Analysis: Grim Retail Sales Data And The Probability Of Bank Of Canada Rate Cuts
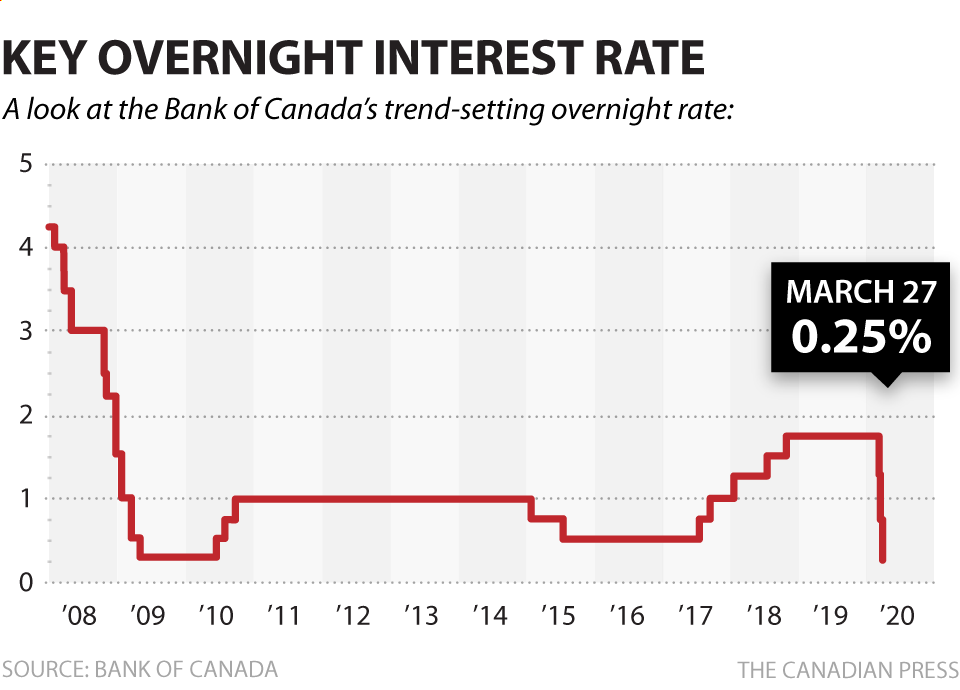
Table of Contents
Recent Retail Sales Data: A Deeper Dive
The most recent retail sales figures paint a concerning picture for the Canadian economy. [Insert link to Statistics Canada data here]. The data reveals a [percentage]% drop in retail sales compared to the previous month/year (specify timeframe), marking a significant decline. This downturn is not uniform across all sectors.
- Magnitude of the decline in retail sales: The [percentage]% decrease represents the steepest fall in [number] months/years.
- Sectors most significantly impacted: The hardest hit sectors include durable goods like furniture and appliances, and certain non-durable goods categories such as clothing and electronics (provide specific percentage drops if available). This suggests consumers are tightening their belts on discretionary spending.
- Geographical distribution of the downturn: While the decline is nationwide, [Province A] and [Province B] appear to be experiencing a more pronounced downturn, possibly reflecting regional economic disparities. Further analysis is needed to confirm this observation.
- Comparison to previous years and seasonal adjustments: Even after accounting for seasonal adjustments, the current decline surpasses typical fluctuations, indicating a deeper underlying economic weakness. [Include comparative data points here].
Factors Contributing to Weak Retail Sales
Several factors contribute to this weak performance in retail sales. The confluence of these issues creates a complex challenge for policymakers.
- High inflation and its impact on consumer spending: Persistently high inflation is eroding consumer purchasing power, forcing households to cut back on spending. The rising cost of essentials is leaving less disposable income for discretionary purchases.
- Rising interest rates and their effect on borrowing and disposable income: The Bank of Canada's previous interest rate hikes, while aimed at curbing inflation, have increased borrowing costs, impacting both consumer spending and business investment. Higher mortgage payments and loan repayments leave less money for other expenses.
- Consumer confidence levels and surveys reflecting pessimism: Surveys consistently reveal declining consumer confidence, suggesting a pessimistic outlook on the economy and reduced willingness to spend. This sentiment feeds the downward spiral of retail sales.
- Impact of global economic uncertainty: Global economic headwinds, including geopolitical instability and potential recessions in other major economies, are adding to the uncertainty and impacting Canadian consumer sentiment and spending.
- Supply chain disruptions (if still relevant): While easing, lingering supply chain disruptions continue to contribute to higher prices and reduced availability of certain goods, further dampening consumer spending.
Inflation's Persistent Grip
Inflation remains a major concern. The current inflation rate stands at [Insert current inflation rate and source], significantly above the Bank of Canada's target of [Insert target inflation rate].
- Current inflation figures and projected trajectory: [Include details on inflation projections and their uncertainties].
- Core inflation vs. headline inflation and implications: [Explain the difference and the implications of each for policy decisions. Core inflation is particularly important for the Bank of Canada's assessment of underlying price pressures].
- Bank of Canada's inflation target and how far it is from being met: The persistent gap between current inflation and the target highlights the challenge faced by the central bank in bringing inflation under control.
The Bank of Canada's Response: Rate Cut Probability
Given the weak retail sales data and persistent inflation, the question of Bank of Canada rate cuts is paramount.
- Summary of the Bank of Canada's recent monetary policy announcements: [Summarize the most recent statements and actions of the Bank of Canada, highlighting their concerns regarding inflation and economic growth].
- Market expectations regarding future rate changes (based on futures contracts, analyst predictions): [Discuss market sentiment and predictions regarding future interest rate adjustments based on available data and analysis]. The market may be pricing in a higher or lower probability of Bank of Canada rate cuts than previously anticipated.
- Factors influencing the Bank of Canada's decision-making (inflation, employment, economic growth): The Bank of Canada will carefully weigh the risks of persistent inflation against the potential for a deeper economic slowdown before making any decisions. Employment data will be crucial in this assessment.
- Analysis of the potential risks and benefits of a rate cut: A rate cut could stimulate economic activity, but also risks reigniting inflationary pressures. A pause in rate hikes allows the Bank of Canada to assess the impact of previous increases and to monitor evolving economic data.
Alternative Monetary Policy Tools
Besides Bank of Canada rate cuts, the central bank has other tools at its disposal.
- Quantitative easing (QE): QE involves the Bank of Canada purchasing government bonds to increase the money supply and lower long-term interest rates.
- Forward guidance: Clear communication from the Bank of Canada about its future intentions can influence market expectations and shape economic behavior.
- Other unconventional monetary policies: The Bank of Canada may consider other less conventional approaches, depending on the economic situation.
Conclusion
This analysis reveals a concerning picture: weak retail sales, persistent inflation, and significant uncertainty regarding the likelihood of imminent Bank of Canada rate cuts. While the weak retail sales data puts downward pressure on interest rates, the persistent inflation poses a significant challenge. The Bank of Canada's response will likely depend on a careful balancing act between stimulating the economy and controlling inflation. Alternative policy tools, such as forward guidance, could play a more prominent role. The probability of a rate cut remains uncertain and heavily dependent on forthcoming economic data.
Call to Action: Stay informed about the evolving economic situation and the Bank of Canada's response. Continue following our analysis for updates on Bank of Canada rate cuts and their impact on the Canadian economy. Regularly check our website for further insights into the Canadian economic landscape and the implications of potential Bank of Canada rate cuts and other monetary policy decisions.

Featured Posts
-
 Musks X Debt A Financial Performance Review Post Sale
Apr 29, 2025
Musks X Debt A Financial Performance Review Post Sale
Apr 29, 2025 -
 How You Tube Is Engaging Older Viewers With Classic And New Content
Apr 29, 2025
How You Tube Is Engaging Older Viewers With Classic And New Content
Apr 29, 2025 -
 The Illusion Of Intelligence How Ai Works And Its Cognitive Limitations
Apr 29, 2025
The Illusion Of Intelligence How Ai Works And Its Cognitive Limitations
Apr 29, 2025 -
 Israeli Airstrike In Beirut Evacuation Warning Issued
Apr 29, 2025
Israeli Airstrike In Beirut Evacuation Warning Issued
Apr 29, 2025 -
 Why Older Viewers Are Choosing You Tube For Their Entertainment
Apr 29, 2025
Why Older Viewers Are Choosing You Tube For Their Entertainment
Apr 29, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Nyr Porsche Macan Allt Um Fyrstu Rafutgafuna
Apr 29, 2025
Nyr Porsche Macan Allt Um Fyrstu Rafutgafuna
Apr 29, 2025 -
 Buy A Pts Riviera Blue Porsche 911 S T Exceptional Condition
Apr 29, 2025
Buy A Pts Riviera Blue Porsche 911 S T Exceptional Condition
Apr 29, 2025 -
 Porsche Macan Fyrsta 100 Rafutgafan Kynnt
Apr 29, 2025
Porsche Macan Fyrsta 100 Rafutgafan Kynnt
Apr 29, 2025 -
 First Look 2026 Porsche Cayenne Ev Spy Photos Unveiled
Apr 29, 2025
First Look 2026 Porsche Cayenne Ev Spy Photos Unveiled
Apr 29, 2025 -
 Discover The Rare Pts Riviera Blue Porsche 911 S T
Apr 29, 2025
Discover The Rare Pts Riviera Blue Porsche 911 S T
Apr 29, 2025
