Is Manila Bay's Vibrancy Sustainable? A Critical Analysis
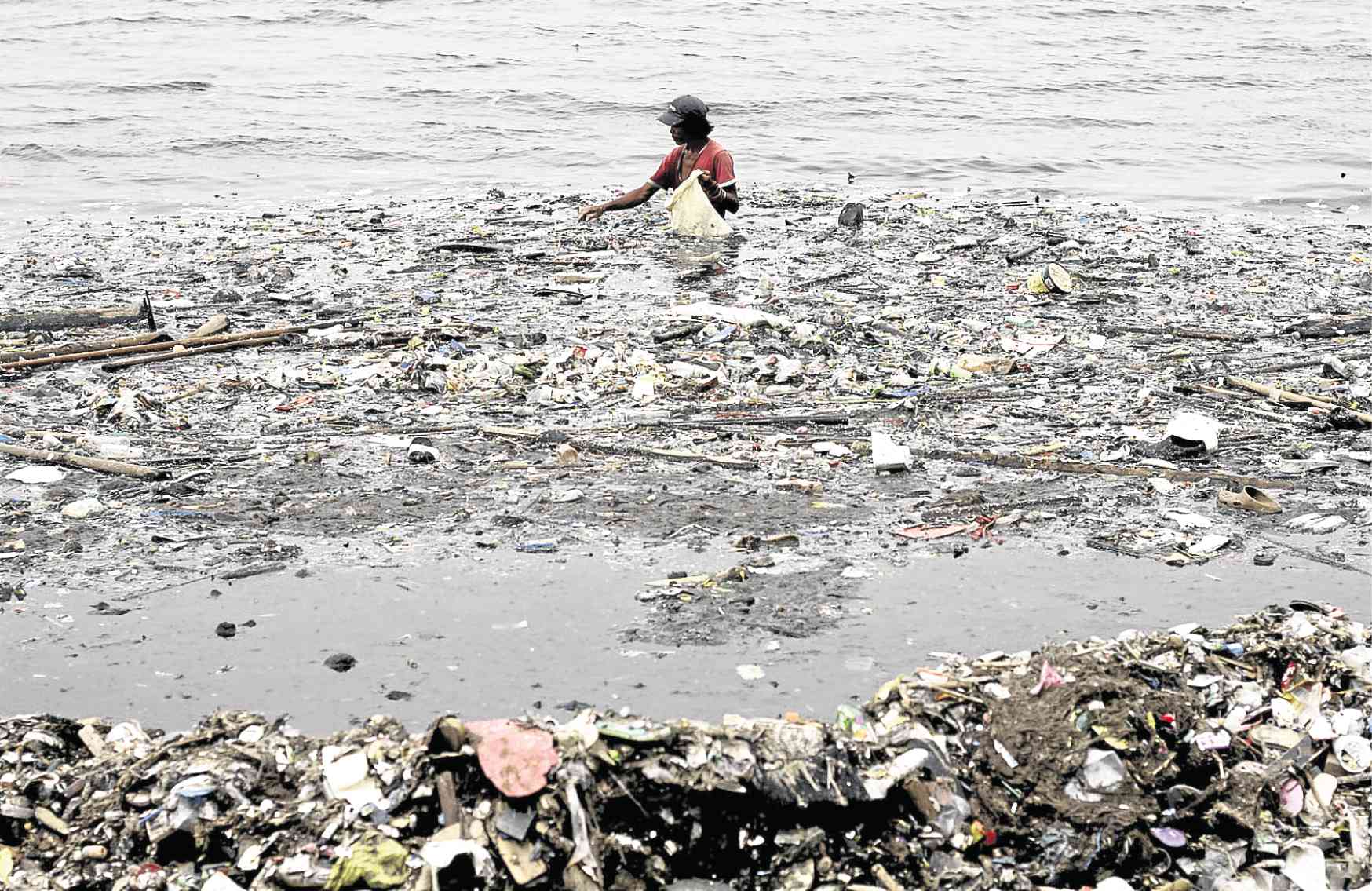

Table of Contents
Manila Bay, once choked by pollution and degradation, has recently undergone a remarkable transformation. Images of its revitalized, clearer waters have captivated the world, sparking renewed hope for its future. But the question remains: is this newfound Manila Bay's vibrancy sustainable in the long term? This article delves into a critical analysis of the environmental, socio-economic, and governmental factors influencing the long-term health and sustainability of this vital ecosystem. We will explore whether the current improvements are merely temporary or represent a genuine shift towards a sustainable future for Manila Bay.
2. Environmental Factors Affecting Manila Bay's Sustainability:
H2: Water Quality and Pollution Control:
The improvement in Manila Bay's water quality is undeniable, yet challenges persist. While cleanup efforts have yielded visible results, consistent monitoring and robust pollution control remain crucial. The current water quality levels, while improved, still require continuous assessment to ensure long-term sustainability.
- Sources of pollution: Industrial discharge, agricultural runoff containing pesticides and fertilizers, and untreated domestic waste continue to pose significant threats.
- Impact on marine life and biodiversity: Pollution leads to oxygen depletion, harming marine life and disrupting the delicate balance of the bay's ecosystem. This negatively impacts biodiversity and the overall health of the bay.
- Effectiveness of government regulations and enforcement: While regulations are in place, stricter enforcement and greater accountability are necessary to curtail illegal dumping and ensure compliance from industries and communities.
H2: Coastal Erosion and Habitat Degradation:
Rapid coastal development and reclamation projects have significantly impacted Manila Bay's coastline. These activities contribute to habitat loss and increased vulnerability to the effects of climate change.
- Loss of mangrove forests: Mangroves, crucial for coastal protection and biodiversity, have been severely depleted. Their loss exacerbates coastal erosion and reduces the bay's natural resilience.
- Impact on fish breeding grounds: The destruction of coastal habitats disrupts crucial fish breeding grounds, affecting fish populations and the livelihoods of those who depend on fishing.
- Mitigation strategies: Implementing sustainable coastal management practices, including mangrove reforestation and the creation of artificial reefs, is crucial to mitigating coastal erosion and habitat degradation. Addressing rising sea levels through climate change mitigation is also paramount.
H2: Biodiversity and Marine Life:
While some signs of marine life recovery are evident, the long-term sustainability of Manila Bay's biodiversity remains precarious.
- Species diversity and population trends: Monitoring species diversity and population trends is crucial to assess the effectiveness of conservation efforts and identify any emerging threats.
- Threats to endangered species: Several endangered species inhabiting Manila Bay are still vulnerable to pollution, habitat loss, and overfishing. Targeted conservation programs are needed to protect them.
- Conservation efforts: Ongoing conservation efforts, including the establishment of protected areas and the implementation of sustainable fishing practices, require continued investment and community engagement to ensure their long-term success.
3. Socio-Economic Factors Impacting Manila Bay's Long-Term Health:
H2: Tourism and its Environmental Footprint:
The revitalization of Manila Bay has attracted a surge in tourism, boosting the local economy. However, uncontrolled tourism can negatively impact the environment.
- Sustainable tourism practices: Implementing sustainable tourism practices, such as waste management programs, responsible waste disposal and eco-friendly transportation options, is crucial to minimize the environmental footprint of tourism.
- Balancing economic benefits with environmental protection: A delicate balance must be struck between economic benefits and environmental protection to ensure the long-term sustainability of Manila Bay's resources.
- Carrying capacity: Determining and managing the carrying capacity of Manila Bay's ecosystems is essential to prevent overexploitation and environmental degradation.
H2: Community Involvement and Participation:
Active community participation is vital for the long-term success of Manila Bay's conservation.
- Community-led projects: Successful community-led projects, such as coastal cleanups and mangrove reforestation initiatives, demonstrate the power of community engagement.
- Challenges in community engagement: Addressing challenges like limited resources, lack of awareness, and conflicting interests requires sustained efforts in community education and outreach.
- Education and awareness campaigns: Continuous education and awareness campaigns are necessary to foster a sense of responsibility and ownership among local communities regarding Manila Bay's preservation.
4. Governmental Policies and Sustainability Strategies:
H2: Government Initiatives and Regulations:
The Philippine government has implemented various initiatives and regulations to protect Manila Bay. However, their long-term effectiveness depends on consistent funding, robust enforcement, and community support.
- Government programs: The impact of specific government programs needs continuous evaluation and adjustment based on emerging challenges and changing environmental conditions.
- Funding and resource allocation: Adequate funding and resource allocation are crucial to support ongoing conservation efforts and the enforcement of environmental regulations.
- Enforcement of regulations: Stricter enforcement of environmental regulations is vital to deter illegal activities that contribute to pollution and habitat destruction.
5. Conclusion: Securing a Sustainable Future for Manila Bay's Vibrancy
The sustainability of Manila Bay's vibrancy hinges on a multi-faceted approach encompassing environmental protection, socio-economic development, and strong governmental policies. While significant progress has been made, ongoing challenges remain, including pollution control, coastal erosion, and the potential negative impacts of increased tourism. The long-term health of Manila Bay depends on continuous monitoring, effective enforcement of regulations, community involvement, and sustainable tourism practices. Let's work together to ensure the continued vibrancy of Manila Bay, advocating for sustainable practices and responsible tourism, securing a healthy and thriving ecosystem for generations to come. Protecting Manila Bay's sustainability is not just a government responsibility; it is a collective duty.

Featured Posts
-
 Measles In Texas New Cases Reported Separate From Current Outbreak
May 30, 2025
Measles In Texas New Cases Reported Separate From Current Outbreak
May 30, 2025 -
 Insults Whistles And Gum The Challenges Faced By Opponents Of French Players At Roland Garros
May 30, 2025
Insults Whistles And Gum The Challenges Faced By Opponents Of French Players At Roland Garros
May 30, 2025 -
 Cts Eventim Reports Strong Early Year Performance
May 30, 2025
Cts Eventim Reports Strong Early Year Performance
May 30, 2025 -
 Measles Cases Rise In Israel Linked To Texas Outbreak
May 30, 2025
Measles Cases Rise In Israel Linked To Texas Outbreak
May 30, 2025 -
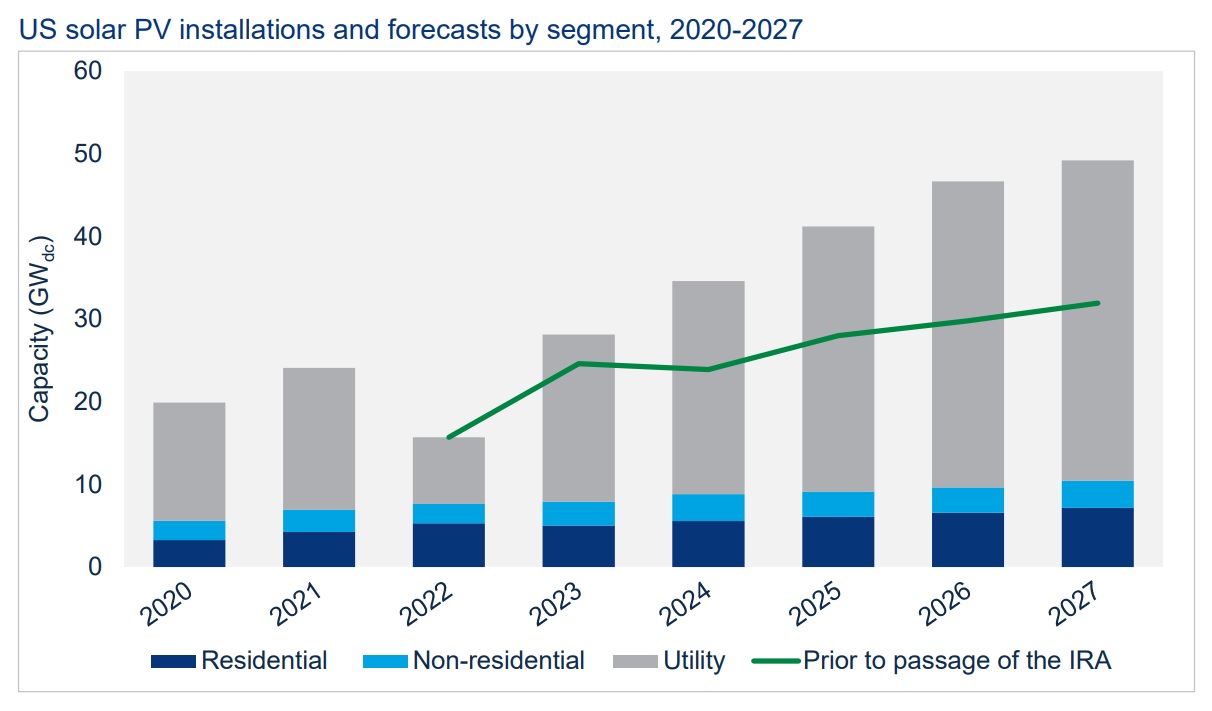 Increased Market Share Sought By Hanwha And Oci Following Us Solar Tariffs
May 30, 2025
Increased Market Share Sought By Hanwha And Oci Following Us Solar Tariffs
May 30, 2025
