Refinancing Federal Student Loans With A Private Lender: What You Need To Know

Table of Contents
Understanding the Pros and Cons of Refinancing Federal Student Loans
Refinancing your federal student loans involves replacing your existing federal loans with a new private loan. This decision offers potential advantages but also carries significant drawbacks. Carefully weigh the benefits and risks before proceeding.
Potential Benefits:
- Lower Monthly Payments: One of the primary attractions of refinancing is the potential for significantly reduced monthly payments. This frees up cash flow for other financial priorities, such as saving for a down payment on a house or paying off other debts. A lower monthly payment can make managing your finances much easier.
- Lower Interest Rate: If you qualify for a lower interest rate with a private lender than your current federal loan interest rate, you could save thousands of dollars in interest over the life of your loan. This is a substantial long-term financial benefit. Interest rate savings are a key motivator for many borrowers considering refinancing federal student loans.
- Simplified Repayment: If you have multiple federal student loans, refinancing can consolidate them into a single loan with one monthly payment. This simplifies the repayment process and makes it easier to track your progress.
- Fixed Interest Rate: Many private student loan refinancing options offer a fixed interest rate, protecting you against future interest rate increases. This provides predictability and budget stability throughout the repayment period.
Potential Drawbacks:
- Loss of Federal Student Loan Benefits: This is perhaps the most crucial drawback. Refinancing with a private lender means losing access to crucial federal benefits like income-driven repayment plans (IDR), deferment, and forbearance. These programs offer crucial protections if you experience financial hardship.
- Higher Interest Rates (Potentially): While lower interest rates are possible, you might not qualify for a better rate than your current federal loan, especially if you have a lower credit score. Always compare rates from multiple lenders before making a decision.
- Risk of Default: Missing payments on a private student loan can severely damage your credit score, making it harder to obtain future loans or credit cards. It can also lead to collection actions.
- Prepayment Penalties (Possibly): Some private lenders may impose penalties if you repay your loan early. Carefully review the loan terms to avoid unexpected fees.
Eligibility Requirements for Private Student Loan Refinancing
Private lenders have specific criteria for approving student loan refinancing applications. Meeting these requirements significantly increases your chances of approval.
Credit Score:
Lenders typically require a good credit score, generally 680 or higher, to approve refinancing applications. A higher credit score demonstrates your creditworthiness and reduces the lender's risk. Improving your credit score before applying is highly recommended.
Income and Debt-to-Income Ratio:
Lenders assess your income to ensure you can comfortably afford the monthly payments. A low debt-to-income (DTI) ratio, which is the percentage of your monthly income going towards debt payments, increases your chances of approval.
Loan Amount:
The amount you can refinance depends on your creditworthiness and the lender's policies. Lenders assess the total amount of debt you can manage responsibly.
Type of Loans:
Private lenders may not refinance all types of federal loans. For example, some may not refinance Parent PLUS loans. Confirm which types of federal student loans are eligible with each lender before applying.
The Refinancing Process: A Step-by-Step Guide
Refinancing your federal student loans involves a series of steps. Following this process carefully will help you navigate the application process smoothly.
Research and Compare Lenders:
Shop around and compare interest rates, fees, and repayment terms offered by several private lenders. Online comparison tools can streamline this process. Consider factors beyond just the interest rate, such as customer service and repayment flexibility.
Check Your Credit Report:
Review your credit report for any inaccuracies that could negatively impact your application. Disputing any errors before applying can improve your chances of approval and secure a better interest rate.
Complete the Application:
Provide accurate and complete information on your application. Inaccurate information can delay the process or lead to rejection.
Review the Loan Documents:
Carefully review all loan documents before signing, paying close attention to the interest rate, fees, and repayment terms. Understanding the terms ensures you're making an informed decision.
Understand the Disbursement Process:
Familiarize yourself with how and when your refinanced loan funds will be disbursed. This ensures a smooth transition from your federal loans to your new private loan.
Alternatives to Refinancing Federal Student Loans
Before deciding to refinance, explore alternatives that might better suit your financial situation.
Income-Driven Repayment Plans:
Explore income-driven repayment (IDR) plans like ICR, PAYE, REPAYE, and IBR. These plans adjust your monthly payments based on your income and family size, potentially offering lower payments than your current plan.
Student Loan Forgiveness Programs:
Investigate eligibility for programs like PSLF (Public Service Loan Forgiveness). These programs can forgive a portion or all of your federal student loans under specific circumstances.
Deferment or Forbearance:
Consider temporary suspension of payments (deferment or forbearance) if facing financial hardship. These options provide temporary relief but do not eliminate your debt.
Conclusion:
Refinancing federal student loans with a private lender can be a financially advantageous decision, but only if approached carefully. Weighing the pros and cons, understanding eligibility requirements, and thoroughly comparing lenders are all crucial steps. Before making a decision, carefully consider the potential loss of federal benefits and explore alternative repayment options such as income-driven repayment plans or loan forgiveness programs. If, after careful consideration, refinancing federal student loans aligns with your financial goals, proceed cautiously and choose a reputable lender. Remember, responsible planning is key to successfully refinancing federal student loans.

Featured Posts
-
 Hondas Production Restructuring Implications For Canada
May 17, 2025
Hondas Production Restructuring Implications For Canada
May 17, 2025 -
 From Disaster To Success Thibodeaus Coaching Evolution And The Knicks Turnaround
May 17, 2025
From Disaster To Success Thibodeaus Coaching Evolution And The Knicks Turnaround
May 17, 2025 -
 Zuckerbergs Leadership In The Age Of Trump
May 17, 2025
Zuckerbergs Leadership In The Age Of Trump
May 17, 2025 -
 The Breen Bridges Exchange Nba Commentary And Player Reactions
May 17, 2025
The Breen Bridges Exchange Nba Commentary And Player Reactions
May 17, 2025 -
 Brunsons Podcast Perkins Call For Cancellation
May 17, 2025
Brunsons Podcast Perkins Call For Cancellation
May 17, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Analyzing Ubers Resilience In A Potential Recession
May 17, 2025
Analyzing Ubers Resilience In A Potential Recession
May 17, 2025 -
 Taking Your Pet On Uber In Mumbai Complete Guide
May 17, 2025
Taking Your Pet On Uber In Mumbai Complete Guide
May 17, 2025 -
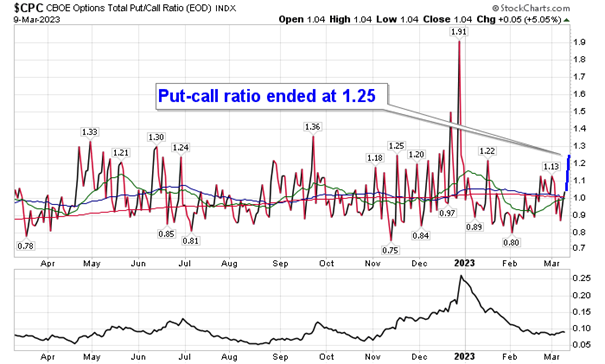 Ubers Stock Performance Defying Recessionary Trends
May 17, 2025
Ubers Stock Performance Defying Recessionary Trends
May 17, 2025 -
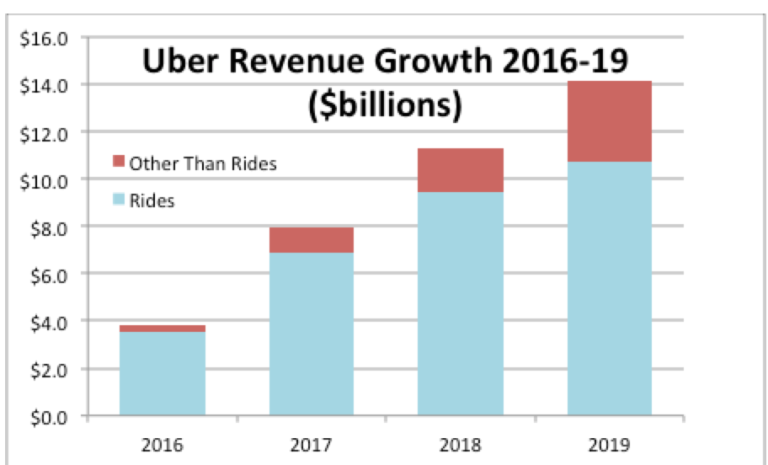 Why Uber Might Weather An Economic Downturn
May 17, 2025
Why Uber Might Weather An Economic Downturn
May 17, 2025 -
 Uber Pet Policy Mumbai How To Transport Your Furry Friend
May 17, 2025
Uber Pet Policy Mumbai How To Transport Your Furry Friend
May 17, 2025
