Rising Global Forest Loss: The Devastating Impact Of Wildfires

Table of Contents
The Causes of Rising Global Forest Loss from Wildfires
Several interconnected factors contribute to the increasing frequency and intensity of wildfires, leading to significant rising global forest loss.
Climate Change and its Role
Climate change is a primary driver of rising global forest loss from wildfires. Rising global temperatures, prolonged droughts, and altered precipitation patterns create ideal conditions for wildfires to ignite and spread rapidly. These conditions are exacerbated by:
- Increased lightning strikes: Warmer temperatures increase the frequency of thunderstorms, leading to more lightning-ignited fires.
- Drier vegetation: Prolonged droughts desiccate vegetation, turning forests into tinderboxes easily ignited and rapidly consumed by fire.
- Longer fire seasons: Warmer springs and autumns extend the periods when wildfires can occur, increasing the overall risk.
Data from the Global Forest Watch indicates a significant correlation between rising temperatures and increased wildfire activity globally. For instance, the area burned in the western United States has dramatically increased in recent decades, directly linked to rising temperatures and drought conditions.
Human Activities and Deforestation
Human activities significantly contribute to rising global forest loss by increasing wildfire risk. Deforestation for agriculture, urbanization, and unsustainable logging practices remove natural firebreaks and create fragmented landscapes more susceptible to fire spread. Other human-induced factors include:
- Removal of natural firebreaks: Clearing forests for development eliminates natural barriers that can slow or stop wildfire progression.
- Increased ignition sources: Discarded cigarettes, improperly maintained power lines, and accidental campfires are common ignition sources for wildfires.
- Poor land management practices: Lack of forest thinning and controlled burns can lead to the accumulation of flammable underbrush, increasing fuel loads and wildfire intensity.
Insect Infestations and Disease
Insect outbreaks and tree diseases weaken forests, making them more vulnerable to wildfires. These infestations and diseases can:
- Reduce tree vitality, making them more susceptible to burning.
- Create large amounts of dead and dying trees, acting as readily available fuel for wildfires.
Examples include the mountain pine beetle infestation in North America, which has devastated vast swathes of pine forests, leaving them highly vulnerable to fire. Similarly, diseases like Dutch elm disease can weaken tree stands, making them more susceptible to wildfire damage.
The Devastating Consequences of Rising Global Forest Loss
The consequences of rising global forest loss due to wildfires are far-reaching and devastating, impacting ecosystems, climate, economies, and human societies.
Biodiversity Loss
Wildfires cause immense biodiversity loss, destroying habitats and threatening countless plant and animal species. The destruction of critical habitats can lead to population declines and even extinction. Examples of species impacted include:
- The koala in Australia, whose habitat has been severely damaged by wildfires.
- The California condor, whose nesting grounds have been affected by wildfires.
- Numerous plant species endemic to specific regions, lost due to habitat destruction.
This loss of biodiversity disrupts ecosystems and food webs, creating cascading effects throughout the environment.
Climate Change Exacerbation
Forest loss from wildfires significantly exacerbates climate change. Burning forests release massive amounts of carbon dioxide (CO2) and other greenhouse gases into the atmosphere, contributing to the greenhouse effect and accelerating global warming. This creates a dangerous feedback loop:
- Climate change increases wildfire risk.
- Wildfires release more greenhouse gases.
- Increased greenhouse gases further accelerate climate change.
Economic and Social Impacts
Wildfires have significant economic and social costs. These include:
- Property damage: Homes, businesses, and infrastructure are destroyed, leading to substantial financial losses.
- Loss of livelihoods: Industries reliant on forests, such as tourism and timber, suffer economic setbacks.
- Healthcare costs: Smoke inhalation and other health problems related to wildfires result in significant healthcare expenses.
- Displacement and trauma: Communities are displaced, and individuals experience emotional trauma and loss.
- Loss of cultural heritage: Indigenous communities often lose culturally significant sites and resources.
Combating Rising Global Forest Loss: Solutions and Mitigation Strategies
Addressing rising global forest loss requires a multi-pronged approach combining improved forest management, climate change mitigation, and enhanced early warning systems.
Improved Forest Management Practices
Sustainable forestry practices are crucial in reducing wildfire risk. These include:
- Controlled burns: Prescribed fires reduce fuel loads and prevent the build-up of flammable underbrush.
- Forest thinning: Removing smaller trees and undergrowth creates space between trees, reducing the intensity of wildfires.
- Community involvement: Engaging local communities in forest management and fire prevention efforts is essential.
Climate Change Mitigation
Reducing greenhouse gas emissions is vital to mitigating climate change and, consequently, reducing wildfire risk. This requires:
- Transitioning to renewable energy sources.
- Improving energy efficiency.
- Implementing sustainable transportation systems.
- International cooperation on climate change policies.
Early Warning Systems and Fire Suppression
Advanced technology and early warning systems are crucial for effective wildfire management. These include:
- Satellite monitoring: Detecting wildfires early through satellite imagery.
- Improved weather forecasting: Predicting fire weather conditions to prepare for potential outbreaks.
- Early warning alerts: Providing timely warnings to communities at risk.
- Trained firefighters and effective emergency response: Investing in trained personnel and resources for rapid fire suppression.
Conclusion
Rising global forest loss due to wildfires presents a grave threat to our planet's ecosystems, climate, and human societies. The interconnected factors of climate change, human activities, and insect infestations contribute to this escalating crisis. The consequences are devastating, impacting biodiversity, exacerbating climate change, and imposing significant economic and social costs. To combat rising global forest loss, we must adopt a multi-faceted approach involving improved forest management, aggressive climate change mitigation, and enhanced early warning systems and fire suppression capabilities. We must act now to prevent further rising global forest loss. Learn more about how you can contribute to the fight against wildfires and protect our planet's vital forests. Support organizations working on forest conservation and advocate for policies promoting sustainable forest management and climate change mitigation. The future of our forests depends on it.

Featured Posts
-
 Last Ditch Effort From Crawley Secures Draw Against Gloucestershire
May 23, 2025
Last Ditch Effort From Crawley Secures Draw Against Gloucestershire
May 23, 2025 -
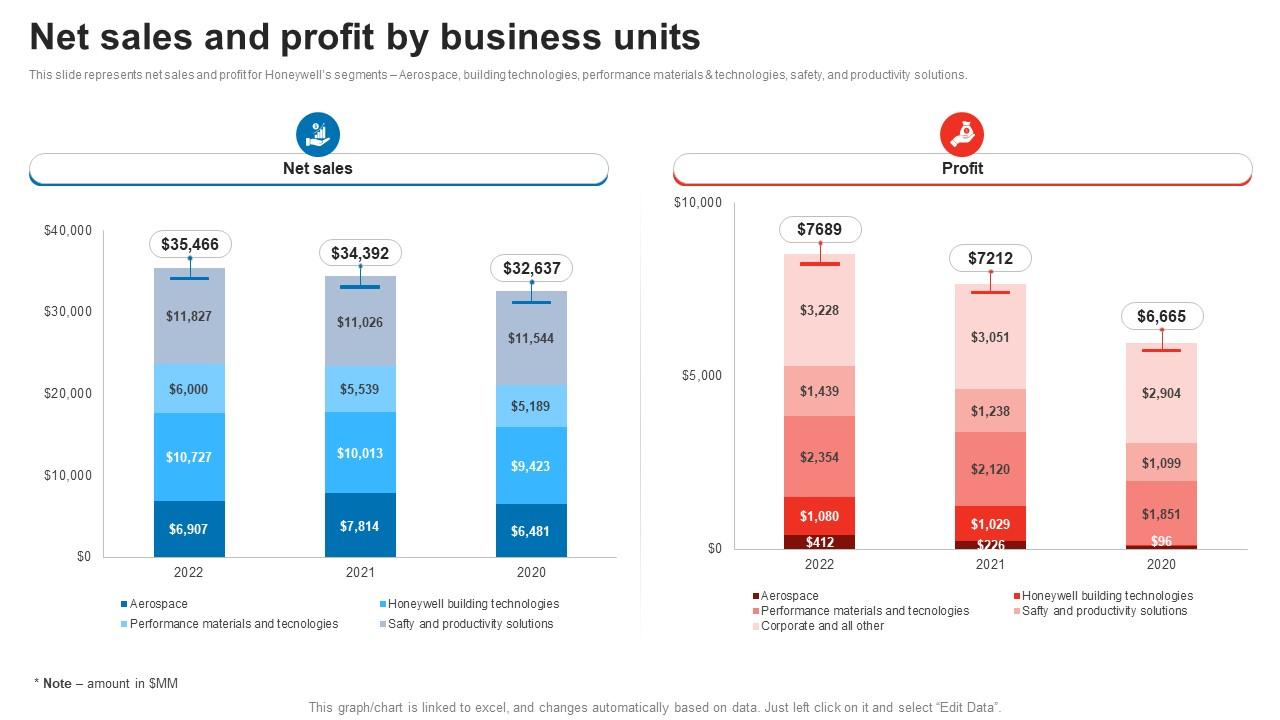 Bt Profit Increase Following Johnson Mattheys Honeywell Sale
May 23, 2025
Bt Profit Increase Following Johnson Mattheys Honeywell Sale
May 23, 2025 -
 Fratii Tate Defileaza Prin Bucuresti Imagini Video De La Sosirea In Romania
May 23, 2025
Fratii Tate Defileaza Prin Bucuresti Imagini Video De La Sosirea In Romania
May 23, 2025 -
 Psl X Sikandar Razas All Round Heroics Power Lahore Qalandars Victory
May 23, 2025
Psl X Sikandar Razas All Round Heroics Power Lahore Qalandars Victory
May 23, 2025 -
 Grand Ole Oprys Historic London Show Royal Albert Hall Broadcast Details
May 23, 2025
Grand Ole Oprys Historic London Show Royal Albert Hall Broadcast Details
May 23, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 80
May 24, 2025
80
May 24, 2025 -
 Top 10 Fastest Standard Production Ferraris On Their Home Track
May 24, 2025
Top 10 Fastest Standard Production Ferraris On Their Home Track
May 24, 2025
