Character AI Chatbots And Free Speech: A Legal Gray Area

Table of Contents
Character AI chatbots are rapidly gaining popularity, offering users engaging and often surprisingly realistic conversational experiences. However, this burgeoning technology presents a significant legal challenge: where does the line between free speech and potentially harmful or illegal content generated by these AI chatbots lie? This article delves into the complex legal landscape surrounding Character AI chatbots and free speech, exploring the ambiguities and potential consequences related to Character AI chatbot free speech issues.
H2: Liability for AI-Generated Content:
The question of liability for AI-generated content is a critical one in the context of Character AI chatbots and free speech. Who bears the responsibility when a chatbot generates offensive, hateful, or illegal material? This section explores the legal ramifications for both developers and users.
H3: The Role of the Developer:
Determining the developer's responsibility is complex. Existing legal frameworks, designed for traditional media, struggle to adapt to the unique characteristics of AI-generated content. Several key aspects need consideration:
-
Section 230 of the Communications Decency Act (CDA): This US law generally protects online platforms from liability for user-generated content. However, its applicability to AI-generated content, where the "user" is an algorithm, is highly debated. Courts may need to clarify whether developers can claim immunity under Section 230 for content generated by their AI chatbots.
-
Negligence Claims: Developers could face negligence claims if they fail to implement reasonable measures to prevent the generation of harmful content. This might include inadequate content filtering, insufficient training data, or a lack of effective moderation tools. The success of such claims hinges on demonstrating a breach of duty of care and a causal link between the developer's negligence and the harm caused.
-
Challenges in Moderation: Moderating user-generated prompts and AI-generated responses is incredibly challenging. The sheer volume of interactions and the unpredictable nature of AI language models make it difficult to identify and remove problematic content in real-time. This presents a significant hurdle for developers seeking to avoid legal repercussions.
H3: The User's Responsibility:
Users also bear some responsibility. While they might not directly create the text, their prompts can influence the output of the Character AI chatbot. Legal implications for users include:
-
Incitement and Conspiracy Laws: If a user prompts a chatbot to generate content that incites violence or participates in criminal conspiracy, they could face legal consequences. Proving intent and causation in such cases will be crucial.
-
Misuse and Malicious Intent: Users may intentionally misuse Character AI chatbots to generate illegal or harmful content. Their actions could be prosecuted under existing laws related to hate speech, harassment, or other criminal activities.
-
Difficulties in Proving Intent: Establishing the user's intent and their direct causal link to the harmful output is a significant challenge. The unpredictable nature of AI could make it difficult to prove that a user specifically intended to generate illegal or harmful content.
H2: Defining "Free Speech" in the Context of AI Chatbots:
The intersection of free speech principles and AI-generated content is uncharted territory. This section explores the application of free speech rights in this context.
H3: The First Amendment and AI:
The US First Amendment protects freedom of speech, but its application to AI-generated speech requires careful consideration. Are AI chatbots considered "speakers" with free speech rights, or are they simply tools used for expression? Several points are relevant:
-
Evolving Understanding of Free Speech: The interpretation of free speech in the digital age is constantly evolving. New legal precedents are required to address the unique challenges posed by AI-generated content.
-
Amplification of Biases: AI models can amplify existing societal biases and prejudices present in their training data. This raises concerns about the potential for AI chatbots to perpetuate harmful stereotypes and discriminatory language.
-
Censorship and Content Moderation: The issue of censorship and content moderation is particularly thorny. Balancing the need to prevent the spread of harmful content with the protection of free speech is a difficult task.
H3: International Legal Frameworks:
Legal frameworks governing AI-generated content and free speech vary considerably across jurisdictions. Understanding these differences is essential:
-
Comparative Legal Approaches: Different countries have varying approaches to regulating online speech, reflecting differing cultural norms and legal traditions. Some may have stricter regulations on hate speech or online harassment than others.
-
Enforcement Challenges: Enforcing international laws and regulations is particularly challenging due to jurisdictional issues and the global nature of the internet.
-
Cultural Norms and Acceptable Speech: The definition of acceptable speech varies across cultures. What might be considered free speech in one country could be considered illegal in another.
H2: The Future of Character AI Chatbots and Legal Regulation:
The future of Character AI chatbots hinges on the development of clearer legal frameworks and ethical guidelines.
H3: The Need for Clearer Legal Frameworks:
Addressing the legal ambiguities surrounding Character AI chatbots requires proactive legislative action:
-
New Laws and Amendments: New laws or amendments to existing laws may be necessary to explicitly address the liability issues surrounding AI-generated content.
-
Industry Self-Regulation: The AI industry could play a role in developing self-regulatory guidelines, but government oversight would likely be needed to ensure accountability.
-
Balancing Freedom and Safety: Finding a balance between protecting freedom of expression and ensuring public safety is a crucial challenge for policymakers.
H3: Technological Solutions and Ethical Considerations:
Technological advancements and ethical considerations are intertwined:
-
AI Safety Research: Investing in AI safety research and development is crucial to mitigate the risks associated with harmful AI-generated content.
-
Addressing AI Bias: Mitigating AI bias and discrimination is an ethical imperative. This requires careful attention to the training data and algorithmic design of AI chatbots.
-
Transparency and Accountability: Transparency and accountability are essential for building trust in AI systems. Developers should be transparent about the limitations of their technologies and accountable for their impact.
Conclusion:
Character AI chatbots and free speech present a complex legal gray area. The rapid advancement of AI technology outpaces the development of legal frameworks, creating significant uncertainty for developers, users, and policymakers alike. Establishing clearer legal boundaries and ethical guidelines is crucial to harnessing the potential benefits of Character AI chatbots while mitigating the risks of harmful or illegal content generation. We need proactive discussion and collaboration between lawmakers, developers, and users to navigate this evolving landscape and ensure responsible innovation in the field of Character AI chatbots and free speech. Further research into the legal implications of Character AI chatbots and free speech is essential for responsible development and use of this powerful technology.

Featured Posts
-
 Rybakina Ya Vsyo Eschyo Ne V Luchshey Forme Chestniy Kommentariy Tennisistki
May 24, 2025
Rybakina Ya Vsyo Eschyo Ne V Luchshey Forme Chestniy Kommentariy Tennisistki
May 24, 2025 -
 Is Apple Stock Headed To 254 Analyst Prediction And Buying Opportunities
May 24, 2025
Is Apple Stock Headed To 254 Analyst Prediction And Buying Opportunities
May 24, 2025 -
 Everything You Need Housing Finance Kids Activities At The Iam Expat Fair
May 24, 2025
Everything You Need Housing Finance Kids Activities At The Iam Expat Fair
May 24, 2025 -
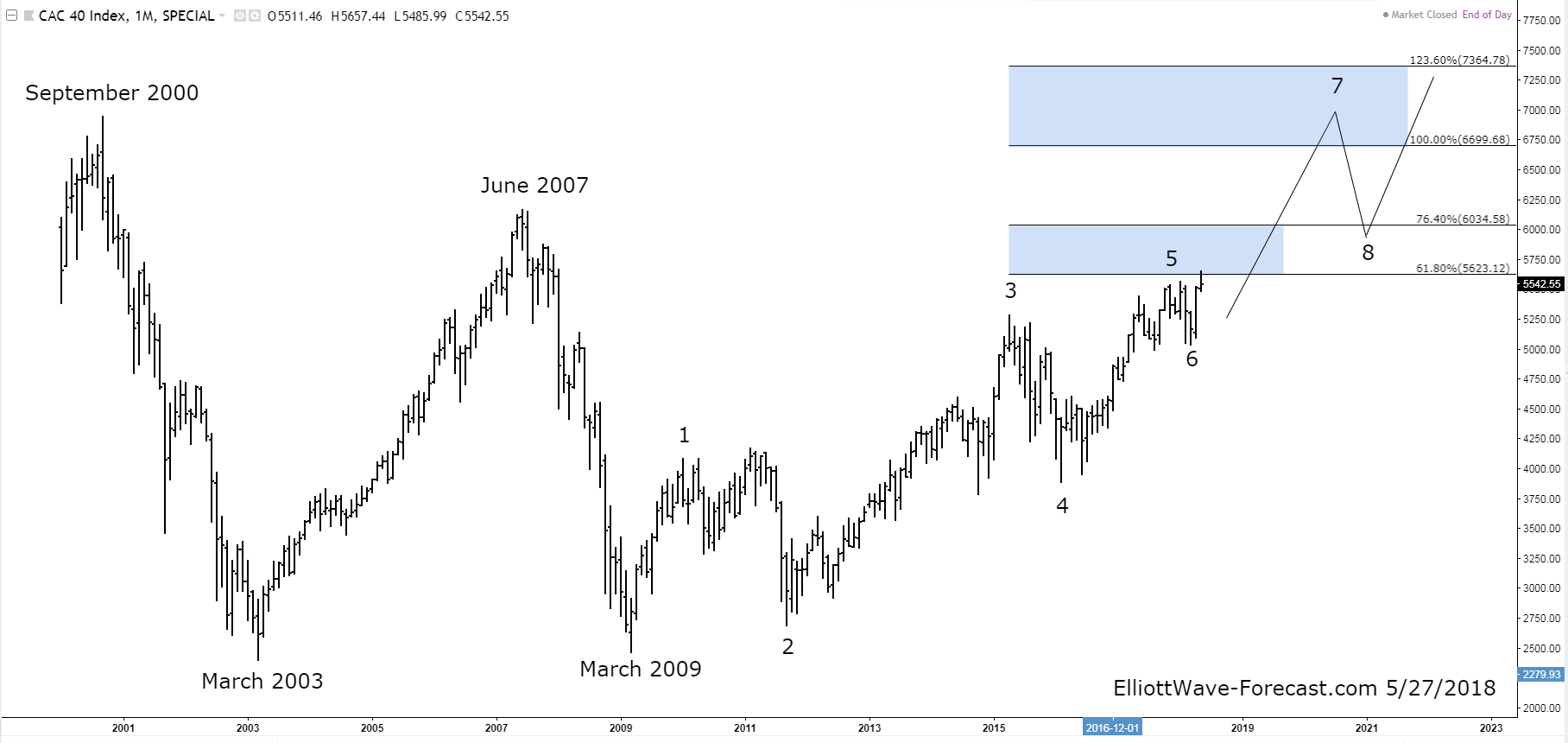 Cac 40 Index Week Ends Lower But Remains Steady Overall March 7 2025
May 24, 2025
Cac 40 Index Week Ends Lower But Remains Steady Overall March 7 2025
May 24, 2025 -
 Amsterdam Stock Exchange Suffers Third Consecutive Major Loss Down 11 Since Wednesday
May 24, 2025
Amsterdam Stock Exchange Suffers Third Consecutive Major Loss Down 11 Since Wednesday
May 24, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Indian Wells 2025 Swiatek And Rybakina Secure Fourth Round Berths
May 24, 2025
Indian Wells 2025 Swiatek And Rybakina Secure Fourth Round Berths
May 24, 2025 -
 Rybakina Otkrovennoe Intervyu O Sostoyanii Formy
May 24, 2025
Rybakina Otkrovennoe Intervyu O Sostoyanii Formy
May 24, 2025 -
 Elena Rybakina Otsenka Tekuschey Sportivnoy Formy
May 24, 2025
Elena Rybakina Otsenka Tekuschey Sportivnoy Formy
May 24, 2025 -
 Sostoyanie Formy Eleny Rybakinoy Slova Samoy Tennisistki
May 24, 2025
Sostoyanie Formy Eleny Rybakinoy Slova Samoy Tennisistki
May 24, 2025 -
 Rybakinas Victory Propels Kazakhstan To Billie Jean King Cup Finals
May 24, 2025
Rybakinas Victory Propels Kazakhstan To Billie Jean King Cup Finals
May 24, 2025
