Sea Level Rise: Urgent Action Needed To Protect Coastal Regions
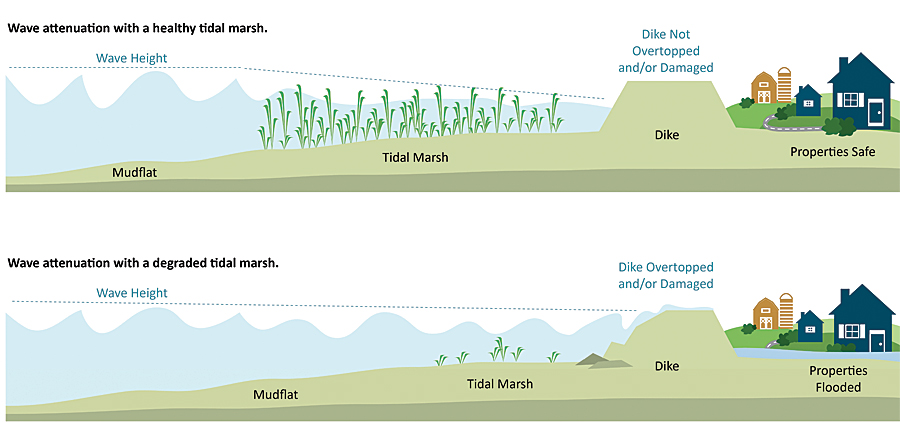
Table of Contents
The Causes of Sea Level Rise
The rise in global sea levels is a complex issue stemming from multiple interconnected factors. Understanding these causes is crucial for developing effective solutions.
Thermal Expansion
As the Earth's climate warms, ocean water expands. This thermal expansion contributes significantly to rising sea levels. The rate of expansion is directly correlated to increases in global temperature. For every degree Celsius of warming, the ocean expands, resulting in measurable sea level rise.
- The relationship between global temperature increase and thermal expansion is well-documented: Studies by the IPCC (Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change) show a clear correlation between rising global temperatures and increased ocean volume.
- Scientific reports consistently highlight the contribution of thermal expansion: Numerous peer-reviewed publications confirm the significant role of thermal expansion in observed sea level rise, emphasizing the urgency to curb greenhouse gas emissions.
Melting Glaciers and Ice Sheets
The melting of glaciers and ice sheets, particularly in Greenland and Antarctica, is another major driver of sea level rise. These massive ice bodies contain immense amounts of frozen water, and their loss contributes significantly to the increase in global sea levels. The rate of ice mass loss is accelerating, posing a severe threat to coastal communities.
- Climate change accelerates glacial melting: Rising temperatures are causing glaciers and ice sheets to melt at an alarming rate. This process is further amplified by positive feedback loops, such as the albedo effect (reduced reflectivity of ice leading to increased absorption of solar radiation).
- Projections for future ice mass loss paint a concerning picture: Scientific models predict significant further contributions to sea level rise from melting ice sheets in the coming decades and centuries. These projections underscore the urgency of addressing climate change.
Land Subsidence
Land subsidence, the gradual sinking of land, exacerbates the effects of sea level rise. In areas experiencing subsidence, the relative sea level rise—the combined effect of rising sea levels and sinking land—is even greater, leading to increased vulnerability to flooding and erosion.
- Groundwater extraction is a major contributor to land subsidence: Excessive pumping of groundwater can cause the land to compact, leading to significant sinking. This is particularly problematic in coastal areas with high populations and intensive agriculture.
- Tectonic activity can also cause land subsidence: Geological processes can contribute to land sinking in certain regions, exacerbating the effects of rising sea levels. Examples include coastal areas prone to earthquakes or tectonic plate movement. Venice, Italy, is a prime example of a region facing both sea level rise and land subsidence.
Impacts of Sea Level Rise on Coastal Regions
The consequences of rising sea levels are far-reaching and devastating for coastal communities worldwide. These impacts affect not only the environment but also human lives, economies, and infrastructure.
Coastal Erosion and Flooding
Increased sea levels lead to more frequent and severe coastal flooding and erosion. This results in the loss of valuable coastal properties, infrastructure damage (roads, buildings, power grids), and the destruction of vital coastal ecosystems, including wetlands and beaches.
- Examples of severely impacted coastal areas abound: Many low-lying island nations and coastal cities are already experiencing significant erosion and flooding. These impacts are costing billions of dollars annually.
- Economic and social costs are substantial: The damage from coastal erosion and flooding affects livelihoods, disrupts economies, and leads to displacement of populations. These costs are expected to rise dramatically in the coming decades.
Saltwater Intrusion
Rising sea levels lead to saltwater intrusion into freshwater aquifers, contaminating drinking water supplies and harming agriculture. This poses a severe threat to food security and public health in many coastal regions.
- Consequences of saltwater intrusion on agriculture are significant: Saltwater contamination renders land unsuitable for agriculture, reducing crop yields and threatening food production.
- Human health is also at risk: Contamination of drinking water sources can lead to various health problems, particularly in areas with limited access to clean water.
Displacement and Migration
The escalating impacts of sea level rise will lead to mass displacement and migration, creating climate refugees. This will exacerbate existing social and political challenges, requiring international cooperation to manage this growing crisis.
- Social and political challenges associated with climate migration are complex: Large-scale displacement puts a strain on resources, infrastructure, and social services in host communities.
- International cooperation is vital: Addressing climate migration requires collaborative efforts to provide support to displaced populations and to implement policies that address the root causes of climate change.
Mitigation and Adaptation Strategies for Sea Level Rise
Combating sea level rise requires a two-pronged approach: mitigating the causes and adapting to its inevitable effects.
Reducing Greenhouse Gas Emissions
The most crucial step in addressing sea level rise is to drastically reduce greenhouse gas emissions. This requires global cooperation to transition to cleaner energy sources and implement sustainable practices.
- International agreements like the Paris Agreement are crucial: These agreements set targets for emissions reductions, but stronger commitments and faster implementation are essential.
- National policies aimed at reducing emissions are vital: Governments must implement effective policies that incentivize renewable energy, improve energy efficiency, and promote sustainable transportation.
Coastal Protection Measures
Various strategies can protect coastal regions from the impacts of sea level rise. These include building seawalls, restoring coastal ecosystems (mangroves, salt marshes, and wetlands), and implementing managed retreat in highly vulnerable areas.
- Seawalls provide physical barriers but have drawbacks: They are expensive, can negatively impact coastal ecosystems, and don't always prevent flooding.
- Restoring coastal ecosystems is a more sustainable solution: Natural barriers such as mangroves and wetlands act as buffers against storm surges and erosion. These ecosystems provide numerous other benefits, including carbon sequestration.
- Managed retreat involves relocating communities away from high-risk areas: This approach requires careful planning and community engagement, but it is sometimes a necessary adaptation measure.
Improved Planning and Infrastructure
Improved urban planning and infrastructure development are crucial for minimizing vulnerability to sea level rise. This involves building resilient infrastructure, implementing early warning systems, and developing effective disaster preparedness plans.
- Resilient infrastructure is essential: Buildings, roads, and other infrastructure should be designed to withstand the impacts of flooding and erosion.
- Early warning systems can save lives and property: These systems provide timely alerts about impending floods and storms, enabling residents to take protective measures.
- Effective disaster preparedness plans are critical: Communities should develop comprehensive plans to respond effectively to coastal flooding and other extreme weather events.
Conclusion
Sea level rise is a significant threat to coastal communities worldwide, driven by thermal expansion, melting glaciers and ice sheets, and land subsidence. The impacts, including coastal erosion, flooding, saltwater intrusion, and displacement, are already being felt, and will only intensify without substantial action. Mitigation strategies, primarily focusing on drastically reducing greenhouse gas emissions, are essential to slow the rate of sea level rise. Simultaneously, adaptation strategies, including coastal protection measures and improved planning and infrastructure, are necessary to protect coastal communities from the inevitable impacts. Addressing sea level rise requires immediate and concerted global action. Learn more about the threat of sea level rise and get involved in protecting our coastlines today! [Link to relevant organization 1] [Link to relevant organization 2]

Featured Posts
-
 Ipswich Town News Sheehan Addresses Recent Disappointment
May 11, 2025
Ipswich Town News Sheehan Addresses Recent Disappointment
May 11, 2025 -
 The Easiest Path To High Dividend Income A Simple Profitable Strategy
May 11, 2025
The Easiest Path To High Dividend Income A Simple Profitable Strategy
May 11, 2025 -
 The Next James Bond Jeff Bezos Fan Poll Delivers A Definitive Answer
May 11, 2025
The Next James Bond Jeff Bezos Fan Poll Delivers A Definitive Answer
May 11, 2025 -
 Masazystka Ksiecia Andrzeja Szokujace Zdradliwe Tajemnice
May 11, 2025
Masazystka Ksiecia Andrzeja Szokujace Zdradliwe Tajemnice
May 11, 2025 -
 Schandaal Prins Andrew Verjaardagskaarten Spionage En Geheime Ontmoetingen
May 11, 2025
Schandaal Prins Andrew Verjaardagskaarten Spionage En Geheime Ontmoetingen
May 11, 2025
