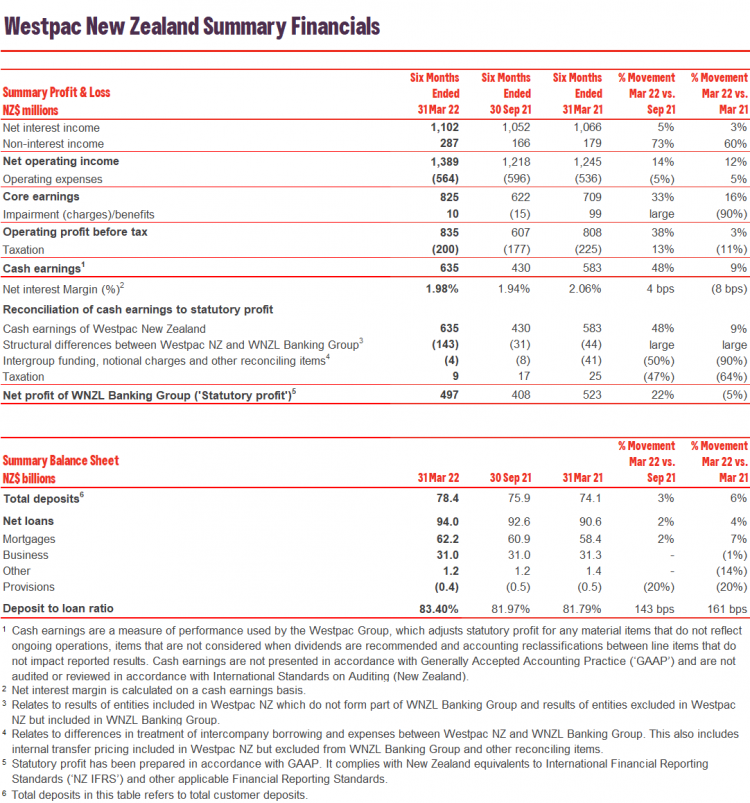 Analysis Of Westpac Wbc Earnings Margin Compression And Future Outlook
May 06, 2025
Analysis Of Westpac Wbc Earnings Margin Compression And Future Outlook
May 06, 2025 -
 Princess Dianas Met Gala Gown The Untold Story Of A Risque Alteration
May 06, 2025
Princess Dianas Met Gala Gown The Untold Story Of A Risque Alteration
May 06, 2025 -
 The I Dont Know Why Collaboration Ariana Grande And Jeff Goldblums New Song
May 06, 2025
The I Dont Know Why Collaboration Ariana Grande And Jeff Goldblums New Song
May 06, 2025 -
 The Wisdom Behind Buffetts Successful Apple Investment
May 06, 2025
The Wisdom Behind Buffetts Successful Apple Investment
May 06, 2025 -
 Livestreaming The 2025 Met Gala A Guide For Viewers In Latin America Mexico And The U S
May 06, 2025
Livestreaming The 2025 Met Gala A Guide For Viewers In Latin America Mexico And The U S
May 06, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Analyzing Spielbergs New Ufo Film A Comparative Study Of His Sci Fi Works
May 06, 2025
Analyzing Spielbergs New Ufo Film A Comparative Study Of His Sci Fi Works
May 06, 2025 -
 Spielbergs Ufo Movie How It Stacks Up Against His Previous Alien Encounters
May 06, 2025
Spielbergs Ufo Movie How It Stacks Up Against His Previous Alien Encounters
May 06, 2025 -
 Priznanieto Na Ed Shiyrn Za Riana Plna Istoriya
May 06, 2025
Priznanieto Na Ed Shiyrn Za Riana Plna Istoriya
May 06, 2025 -
 Spielbergs New Ufo Movie A Comparison To His Classic Alien Sci Fi Films
May 06, 2025
Spielbergs New Ufo Movie A Comparison To His Classic Alien Sci Fi Films
May 06, 2025 -
 Savage X Fentys New Bridal Collection Designed By Rihanna
May 06, 2025
Savage X Fentys New Bridal Collection Designed By Rihanna
May 06, 2025
