Bank Of Canada's Inflation Dilemma: Rising Core Prices Force Tough Choices
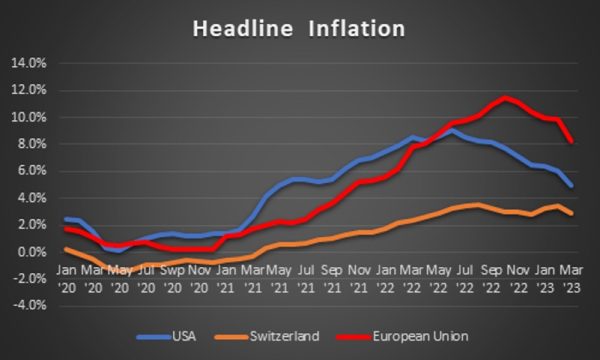
Table of Contents
Understanding the Current Inflationary Pressure
Canada's inflation rate, as measured by the Consumer Price Index (CPI), remains elevated. While headline inflation, which includes volatile items like energy prices, may fluctuate, core inflation—a measure that excludes these volatile components—provides a more accurate picture of underlying inflationary pressures. Currently, core inflation remains stubbornly high, signaling persistent inflationary pressures within the Canadian economy.
Several factors contribute to this rising core inflation:
- Supply Chain Disruptions: Lingering supply chain bottlenecks continue to constrain production and drive up prices for various goods. Global shipping delays and shortages of key inputs contribute to higher production costs, which are ultimately passed on to consumers.
- Strong Consumer Demand: Robust consumer spending, fueled by pent-up demand following the pandemic and government stimulus measures, has put upward pressure on prices. Increased demand exceeding supply leads to price increases.
- Wage Pressures: Rising wages, while positive for workers, can contribute to inflationary pressures if they outpace productivity growth. Businesses may pass increased labor costs onto consumers in the form of higher prices.
- Global Inflationary Pressures: Canada is not immune to global inflationary trends. Rising energy prices, commodity costs, and global supply chain issues all contribute to inflationary pressures within the Canadian economy.
The Bank of Canada's Policy Tools and Challenges
The Bank of Canada's primary tool for managing inflation is adjusting interest rates. By raising interest rates, the central bank aims to cool down the economy, reduce consumer spending and investment, and ultimately curb inflation. However, this strategy involves significant trade-offs:
- Slowing Economic Growth and Potential Recession: Higher interest rates increase borrowing costs for businesses and consumers, potentially leading to reduced investment, decreased consumer spending, and a slower pace of economic growth. In extreme cases, this could even trigger a recession.
- Increased Unemployment: As economic activity slows down, businesses might reduce hiring or even lay off workers, leading to an increase in the unemployment rate.
- Impact on Housing Market: Higher interest rates significantly impact the housing market, making mortgages more expensive and potentially leading to a decline in housing prices and construction activity.
The Bank of Canada faces considerable challenges in predicting the effectiveness of interest rate hikes and the time lag before their impact is fully felt. The effects of monetary policy are not immediate and can be difficult to forecast accurately.
Alternative Policy Options and Their Implications
Beyond interest rate adjustments, the Bank of Canada could consider alternative policy options:
- Quantitative Easing (QE) or its Reversal: QE involves the Bank of Canada injecting liquidity into the financial system by purchasing government bonds. Reversing QE, or quantitative tightening, involves selling these bonds to reduce liquidity and curb inflation. The effectiveness of these measures depends on various market conditions.
- Forward Guidance on Future Policy Decisions: Clearly communicating the Bank of Canada's intentions regarding future interest rate adjustments can help shape inflation expectations. Managing expectations can influence consumer and business behavior and assist in stabilizing the economy.
- Communication Strategies to Manage Inflation Expectations: Effective communication with the public is crucial for managing inflation expectations. Transparency and clear explanations of the Bank's actions can help anchor inflation expectations and improve the effectiveness of monetary policy.
The Outlook for Inflation and the Canadian Economy
Forecasting inflation remains a challenge, but most analysts predict a gradual decline in inflation over the coming year. However, the path to price stability is not guaranteed, and several scenarios are possible depending on the Bank of Canada's actions, global economic developments, and the evolution of supply chains. The potential impact on different sectors of the Canadian economy will vary, with some sectors more sensitive to interest rate changes than others. The housing market, for example, is particularly vulnerable to interest rate hikes. Continued monitoring of GDP growth and sectoral impact are crucial for understanding the overall economic health.
Conclusion: Navigating the Bank of Canada's Inflation Dilemma
The Bank of Canada faces a complex and challenging task in managing rising core inflation. Balancing the need to control inflation with the goal of maintaining economic stability requires careful consideration of various economic factors and potential consequences. The trade-offs between controlling inflation and fostering economic growth are significant. The likely path of monetary policy in the coming months will depend on the evolution of inflation, economic growth, and other key economic indicators. Stay informed about the Bank of Canada's decisions and their impact on the Canadian economy by following news and updates on the Bank of Canada's inflation dilemma and related monetary policies. Understanding the nuances of the Bank of Canada's actions is crucial for navigating the current economic climate.

Featured Posts
-
 Dauphin County Apartment Building Destroyed In Overnight Fire
May 22, 2025
Dauphin County Apartment Building Destroyed In Overnight Fire
May 22, 2025 -
 Switzerland Condemns Chinas Military Drills Near Taiwan
May 22, 2025
Switzerland Condemns Chinas Military Drills Near Taiwan
May 22, 2025 -
 Thuc Day Phat Trien 7 Vi Tri Ket Noi Khan Cap Tp Hcm Long An
May 22, 2025
Thuc Day Phat Trien 7 Vi Tri Ket Noi Khan Cap Tp Hcm Long An
May 22, 2025 -
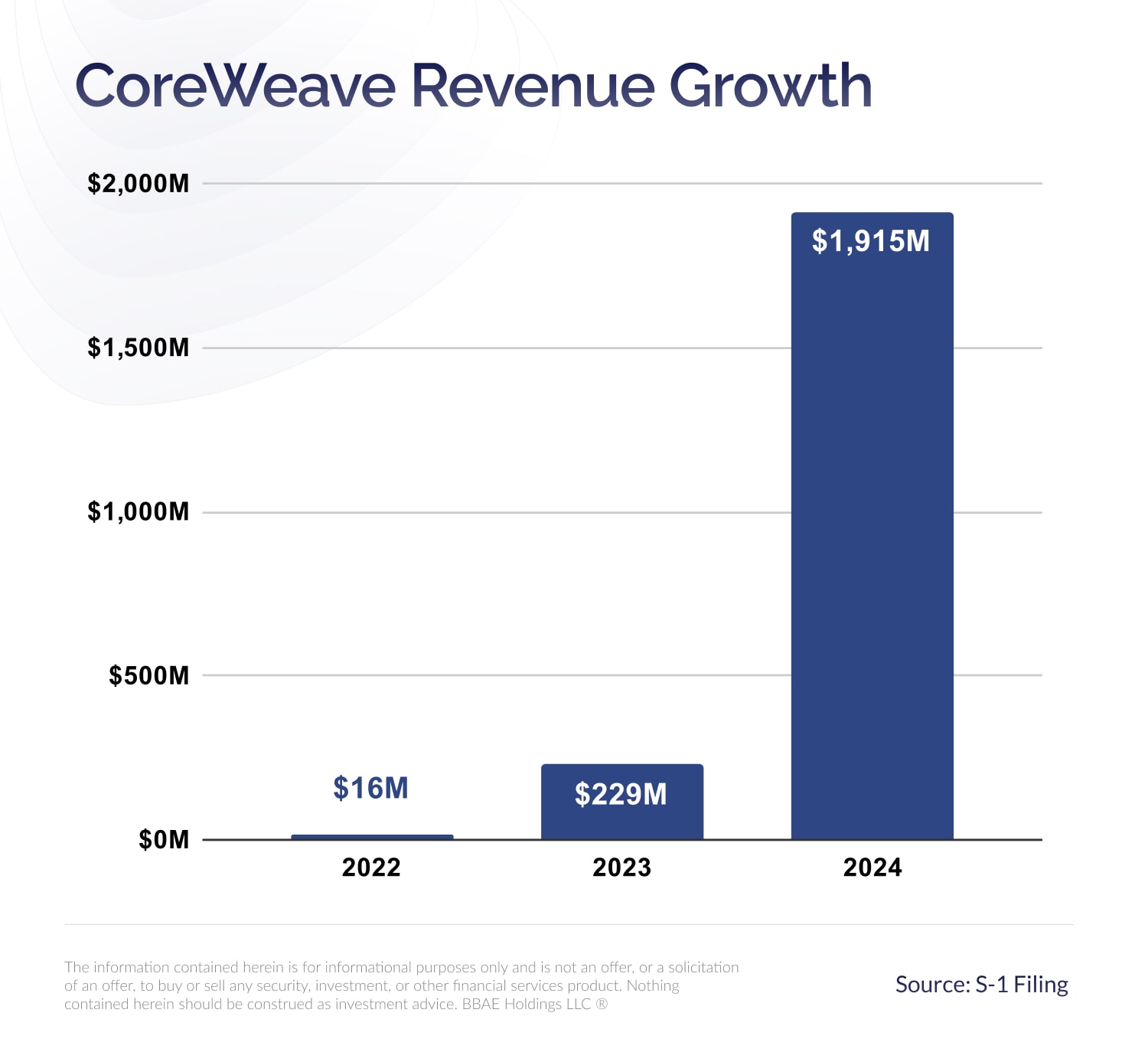 Why Did Core Weave Crwv Stock Price Jump Last Week
May 22, 2025
Why Did Core Weave Crwv Stock Price Jump Last Week
May 22, 2025 -
 Switzerlands Cassis Issues Statement On Pahalgam Terrorism
May 22, 2025
Switzerlands Cassis Issues Statement On Pahalgam Terrorism
May 22, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Produce Laden Tractor Trailer Crash On I 83
May 22, 2025
Produce Laden Tractor Trailer Crash On I 83
May 22, 2025 -
 Fed Ex Truck Fire On Route 283 In Lancaster County Pa
May 22, 2025
Fed Ex Truck Fire On Route 283 In Lancaster County Pa
May 22, 2025 -
 Significant Route 581 Traffic Disruption Due To Box Truck Crash
May 22, 2025
Significant Route 581 Traffic Disruption Due To Box Truck Crash
May 22, 2025 -
 Route 581 Traffic Stopped After Box Truck Collision
May 22, 2025
Route 581 Traffic Stopped After Box Truck Collision
May 22, 2025 -
 Box Truck Accident Shuts Down Section Of Route 581
May 22, 2025
Box Truck Accident Shuts Down Section Of Route 581
May 22, 2025
