Reduced Budgets, Reduced Accessibility: The Current State Of Game Development

Table of Contents
The Impact of Budget Cuts on Accessibility Features
Reduced budgets significantly constrain the development and implementation of accessibility features in video games. This impact manifests in several key ways:
Reduced Development Time
Shorter development cycles, a common consequence of lower budgets, severely limit the time allocated for accessibility. This leads to several issues:
- Less time for usability testing with disabled players: Meaningful feedback from the target audience is crucial, but rushed schedules often preclude thorough testing.
- Fewer resources allocated to accessibility consultants: Expert guidance is vital for designing inclusive experiences, but budget constraints often eliminate this crucial support.
- Rushed implementation leading to bugs and incomplete features: The pressure to meet deadlines can result in poorly implemented accessibility features, rendering them unusable or even counterproductive. This impacts the overall quality of the budget constraints and accessibility testing within the game development timeline.
Prioritization of Core Gameplay
Limited budgets force developers to prioritize core gameplay mechanics over secondary features, often including accessibility options. This prioritization can manifest as:
- Features like subtitle customization, controller remapping, and difficulty adjustments may be cut or simplified: These essential features are often sacrificed to meet budget targets.
- Focus shifts towards attracting a wider audience, potentially neglecting niche accessibility needs: The pressure to maximize sales can overshadow the need to cater to the specific needs of disabled gamers. This highlights the tension between core gameplay, accessibility options, and game design priorities.
Lack of Specialized Expertise
Smaller teams often lack the specialized knowledge needed to effectively design and implement accessibility features. This translates into:
- Difficulty hiring accessibility specialists: These specialists command competitive salaries, often beyond the reach of smaller studios.
- Reliance on less experienced team members: Tasks are delegated to individuals without the necessary expertise in inclusive game design and accessibility standards, resulting in subpar implementations.
- Potential for overlooking critical accessibility standards: Without dedicated expertise, teams may unintentionally fail to comply with established accessibility guidelines.
The Consequences of Reduced Accessibility
The reduction of accessibility features has significant and far-reaching consequences:
Exclusion of Disabled Gamers
The lack of accessibility features directly impacts the ability of disabled gamers to play and enjoy games:
- Loss of potential customers: The gaming market is missing out on a significant demographic.
- Negative impact on brand reputation: Companies risk damaging their image by excluding potential players.
- Missed opportunities for diverse representation in gaming: The absence of accessibility features hinders the creation of genuinely inclusive gaming experiences. This reinforces the need for disabled gamers, inclusive gaming, and better player representation.
Legal and Ethical Implications
Failing to incorporate adequate accessibility can trigger legal challenges and ethical issues:
- Potential lawsuits under disability discrimination laws: In some jurisdictions, failing to provide reasonable accommodations can lead to legal action.
- Negative public perception and boycotts: Consumers are increasingly aware of accessibility issues and may choose to boycott companies with poor accessibility records.
- Damage to the reputation of developers and publishers: Negative publicity can significantly impact a company’s image and financial performance. These points highlight the importance of understanding accessibility laws, ethical gaming, and avoiding disability discrimination.
Potential Solutions and the Future of Accessible Game Development
Addressing the issue of reduced accessibility requires a multifaceted approach:
Investing in Accessibility from the Start
Integrating accessibility considerations from the initial design phase is crucial for cost-effectiveness and inclusivity:
- Conducting thorough accessibility audits: Regular reviews can identify and address potential accessibility issues early in development.
- Employing accessibility consultants: Experts can provide guidance and ensure compliance with accessibility standards.
- Using accessible design tools and frameworks: Using appropriate tools can streamline the process and improve accessibility outcomes. This emphasis on inclusive game design, accessible development, and accessibility frameworks improves the quality of the final product.
Utilizing Open-Source Tools and Resources
Leveraging freely available resources can mitigate budgetary constraints:
- Employing open-source accessibility libraries: These libraries offer pre-built solutions, saving development time and resources.
- Using community-created accessibility tools: Collaboration within the gaming community can foster innovation and reduce costs.
- Collaborating with other developers on accessibility solutions: Sharing resources and knowledge can benefit the entire industry. This highlights the value of open-source accessibility, collaborative game development, and accessible game tools.
Advocacy and Community Engagement
Raising awareness and engaging with the disability community is paramount for creating truly inclusive games:
- Collaborating with disability advocacy groups: These groups can provide valuable insights and guidance.
- Seeking feedback from disabled players during development: Direct feedback is essential for ensuring that accessibility features meet actual needs.
- Promoting inclusive gaming practices: Raising awareness within the industry can encourage broader adoption of accessible design principles. This focuses on the importance of accessibility advocacy, a strong inclusive game development community, and meaningful disability community engagement.
Conclusion
The decline in accessibility features due to reduced budgets in game development poses a significant challenge. While financial pressures are undeniable, ignoring the needs of disabled gamers is ethically questionable and ultimately detrimental to the gaming community. By prioritizing accessibility from the outset, leveraging available resources, and actively engaging with the disability community, developers can create more inclusive and engaging experiences for everyone. Let's work together to ensure that reduced budgets don't translate to reduced accessibility in future game development. Invest in accessible game development today and build a more inclusive gaming future.

Featured Posts
-
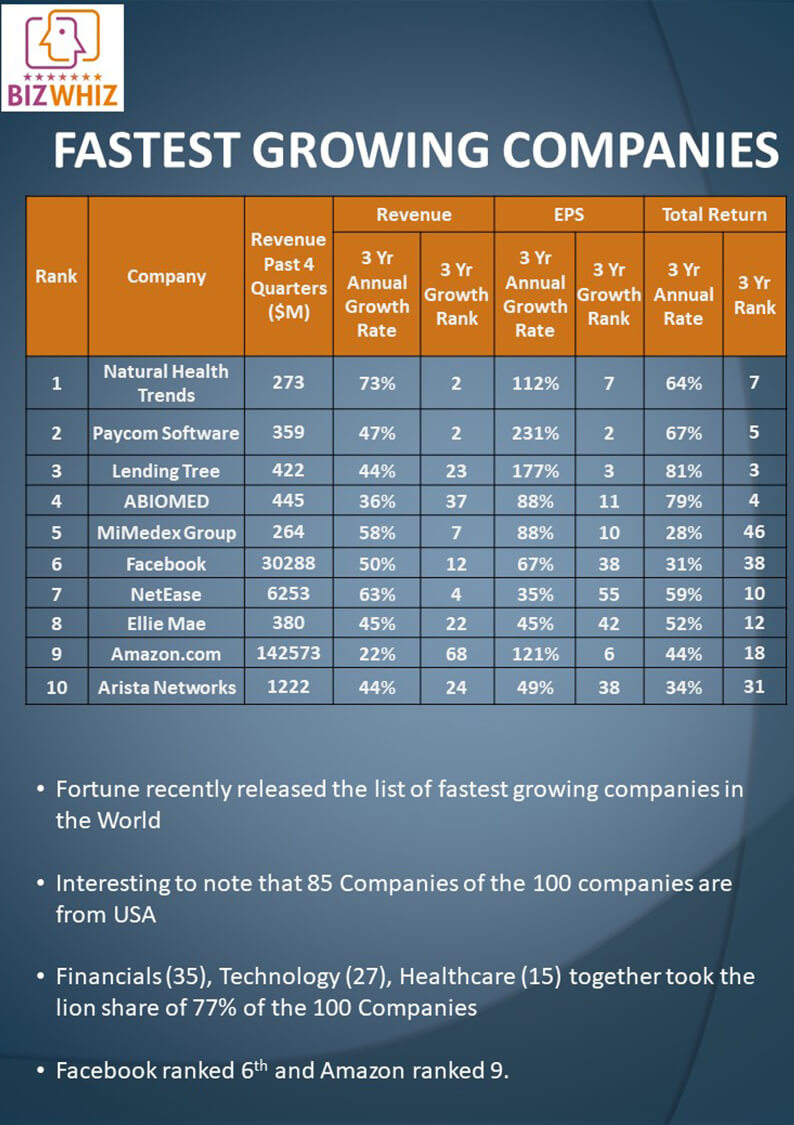 Where To Invest Now The Countrys Fastest Growing Business Regions
May 24, 2025
Where To Invest Now The Countrys Fastest Growing Business Regions
May 24, 2025 -
 Demna And Gucci A Fashion Partnership Analyzed
May 24, 2025
Demna And Gucci A Fashion Partnership Analyzed
May 24, 2025 -
 Sag Aftra Strike Hollywood Production Faces Complete Shutdown
May 24, 2025
Sag Aftra Strike Hollywood Production Faces Complete Shutdown
May 24, 2025 -
 The Case For News Corp Undervalued And Ready For Growth
May 24, 2025
The Case For News Corp Undervalued And Ready For Growth
May 24, 2025 -
 Pertimbangan Investasi Mtel And Mbma Di Msci Small Cap Index
May 24, 2025
Pertimbangan Investasi Mtel And Mbma Di Msci Small Cap Index
May 24, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Horoscopo Semanal 11 17 Marzo 2025 Descubre Tu Futuro
May 24, 2025
Horoscopo Semanal 11 17 Marzo 2025 Descubre Tu Futuro
May 24, 2025 -
 Following A Mishap Dylan Dreyers Distance From Today Show Co Stars
May 24, 2025
Following A Mishap Dylan Dreyers Distance From Today Show Co Stars
May 24, 2025 -
 Hospital Update Dylan Dreyers Son After Surgery
May 24, 2025
Hospital Update Dylan Dreyers Son After Surgery
May 24, 2025 -
 Horoscopo De La Semana Del 11 Al 17 De Marzo De 2025 Tu Guia Astrologica Completa
May 24, 2025
Horoscopo De La Semana Del 11 Al 17 De Marzo De 2025 Tu Guia Astrologica Completa
May 24, 2025 -
 Dylan Dreyers Post Mishap Relationship With Today Show Colleagues
May 24, 2025
Dylan Dreyers Post Mishap Relationship With Today Show Colleagues
May 24, 2025
