How The Pope Is Elected: A Guide To The Conclave Process

Table of Contents
The papal election holds immense significance. The newly elected Pope leads over a billion Catholics worldwide, shaping the Church's doctrine, guiding its moral compass, and influencing global affairs. The selection of the next Vicar of Christ is a pivotal moment, rich in history and ritual. This guide will delve into the intricacies of this momentous occasion.
Understanding the Papal Election Process
The journey to electing a new Pope begins with the death or resignation of the incumbent. This triggers the Sede Vacante period, a time when the papacy is vacant. During this period, the College of Cardinals, a body of high-ranking clergy appointed by previous Popes, assumes responsibility for the Church's governance. Key terms to understand include:
- Conclave: The highly secretive meeting of Cardinals to elect the next Pope.
- Cardinals: High-ranking clergy of the Catholic Church, eligible to vote in a Papal Conclave.
- College of Cardinals: The body of Cardinals responsible for electing the Pope.
The College of Cardinals plays a crucial role in choosing the next Pope. Their responsibilities during the Sede Vacante period include:
- Managing the day-to-day affairs of the Church.
- Preparing for the Conclave.
- Ensuring a smooth transition of power.
The Conclave: Seclusion and Selection
The Conclave itself takes place in the Sistine Chapel within Vatican City. This location, renowned for its artistic splendor, becomes the stage for a highly regulated and secretive process. Strict rules govern the Conclave, emphasizing secrecy and preventing external influence on the Cardinals' deliberations.
The voting process is meticulously detailed:
- Secret ballots are cast by each Cardinal elector.
- A two-thirds majority is required for the election to be valid.
- Multiple rounds of voting may be necessary.
The iconic "fumata bianca" (white smoke) signals the election of a new Pope, while the "fumata nera" (black smoke) indicates that no candidate has achieved the necessary majority. These visual cues provide the world with updates on the progress of the Conclave.
The Role of the Cardinals in the Papal Election
To be eligible to vote in a Papal Conclave, a Cardinal must be under 80 years of age. The Cardinals' choices are influenced by various factors:
- Theological views: The candidate's understanding and interpretation of Catholic doctrine.
- Pastoral experience: Their track record of leading and guiding a diocese or other significant Church role.
- Political considerations: While officially discouraged, geopolitical considerations and alliances within the Church can sometimes play a role.
Different types of Cardinals might hold varying degrees of influence:
- Cardinal-Bishops: The highest rank, often holding significant administrative positions.
- Cardinal-Priests: Typically diocesan bishops.
- Cardinal-Deacons: Usually hold important positions within the Roman Curia.
History and Evolution of the Papal Election Process
The process of how the Pope is elected has evolved considerably over the centuries. Early papal elections were often marred by political interference and factionalism. Significant reforms throughout history aimed to create a more transparent and impartial system.
- The introduction of the Conclave itself was a major step towards greater secrecy and reduced external influence.
- Later reforms emphasized the importance of a two-thirds majority to ensure broader consensus.
The history of Papal elections also includes examples of highly contentious elections and even some unusual circumstances. Studying these historical examples provides valuable context for understanding the complexities of the process.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about Papal Elections
Q: What happens if there's a tie? Further rounds of voting continue until a two-thirds majority is achieved.
Q: How long does the conclave typically last? The duration varies, but it usually concludes within a few days.
Q: Can non-Catholics participate? No, only Cardinals under the age of 80 who are in full communion with the Catholic Church can participate in the Conclave.
Q: What are the immediate steps after a Pope is elected? The newly elected Pope is formally confirmed, and then typically addresses the world from the balcony of St. Peter's Basilica.
Understanding the Election of the Next Pope
In summary, the election of a new Pope, governed by the Conclave process within the College of Cardinals, is a complex yet crucial event for the Catholic Church. Understanding how the Pope is elected requires knowledge of the Sede Vacante period, the rules and regulations of the Conclave, and the crucial role played by the Cardinal electors in the Sistine Chapel. The use of the fumata bianca and fumata nera signals marks a critical stage in this process. This process, honed over centuries, strives for a balance between tradition and fairness in selecting the next leader of the global Catholic community.
Share this article with anyone interested in learning more about how the Pope is elected and the fascinating intricacies of the Conclave process! For further reading, explore biographies of influential Popes and delve deeper into the rich history of the Catholic Church.

Featured Posts
-
 Zalostna Slovesnost Pokop Zrtev Pozara V Nocnem Klubu V Kocanih In Okolici
May 07, 2025
Zalostna Slovesnost Pokop Zrtev Pozara V Nocnem Klubu V Kocanih In Okolici
May 07, 2025 -
 Multidao Dorme Nas Ruas Do Vaticano Em Homenagem Ao Papa Francisco
May 07, 2025
Multidao Dorme Nas Ruas Do Vaticano Em Homenagem Ao Papa Francisco
May 07, 2025 -
 Met Gala 2025 Top Looks And Fashion Statements From The Red Carpet
May 07, 2025
Met Gala 2025 Top Looks And Fashion Statements From The Red Carpet
May 07, 2025 -
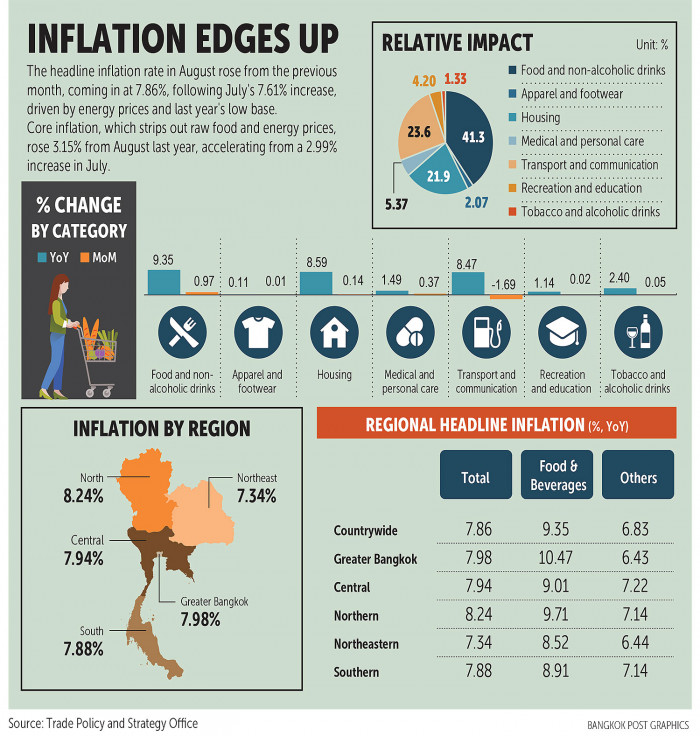 Interest Rate Cuts Expected In Thailand Following Negative Inflation
May 07, 2025
Interest Rate Cuts Expected In Thailand Following Negative Inflation
May 07, 2025 -
 Cobra Kai Exploring The Shows Continuity With The Karate Kid
May 07, 2025
Cobra Kai Exploring The Shows Continuity With The Karate Kid
May 07, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Counting Crows The Snl Effect And Its Lasting Influence
May 08, 2025
Counting Crows The Snl Effect And Its Lasting Influence
May 08, 2025 -
 The Night Counting Crows Changed Their Saturday Night Live Performance
May 08, 2025
The Night Counting Crows Changed Their Saturday Night Live Performance
May 08, 2025 -
 Saturday Night Live And Counting Crows A Career Defining Moment
May 08, 2025
Saturday Night Live And Counting Crows A Career Defining Moment
May 08, 2025 -
 The Night Counting Crows Changed Their Trajectory On Saturday Night Live
May 08, 2025
The Night Counting Crows Changed Their Trajectory On Saturday Night Live
May 08, 2025 -
 How Saturday Night Live Launched Counting Crows To Success
May 08, 2025
How Saturday Night Live Launched Counting Crows To Success
May 08, 2025
