The Undervalued Asset: Why Middle Managers Are Crucial For Organizational Success

Table of Contents
The Bridge Between Leadership and Employees
Middle managers are the crucial link connecting high-level strategic goals with the day-to-day operations of a company. They act as a vital bridge, ensuring effective communication and collaboration across all levels.
Translating Vision into Action
Middle managers are responsible for interpreting and translating the overarching vision set by senior leadership into actionable plans for their teams. This requires exceptional communication skills and the ability to break down complex objectives into manageable tasks. Effective middle managers ensure that every team member understands their role in achieving the company's goals.
- Effective communication strategies: Employing clear, concise language; using multiple communication channels; actively soliciting feedback.
- Delegation techniques: Assigning tasks based on individual strengths; providing clear instructions and expectations; empowering team members.
- Project management skills: Developing project plans; monitoring progress; managing resources effectively; adapting to changing priorities.
- Performance monitoring: Tracking progress towards goals; providing regular feedback; identifying areas for improvement; celebrating successes.
Fostering Collaboration and Teamwork
Beyond individual task management, middle managers cultivate a collaborative environment within their teams and across departments. This involves breaking down silos, fostering open communication, and resolving conflicts constructively.
- Team-building activities: Organizing events that promote team bonding and collaboration; encouraging social interaction among team members.
- Conflict management strategies: Mediating disagreements; facilitating constructive dialogue; finding mutually acceptable solutions.
- Open communication channels: Creating an environment where team members feel comfortable sharing ideas and concerns; actively listening to feedback.
- Fostering a collaborative culture: Promoting teamwork; recognizing and rewarding collaborative efforts; encouraging knowledge sharing.
Driving Operational Efficiency and Productivity
Middle managers are directly responsible for the day-to-day efficiency and productivity within their teams. Their actions have a tangible impact on the company's bottom line.
Optimizing Processes and Resources
Effective middle managers constantly seek ways to improve workflows, eliminate bottlenecks, and optimize resource allocation. This involves utilizing various methodologies and tools to streamline operations and increase productivity.
- Process improvement methodologies (e.g., Lean, Six Sigma): Implementing techniques to identify and eliminate waste in processes; optimizing workflows for maximum efficiency.
- Resource allocation strategies: Distributing resources effectively to maximize productivity; ensuring that teams have the tools and support they need.
- Performance metrics tracking: Monitoring key performance indicators (KPIs); identifying areas for improvement; using data to drive decision-making.
- Technology implementation: Leveraging technology to automate tasks, improve communication, and enhance overall efficiency.
Mentoring and Developing Talent
Middle managers play a critical role in nurturing and developing the talent within their teams. Investing in their team's growth directly benefits the organization as a whole.
- Performance reviews and feedback: Providing regular and constructive feedback to team members; identifying areas for improvement and growth.
- Training and development programs: Identifying training needs and providing opportunities for professional development; supporting employees in their career aspirations.
- Succession planning: Identifying and developing high-potential employees; creating a pipeline of talent for future leadership roles.
- Employee motivation techniques: Creating a positive and supportive work environment; recognizing and rewarding employee contributions; fostering a sense of purpose and belonging.
Championing Company Culture and Values
Middle managers are often the face of the company to their teams. Their actions directly influence the company's culture and values.
Embodying Organizational Culture
Middle managers model the desired behaviors and attitudes that define the company culture. Their leadership style and actions profoundly impact team morale and overall work ethic.
- Leading by example: Demonstrating the company values through their own actions and behaviors; setting a positive tone for the team.
- Promoting positive work relationships: Encouraging collaboration and respect among team members; fostering a sense of community within the team.
- Upholding company values: Ensuring that team members understand and adhere to the company's values; acting as a role model for ethical conduct.
- Fostering a sense of belonging: Creating an inclusive and welcoming environment where all team members feel valued and respected.
Identifying and Addressing Challenges
Middle managers are often the first to detect emerging problems or challenges within their teams. Their ability to proactively address these issues prevents larger problems down the line.
- Proactive problem-solving: Identifying potential issues before they escalate; developing and implementing solutions to prevent problems.
- Risk management: Assessing potential risks; developing mitigation strategies; proactively addressing potential threats to the team or the organization.
- Identifying areas for improvement: Continuously looking for ways to improve processes, efficiency, and team performance.
- Reporting and escalation procedures: Following established procedures for reporting problems; escalating issues to senior management when necessary.
Conclusion
Middle managers are not simply cogs in the organizational machine; they are the crucial link between leadership and employees, directly impacting operational efficiency, productivity, and company culture. Investing in their development, empowering them with the right tools, and recognizing their invaluable contributions is essential for any organization striving for sustainable success. By understanding the critical role of middle managers, businesses can unlock their full potential and build a more productive, engaged, and successful workforce. Don't undervalue this vital asset – invest in your middle management today!

Featured Posts
-
 Willie Nelsons 154th Album Release Amidst Family Dispute
Apr 29, 2025
Willie Nelsons 154th Album Release Amidst Family Dispute
Apr 29, 2025 -
 Exploring The Cognitive Capacity Of Ai Beyond The Hype
Apr 29, 2025
Exploring The Cognitive Capacity Of Ai Beyond The Hype
Apr 29, 2025 -
 Anthony Edwards Injury Update Will He Play Lakers Vs Timberwolves
Apr 29, 2025
Anthony Edwards Injury Update Will He Play Lakers Vs Timberwolves
Apr 29, 2025 -
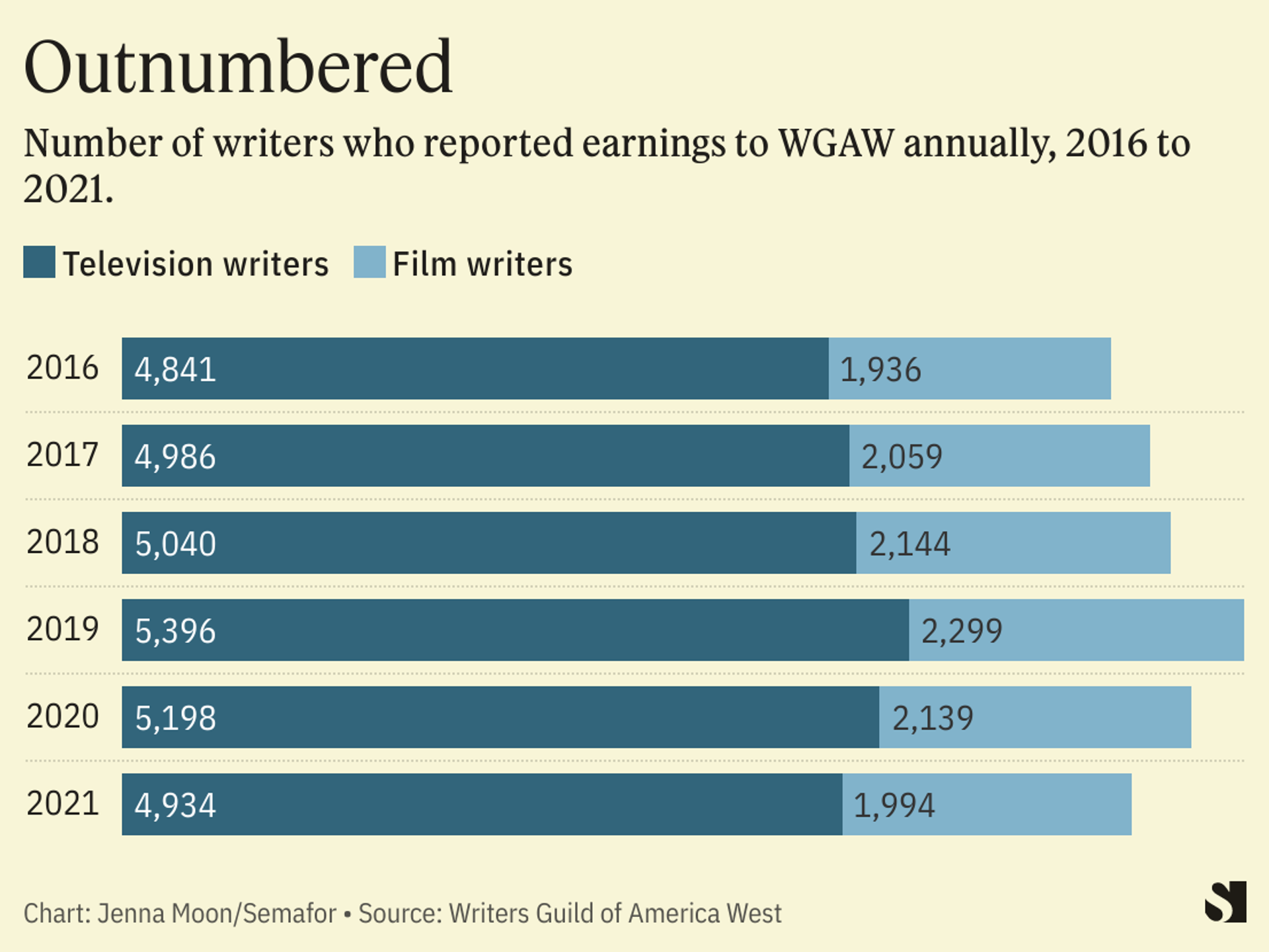 Double Strike Cripples Hollywood Actors And Writers Demand Fair Treatment
Apr 29, 2025
Double Strike Cripples Hollywood Actors And Writers Demand Fair Treatment
Apr 29, 2025 -
 Attorney Generals Transgender Sports Ban Legal Showdown With Minnesota
Apr 29, 2025
Attorney Generals Transgender Sports Ban Legal Showdown With Minnesota
Apr 29, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Nyt Spelling Bee Answers February 12 2025 Complete Guide
Apr 29, 2025
Nyt Spelling Bee Answers February 12 2025 Complete Guide
Apr 29, 2025 -
 Solve The Nyt Spelling Bee February 10 2025 Answers And Strategies
Apr 29, 2025
Solve The Nyt Spelling Bee February 10 2025 Answers And Strategies
Apr 29, 2025 -
 February 27 2025 Nyt Strands Answers And Helpful Hints
Apr 29, 2025
February 27 2025 Nyt Strands Answers And Helpful Hints
Apr 29, 2025 -
 Todays Nyt Spelling Bee Hints Answers And Help For February 26th Puzzle 360
Apr 29, 2025
Todays Nyt Spelling Bee Hints Answers And Help For February 26th Puzzle 360
Apr 29, 2025 -
 April 3 2025 Nyt Strands Find The Spangram And Answers
Apr 29, 2025
April 3 2025 Nyt Strands Find The Spangram And Answers
Apr 29, 2025
