Rising Temperatures, Falling Credit Scores: Understanding Climate Risk In Home Financing

Table of Contents
How Climate Change Impacts Property Values
Climate change significantly impacts property values through a direct link to climate-related disasters. Floods, wildfires, hurricanes, and even prolonged droughts can cause devastating damage, leading to immediate and significant devaluation. Beyond the direct damage, the increased risk of future events makes properties less desirable, further depressing prices. The impact extends to insurance, with increased premiums and difficulty securing coverage, especially in high-risk areas. This makes properties less attractive to buyers, further impacting value.
- Increased frequency of extreme weather events: More frequent and intense storms, floods, and wildfires are directly damaging properties and creating uncertainty for potential buyers.
- Rising sea levels and coastal erosion: Coastal properties are increasingly vulnerable to flooding and erosion, diminishing their long-term value and insurability.
- Wildfire risk and proximity to fire-prone areas: Homes located near forests or in areas with dry brush face significant wildfire risks, impacting their value and insurability.
- Changes in water availability impacting property value: Prolonged droughts can severely impact agricultural land and water access, leading to decreased property values in affected regions.
Examples of areas heavily impacted include coastal communities in Florida and Louisiana, wildfire-prone regions of California and the American West, and areas prone to severe flooding across the Midwest. For detailed information on climate risk in your specific area, consult resources like the Federal Emergency Management Agency (FEMA) and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA).
The Ripple Effect on Credit Scores
The decreased property value resulting from climate change directly impacts homeowner equity. Lower equity means a higher Loan-to-Value (LTV) ratio, potentially making it harder to refinance or access home equity loans. Difficulties securing or maintaining adequate insurance, particularly flood or wildfire insurance, also creates financial strain. Increased premiums can impact monthly budgets, potentially leading to late mortgage payments. In extreme cases, uninsured climate-related damage can result in foreclosure, severely damaging credit scores.
- Lower home equity leading to higher Loan-to-Value (LTV) ratios: This limits refinancing options and reduces access to home equity.
- Increased insurance premiums impacting monthly budgets: Higher premiums strain household finances, increasing the risk of late payments.
- Potential for foreclosure due to uninsured damage: Damage from climate events without adequate insurance can lead to financial hardship and foreclosure.
- Impact on credit scores through late payments or defaults: Financial strain from climate-related damage can lead to missed payments and a significant drop in credit scores.
Statistics show a clear correlation between climate-related disasters and mortgage defaults. The financial consequences can be devastating, impacting not just your home but your overall financial health for years to come.
Mitigating Climate Risk in Your Home Financing Strategy
Protecting your home and credit score from climate risk requires proactive measures. Understanding local climate risks is the first step. This involves researching historical weather patterns, assessing your property's vulnerability to specific threats (floods, wildfires, etc.), and understanding your local zoning regulations regarding climate-related risks. Investing in home resilience, such as flood mitigation systems, fire-resistant landscaping, and reinforced structures, can significantly reduce your risk and protect your investment.
- Regular home inspections and preventative maintenance: Early detection of problems can prevent costly repairs and maintain your property's value.
- Investing in climate-resilient home improvements: Upgrades like raised foundations, reinforced roofs, and fire-resistant materials can significantly reduce your risk.
- Securing adequate insurance coverage (including flood and wildfire insurance): Ensure you have sufficient coverage to protect against potential climate-related damage.
- Diversifying investments to mitigate financial risk: Don't put all your financial eggs in one basket. Diversification can help protect you from significant losses.
Consulting with financial advisors and insurance professionals is crucial to developing a comprehensive strategy to protect your financial future.
The Role of Lenders and the Future of Home Financing
Lenders are increasingly incorporating climate risk assessment into mortgage lending. This involves scrutinizing properties in high-risk areas, potentially leading to higher interest rates or stricter lending criteria. Climate risk disclosure is becoming increasingly important in real estate transactions, with buyers and sellers needing more transparency about potential climate-related hazards. We are likely to see changes in mortgage underwriting practices, potentially including the development of new climate-resilient mortgage products designed for properties with enhanced resilience features.
- Increased scrutiny of properties in high-risk areas: Lenders are becoming more cautious about lending in areas with high climate risk.
- Higher interest rates for properties in climate-vulnerable zones: Borrowers in high-risk areas may face higher interest rates to reflect the increased risk.
- Development of new climate-resilient mortgage products: New mortgage products may incentivize investments in climate-resilient upgrades.
- Greater emphasis on climate risk disclosure in loan applications: Transparency about climate risks will be crucial in the future of home financing.
Rising Temperatures, Falling Credit Scores – Protecting Your Financial Future
Climate change poses a significant threat to home values and credit scores. Proactive measures are essential to mitigate these risks. Assess your climate risk, research climate-resilient home improvements, and consult with financial professionals to safeguard your financial future. Understanding climate risk in home financing is no longer optional; it's essential for protecting your investment and creditworthiness. Learn more about climate risk in home financing and its implications today.

Featured Posts
-
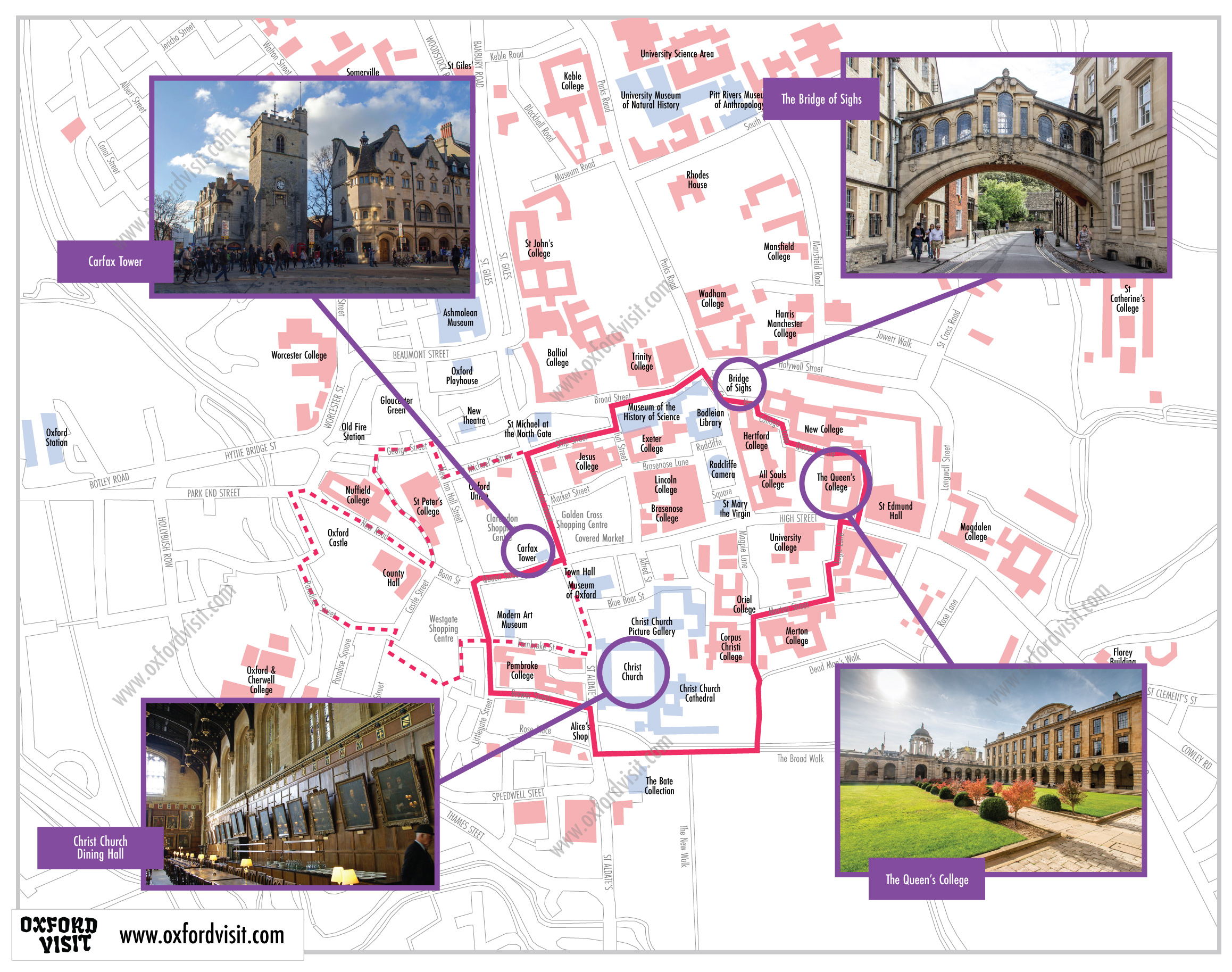 From The Mountains To The Med A Self Guided Walking Tour Of Provence
May 21, 2025
From The Mountains To The Med A Self Guided Walking Tour Of Provence
May 21, 2025 -
 Dexter Pops Funko Unveils Its First Ever Collection
May 21, 2025
Dexter Pops Funko Unveils Its First Ever Collection
May 21, 2025 -
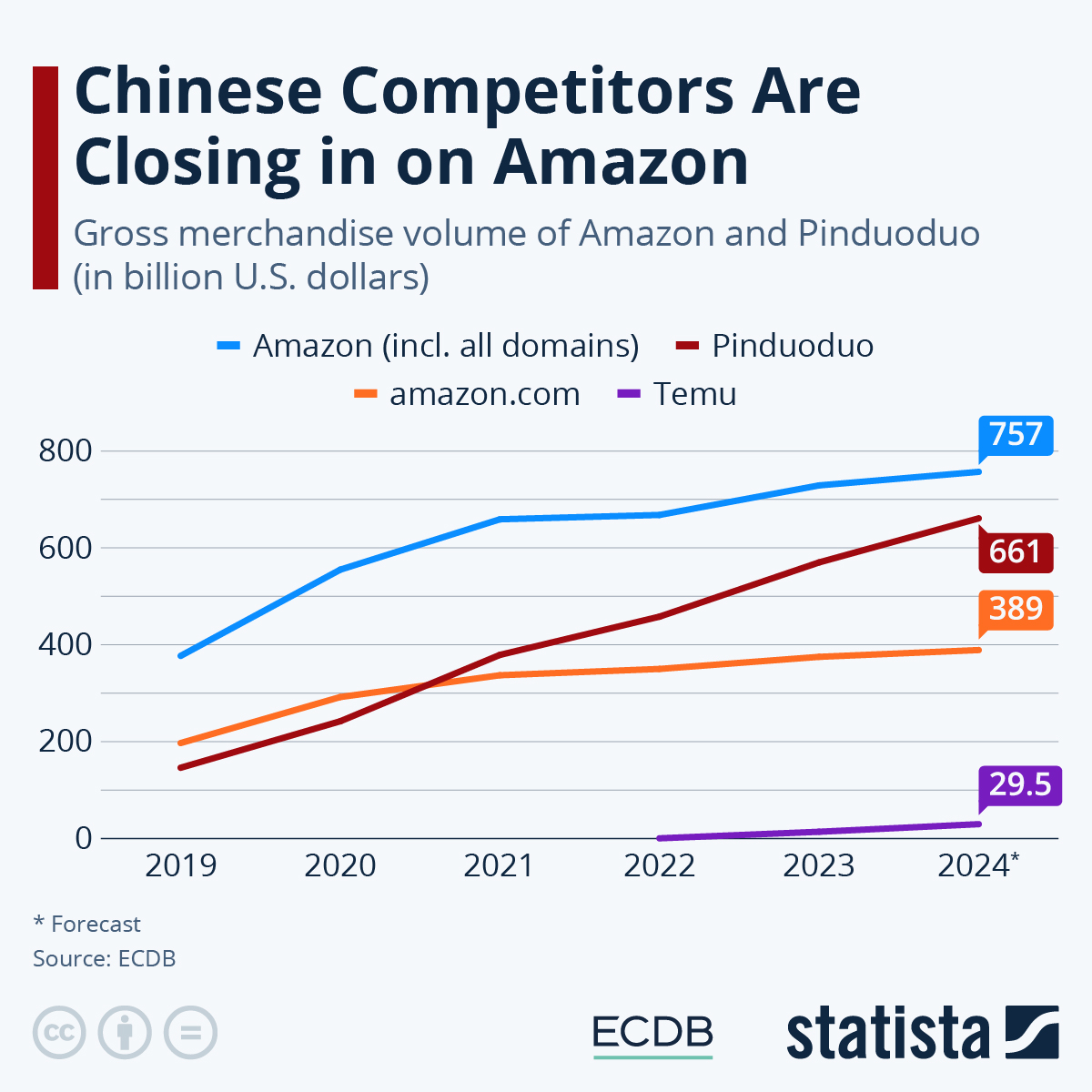 Home And Abroad Fp Videos Perspective On Persistent Tariff Challenges
May 21, 2025
Home And Abroad Fp Videos Perspective On Persistent Tariff Challenges
May 21, 2025 -
 Aimscap At The World Trading Tournament Wtt Strategies And Results
May 21, 2025
Aimscap At The World Trading Tournament Wtt Strategies And Results
May 21, 2025 -
 5 Podcasts De Terror Misterio Y Suspenso Para No Dormir En La Noche
May 21, 2025
5 Podcasts De Terror Misterio Y Suspenso Para No Dormir En La Noche
May 21, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Huuhkajien Kokoonpanossa Merkittaeviae Muutoksia Kaellman Pois Avauksesta
May 21, 2025
Huuhkajien Kokoonpanossa Merkittaeviae Muutoksia Kaellman Pois Avauksesta
May 21, 2025 -
 Huuhkajien Avauskokoonpano Naein Se Muuttuu Kaellman Ja Muut
May 21, 2025
Huuhkajien Avauskokoonpano Naein Se Muuttuu Kaellman Ja Muut
May 21, 2025 -
 Kolme Muutosta Huuhkajien Avauskokoonpanoon Kaellman Sivussa
May 21, 2025
Kolme Muutosta Huuhkajien Avauskokoonpanoon Kaellman Sivussa
May 21, 2025 -
 Huuhkajien Avauskokoonpano Naein Se Muuttui
May 21, 2025
Huuhkajien Avauskokoonpano Naein Se Muuttui
May 21, 2025 -
 Jalkapallo Kaellman Ja Hoskonen Jaettaevaet Puolan
May 21, 2025
Jalkapallo Kaellman Ja Hoskonen Jaettaevaet Puolan
May 21, 2025
