The Bubble Blasters And Other Chinese Goods: Trade Chaos And Its Impact
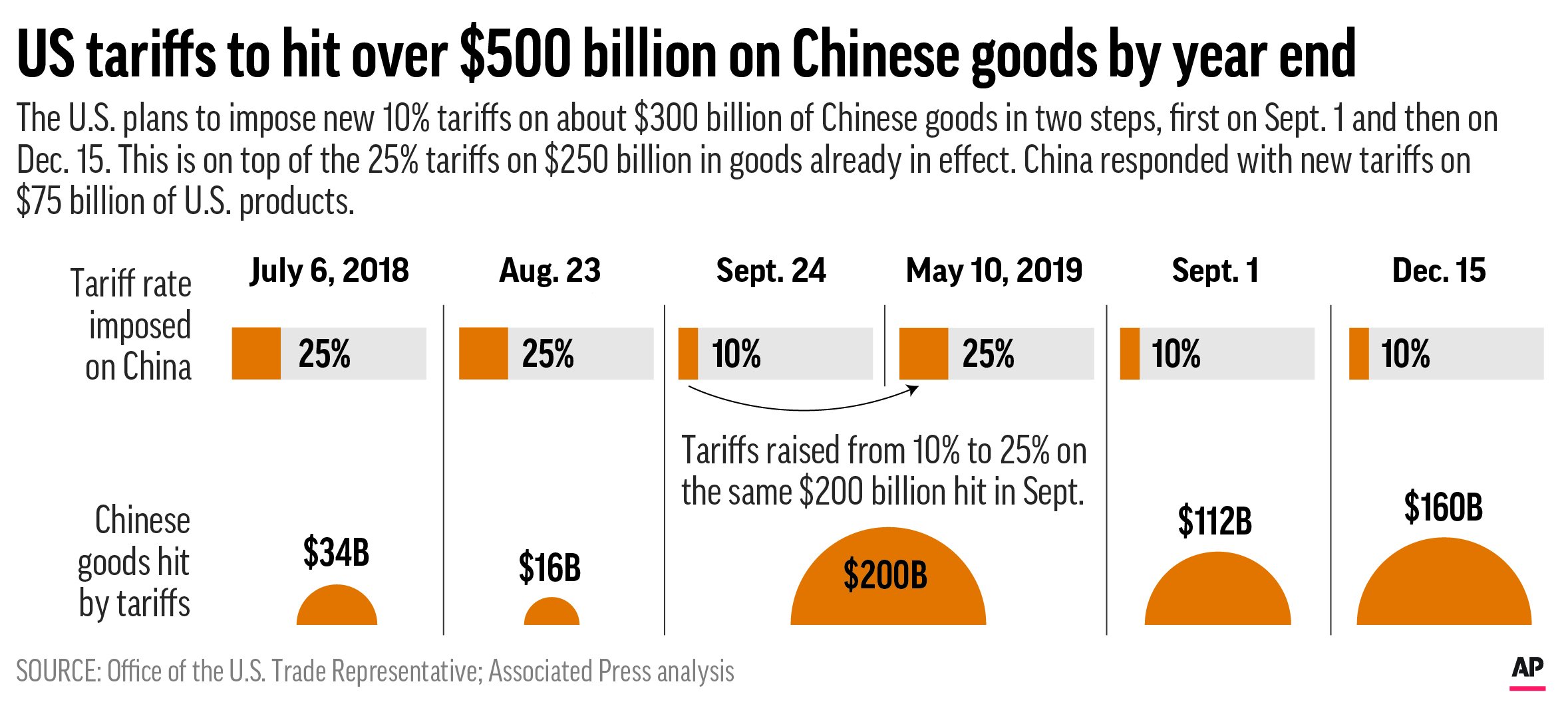
Table of Contents
The Rise and Fall (and Rise Again?) of Chinese Manufacturing
China's emergence as the "world's factory" is a remarkable story. Cheap labor, government support for export-oriented industries, and significant investments in infrastructure fueled this explosive growth. This propelled China to become a central node in global supply chains, impacting everything from electronics and textiles to toys like our bubble blaster.
- Exploration of China's role in global supply chains: China's vast manufacturing capacity allowed it to become the primary supplier for many multinational corporations, integrating deeply into global supply chains. This created intricate webs of interdependence, making China a crucial link in the global production process.
- Analysis of the impact of automation and technological advancements on Chinese manufacturing: While initially reliant on low-cost labor, China has increasingly invested in automation and robotics, shifting towards higher-value manufacturing and reducing reliance on purely labor-intensive processes. This modernization has implications for job markets both within China and globally.
- Discussion of the shift from low-cost manufacturing to higher-value added products: China is no longer solely focused on low-cost manufacturing. It's actively transitioning to higher-value-added industries, such as electronics, telecommunications equipment, and renewable energy technologies. This strategic shift positions China to compete in more sophisticated global markets.
However, this dominance hasn't been without its challenges. Rising labor costs, the impact of trade wars, and the disruptions caused by the COVID-19 pandemic have presented significant hurdles for Chinese manufacturers. The future of Chinese manufacturing depends on its ability to adapt and innovate in the face of these ongoing pressures.
The Impact of Trade Wars and Geopolitical Tensions
The US-China trade war, initiated in 2018, significantly impacted the flow of Chinese goods. Tariffs imposed by both countries led to increased prices for consumers and disrupted supply chains.
- Analysis of tariffs and their effect on prices and consumer choice: Tariffs directly increased the cost of many Chinese goods, impacting consumer spending and forcing businesses to adjust pricing strategies. Consumers faced higher prices or limited choices, depending on the availability of alternative suppliers.
- Discussion of the impact on specific sectors (e.g., technology, textiles): The impact varied across sectors. The technology sector, for instance, experienced heightened scrutiny over intellectual property rights and national security concerns. The textile industry faced challenges due to increased tariffs on fabrics and finished goods.
- Examination of the strategies employed by businesses to mitigate the effects of trade wars: Businesses adopted various strategies, including diversifying sourcing, relocating production facilities, and seeking alternative suppliers to reduce their reliance on China and mitigate the impact of tariffs.
Beyond tariffs, broader geopolitical tensions, including concerns about intellectual property theft and national security, have further complicated the landscape of Chinese goods trade, prompting many countries to re-evaluate their reliance on Chinese manufacturing and supply chains.
Supply Chain Disruptions and Their Global Ripple Effects
The COVID-19 pandemic exposed vulnerabilities within global supply chains, highlighting the over-reliance on China for many goods. Port congestion, shipping delays, and factory closures caused widespread disruptions, leading to shortages and increased prices across various sectors.
- Discussion of port congestion and shipping delays: The pandemic triggered significant port congestion and shipping delays, disrupting the timely delivery of goods globally. This resulted in significant costs for businesses and created uncertainty in supply chains.
- Examination of the impact on businesses reliant on Chinese goods: Businesses heavily reliant on Chinese goods faced significant challenges, including production delays, increased costs, and unmet consumer demand.
- Analysis of efforts to diversify supply chains and reduce reliance on China: Many countries and businesses are actively seeking to diversify their supply chains and reduce their reliance on China. This involves exploring alternative sourcing options and investing in domestic manufacturing capabilities.
These disruptions underscore the need for greater resilience and diversification within global supply chains. The consequences of these disruptions were felt globally, underscoring the interconnectedness of the global economy and the fragility of supply chains.
The Future of Chinese Goods Trade
The future of Chinese goods trade is complex and uncertain, shaped by several interacting forces.
- Discussion of the potential for continued growth in specific sectors: China is likely to maintain its competitive advantage in certain sectors, particularly those requiring large-scale manufacturing and technological expertise.
- Analysis of the challenges and opportunities for Chinese manufacturers: Chinese manufacturers face ongoing challenges, including rising labor costs, trade tensions, and the need for technological innovation. However, they also have significant opportunities, particularly in emerging technologies and higher-value-added manufacturing.
- Exploration of the evolving role of technology and automation in shaping future trade patterns: Technological advancements will likely play a pivotal role in shaping future trade patterns, influencing the competitiveness of Chinese manufacturers and the structure of global supply chains.
Conclusion:
The trade in Chinese goods, epitomized by everyday items like bubble blasters, is undergoing a period of significant transformation. The interplay of economic policies, geopolitical tensions, and global supply chain dynamics creates a complex and uncertain future. Understanding the nuances of Chinese goods trade is crucial for businesses, consumers, and policymakers alike. To stay informed about the latest developments and their impact on your sector, continue researching the evolving landscape of Chinese goods trade and its implications for the global economy. By staying informed, you can better navigate the complexities and capitalize on the opportunities presented by this dynamic market.

Featured Posts
-
 Frantsiya Polsha Unian Soobschaet O Novom Dogovore Makrona I Tuska
May 10, 2025
Frantsiya Polsha Unian Soobschaet O Novom Dogovore Makrona I Tuska
May 10, 2025 -
 Double Trouble In Hollywood The Writers And Actors Strike
May 10, 2025
Double Trouble In Hollywood The Writers And Actors Strike
May 10, 2025 -
 Is This Canadian Billionaire The Next Warren Buffett A Deep Dive Into Berkshire Hathaways Future
May 10, 2025
Is This Canadian Billionaire The Next Warren Buffett A Deep Dive Into Berkshire Hathaways Future
May 10, 2025 -
 Living Legends Of Aviation A Tribute To Firefighters And First Responders
May 10, 2025
Living Legends Of Aviation A Tribute To Firefighters And First Responders
May 10, 2025 -
 Is Young Thugs Back Outside Album Finally Dropping Soon
May 10, 2025
Is Young Thugs Back Outside Album Finally Dropping Soon
May 10, 2025
