Inside Our ADHD Minds: Navigating Challenges And Embracing Strengths

Table of Contents
Understanding the ADHD Brain: Challenges and Symptoms
Living with ADHD presents a unique set of challenges stemming from neurological differences in brain function. Understanding these challenges is the first step towards effective management.
Executive Function Deficits
Individuals with ADHD often experience significant difficulties with executive functions – the cognitive processes that enable us to plan, organize, and execute tasks. This executive dysfunction manifests in several ways:
- Difficulty prioritizing tasks: Struggling to determine which tasks are most important and tackling them first.
- Procrastination: Delaying tasks, even when aware of the consequences.
- Forgetfulness: Misplacing items, forgetting appointments, and struggling with working memory.
- Time management issues: Underestimating the time needed to complete tasks, leading to missed deadlines.
- Impulsivity: Acting without thinking, leading to regrettable decisions.
- Hyperactivity: Excessive restlessness and difficulty remaining still, especially in quiet settings.
These difficulties can significantly impact academic performance, professional productivity, and personal relationships.
Emotional Regulation
The emotional landscape for someone with ADHD can be a rollercoaster. Emotional dysregulation is a common feature, leading to:
- Emotional outbursts: Sudden shifts in mood, often disproportionate to the situation.
- Heightened sensitivity: Increased sensitivity to criticism, rejection, and environmental stimuli.
- Difficulty managing frustration: Experiencing intense frustration and difficulty coping with setbacks.
- Mood swings: Frequent and unpredictable changes in mood.
- Irritability: Increased irritability and impatience.
Understanding these emotional challenges is crucial for developing effective coping strategies.
Attention and Focus Challenges
The core characteristic of ADHD is, of course, difficulty with attention and focus. This attention deficit manifests as:
- Easily distracted: Being easily sidetracked by internal thoughts or external stimuli.
- Difficulty completing tasks: Struggling to maintain focus long enough to finish tasks, especially those that are tedious or require sustained effort.
- Hyperfocus: Conversely, sometimes experiencing intense focus on a specific activity, to the exclusion of all else. While this can be beneficial, it can also be disruptive if it prevents engagement in other necessary activities.
- Inattention: Failing to pay attention to details or making careless mistakes.
Strategies for Navigating ADHD Challenges
While ADHD presents significant challenges, effective management strategies can dramatically improve quality of life.
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT)
ADHD therapy, particularly Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT), provides valuable tools for managing ADHD symptoms. CBT helps individuals:
- Self-monitor: Track their thoughts, feelings, and behaviors to identify patterns and triggers.
- Cognitive restructuring: Challenge and modify negative or unhelpful thoughts.
- Behavioral activation: Engage in activities that increase positive emotions and reduce avoidance behaviors.
- Develop coping mechanisms: Learn strategies for managing stress, frustration, and impulsivity.
- Improve stress management: Implement techniques to reduce stress levels and improve overall well-being.
Medication Management
ADHD medication can be a crucial part of a comprehensive treatment plan. Medications, including stimulant and non-stimulant options, can help improve focus, reduce impulsivity, and improve emotional regulation. However:
- Different types of medication have different effects: It's important to work with a doctor to find the right medication and dosage.
- Potential side effects: Side effects vary, and it's essential to discuss any concerns with a healthcare professional.
- Medication is not a cure: Medication works best in conjunction with therapy and lifestyle adjustments.
Lifestyle Adjustments
Lifestyle changes play a vital role in managing ADHD. These adjustments can include:
- Regular exercise: Physical activity helps improve focus, mood, and sleep.
- Healthy diet: A balanced diet supports brain function and overall well-being.
- Sufficient sleep: Adequate sleep is crucial for cognitive function and emotional regulation. Good sleep hygiene is essential.
- Mindfulness techniques: Mindfulness practices, such as meditation, can enhance focus and emotional regulation. Mindfulness for ADHD is a growing area of research.
Embracing the Strengths of an ADHD Mind
While challenges exist, individuals with ADHD often possess unique strengths and talents.
Creativity and Innovation
ADHD is frequently associated with exceptional creativity and innovative thinking. This stems from:
- Out-of-the-box thinking: The ability to think differently and generate novel ideas.
- Innovative problem-solving: Finding creative solutions to complex problems.
- Artistic talent: A heightened capacity for artistic expression and creativity in various forms. ADHD creativity can lead to remarkable achievements in artistic fields.
Hyperfocus and Intense Passion
The ability to hyperfocus, while sometimes problematic, can be harnessed for productive pursuits:
- Deep engagement in hobbies: Achieving mastery in areas of interest through intense focus.
- Achieving exceptional results: Producing outstanding work when deeply engaged in a task. Hyperfocus ADHD can be a significant advantage in focused tasks.
- Passion projects: Pursuing personal projects with unwavering dedication and achieving impressive results.
Adaptability and Resilience
Individuals with ADHD often develop exceptional adaptability and resilience:
- Navigating unexpected challenges: Successfully adapting to changing circumstances and unexpected setbacks.
- Bouncing back from setbacks: Demonstrating remarkable resilience in overcoming adversity. ADHD resilience is a testament to their ability to persevere.
Conclusion
Understanding ADHD involves acknowledging both its challenges and its strengths. While executive dysfunction, emotional dysregulation, and attention deficits can pose significant difficulties, individuals with ADHD often possess remarkable creativity, hyperfocus capabilities, and impressive resilience. By employing strategies like CBT, medication management, and lifestyle adjustments, individuals can effectively navigate these challenges and unlock their full potential. Learning to manage attention deficit hyperactivity disorder isn't about eliminating the condition, but about optimizing its unique contributions to a fulfilling life. Learn more about managing your ADHD and unlocking your full potential. Take the first step towards a better life by [link to resources/help].

Featured Posts
-
 Ali Larter Returns In New Landman Season 2 Behind The Scenes Photos
May 13, 2025
Ali Larter Returns In New Landman Season 2 Behind The Scenes Photos
May 13, 2025 -
 Programma Podderzhki Veteranov Eao K 80 Letiyu Pobedy
May 13, 2025
Programma Podderzhki Veteranov Eao K 80 Letiyu Pobedy
May 13, 2025 -
 Cubs Rally Past Dodgers Happ Delivers Walk Off Victory
May 13, 2025
Cubs Rally Past Dodgers Happ Delivers Walk Off Victory
May 13, 2025 -
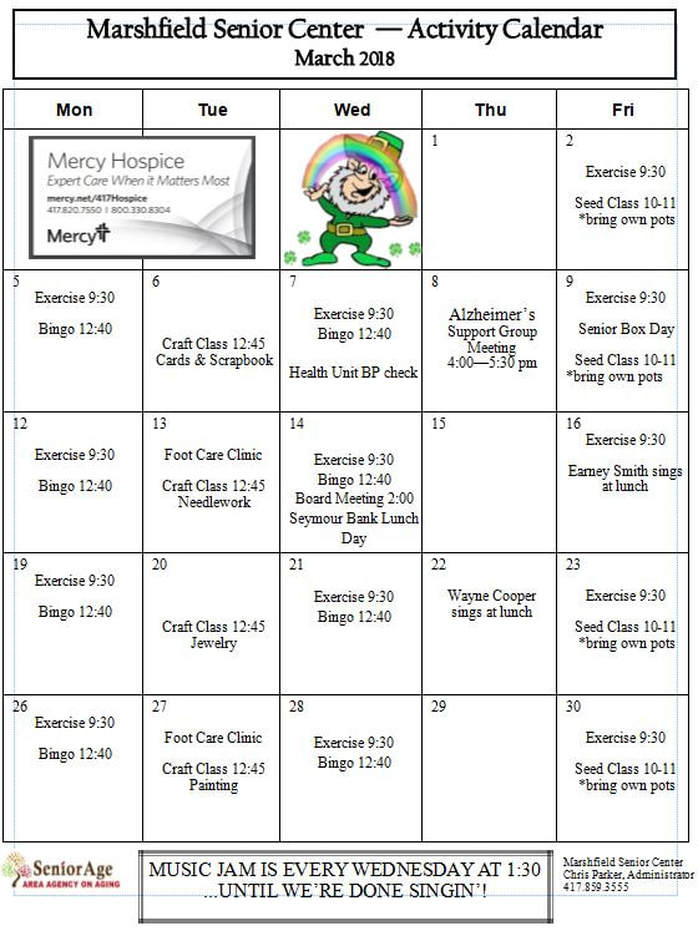 Comprehensive Senior Activities Calendar Trips And Events
May 13, 2025
Comprehensive Senior Activities Calendar Trips And Events
May 13, 2025 -
 The Enduring Nightmare Gaza Hostages And Their Families
May 13, 2025
The Enduring Nightmare Gaza Hostages And Their Families
May 13, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Addendum Analyzing Byds Success In The Ev Battery Market A Case Study
May 13, 2025
Addendum Analyzing Byds Success In The Ev Battery Market A Case Study
May 13, 2025 -
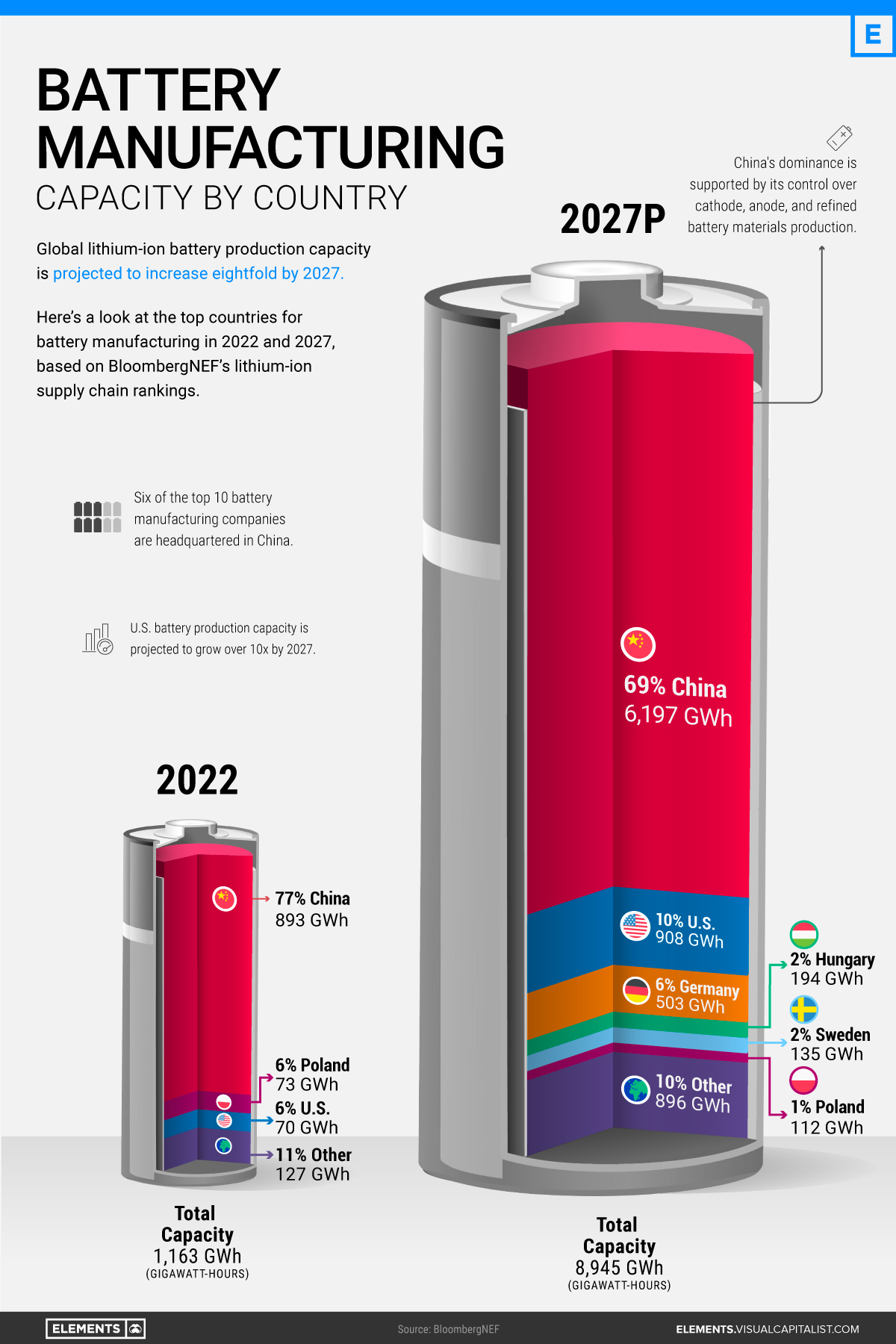 Byd Case Study Examining Their Leading Position In Ev Battery Manufacturing
May 13, 2025
Byd Case Study Examining Their Leading Position In Ev Battery Manufacturing
May 13, 2025 -
 Case Study Addendum Byds Leadership In Electric Vehicle Battery Production
May 13, 2025
Case Study Addendum Byds Leadership In Electric Vehicle Battery Production
May 13, 2025 -
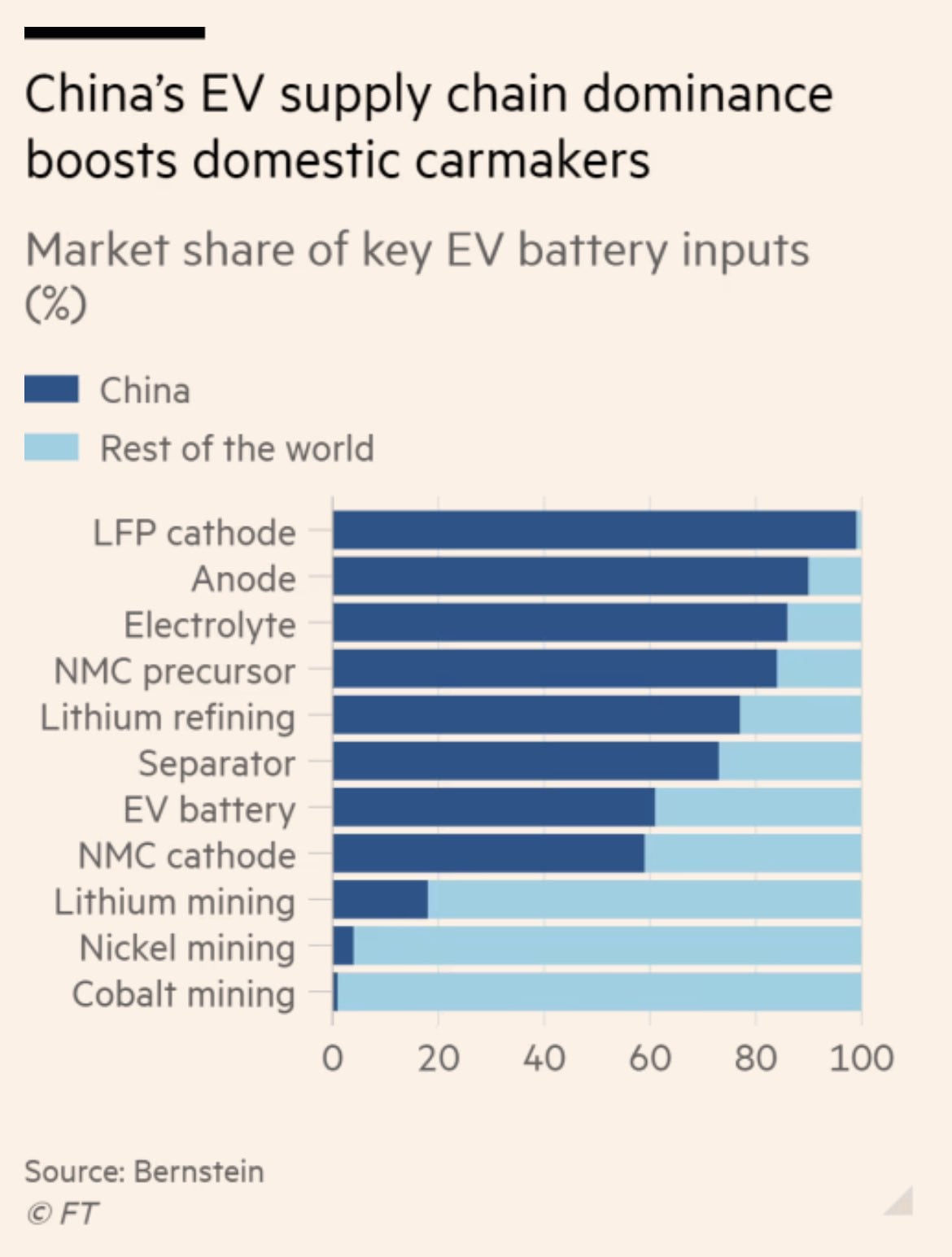 Byds Ev Battery Dominance A Case Study Addendum
May 13, 2025
Byds Ev Battery Dominance A Case Study Addendum
May 13, 2025 -
 Fords Brazilian Legacy Faces Byds Electric Vehicle Challenge
May 13, 2025
Fords Brazilian Legacy Faces Byds Electric Vehicle Challenge
May 13, 2025
