Deadly Fungi: The Emerging Superbug Crisis
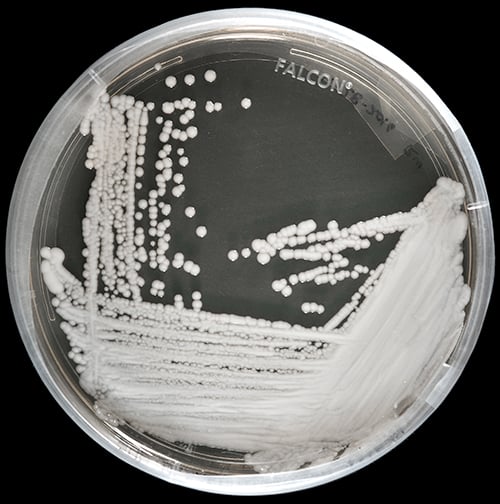
Table of Contents
The Growing Threat of Antifungal Resistance
Antifungal resistance occurs when fungi develop the ability to survive and reproduce even when exposed to antifungal drugs designed to kill them. This resistance develops through various mechanisms, including mutations in fungal genes that alter the drug's target site or the development of efflux pumps that expel the antifungal from the fungal cell. Different fungal species exhibit different resistance mechanisms. For example, Candida species, a common cause of bloodstream infections, can develop resistance to azoles through mutations in the ERG11 gene, while Aspergillus species, known for causing severe lung infections, may exhibit resistance to various antifungals via multiple mechanisms.
The widespread use of broad-spectrum antifungals accelerates the development of resistance. When a broad-spectrum drug is used, it targets a wide range of fungal species, increasing the selection pressure for resistance. The overuse of these medications, even in seemingly minor cases, significantly contributes to the problem.
- Increased mortality rates: Resistant fungal infections lead to significantly higher death rates compared to infections caused by susceptible fungi.
- Extended hospital stays: Treatment of resistant infections is more complex and prolonged, leading to increased hospital stays and healthcare costs.
- Limited treatment options: Once a fungus becomes resistant to multiple antifungal drugs, treatment options become severely limited, often resulting in difficult-to-treat infections.
- Vulnerable populations: Immunocompromised individuals, such as those with HIV/AIDS, cancer, or organ transplants, are at a substantially higher risk of developing serious, potentially fatal, resistant fungal infections.
Factors Contributing to the Superbug Crisis
Several interconnected factors fuel the rise of deadly fungi and the antifungal resistance crisis:
Overuse and Misuse of Antifungal Drugs
The excessive and often inappropriate use of antifungals in various sectors contributes significantly to resistance. In agriculture, antifungals are used extensively to prevent crop damage, leading to the selection of resistant fungal strains that can then spread to humans. Similarly, the use of antifungals in livestock contributes to the development and spread of resistance. In human medicine, the overprescription of antifungals, particularly broad-spectrum agents, for non-fungal infections or minor fungal infections, further accelerates the problem.
Lack of New Antifungal Drug Development
The pipeline for new antifungal drugs is alarmingly thin. The development of new antifungals is a complex and expensive process, with limited financial incentives for pharmaceutical companies. The lengthy development times and lower profit margins compared to antibacterial drugs have resulted in a significant lack of investment in this crucial area.
Global Health Inequalities
Limited access to accurate diagnostics, timely treatment, and appropriate infection control measures in low-resource settings disproportionately impacts vulnerable populations and accelerates the spread of resistant fungi globally. A lack of resources hinders early detection, effective treatment, and prevention efforts, leading to more severe outcomes and the emergence of resistant strains.
- Agricultural Antifungal Use: The widespread application of antifungals in agriculture is a major driver of antifungal resistance.
- Climate Change Impact: Climate change is increasing the prevalence and geographic distribution of certain fungal species, leading to a rise in infections.
- Diagnostic Limitations: The lack of rapid and accurate diagnostic tools for fungal infections delays treatment and contributes to the spread of resistance.
- Poor Infection Control: Inadequate infection control practices in healthcare settings, such as improper hygiene and sterilization protocols, promote the transmission of resistant fungi.
Combating the Deadly Fungi Threat: Strategies for the Future
Addressing the deadly fungi crisis requires a multifaceted, global approach focusing on several key strategies:
Developing New Antifungal Drugs and Therapies
Innovative approaches are needed to combat antifungal resistance. This includes repurposing existing drugs for antifungal activity, exploring novel drug targets within fungal cells, and utilizing advanced technologies such as artificial intelligence and high-throughput screening to accelerate drug discovery.
Improving Infection Prevention and Control
Stricter infection prevention and control measures within healthcare settings are crucial. This involves robust hygiene protocols, appropriate use of antifungals (only when necessary and with the correct dosage), and early detection of infections. Implementing comprehensive strategies to prevent the spread of fungi is vital.
Strengthening Global Surveillance and Research
Enhanced global surveillance systems are needed to monitor the emergence and spread of resistant fungal strains. Increased investment in research is paramount to develop new diagnostic tools, antifungal drugs, and effective treatment strategies. Collaborative efforts involving researchers, healthcare professionals, and policymakers are crucial to effectively tackle this global health challenge.
- Investing in R&D: Increased funding for research and development of novel antifungal agents is essential.
- Infection Control Protocols: Implementing and enforcing stringent infection control protocols in healthcare facilities is critical.
- Public Health Education: Public health campaigns aimed at raising awareness about fungal infections and the importance of responsible antifungal use are necessary.
- Rapid Diagnostics: Developing rapid and accurate diagnostic tests for fungal infections will enable timely and appropriate treatment.
Conclusion: Addressing the Deadly Fungi Crisis – A Call to Action
The rise of deadly fungi and the escalating crisis of antifungal resistance pose a significant and growing threat to global health. Addressing this requires an urgent and coordinated global effort. We must prioritize the development of new antifungal drugs, improve infection prevention and control measures, and strengthen global surveillance systems. By working collaboratively, researchers, healthcare professionals, policymakers, and the public can make a tangible difference in combating this emerging superbug crisis. Learn more about fungal infections, support research initiatives focused on developing new antifungals, and advocate for improved infection control practices to help fight the deadly fungi superbug crisis. Speak to your doctor about fungal infections and the responsible use of antifungal medications. Together, we can mitigate the devastating impact of these deadly fungi.

Featured Posts
-
 Is War Imminent Examining The Kashmir Dispute And India Pakistan Relations
May 08, 2025
Is War Imminent Examining The Kashmir Dispute And India Pakistan Relations
May 08, 2025 -
 Arsenal Manager Arteta Under Fire From Collymore Latest News
May 08, 2025
Arsenal Manager Arteta Under Fire From Collymore Latest News
May 08, 2025 -
 Rogues Team A Look At Her Place In Marvels Universe
May 08, 2025
Rogues Team A Look At Her Place In Marvels Universe
May 08, 2025 -
 Le Surprenant Talent Geometrique Des Corneilles Et Sa Superiorite Face Aux Babouins
May 08, 2025
Le Surprenant Talent Geometrique Des Corneilles Et Sa Superiorite Face Aux Babouins
May 08, 2025 -
 Ethereum Price Strength Bulls In Control Upside Potential High
May 08, 2025
Ethereum Price Strength Bulls In Control Upside Potential High
May 08, 2025
