Transferred Data: A Comprehensive Guide To Secure Data Migration
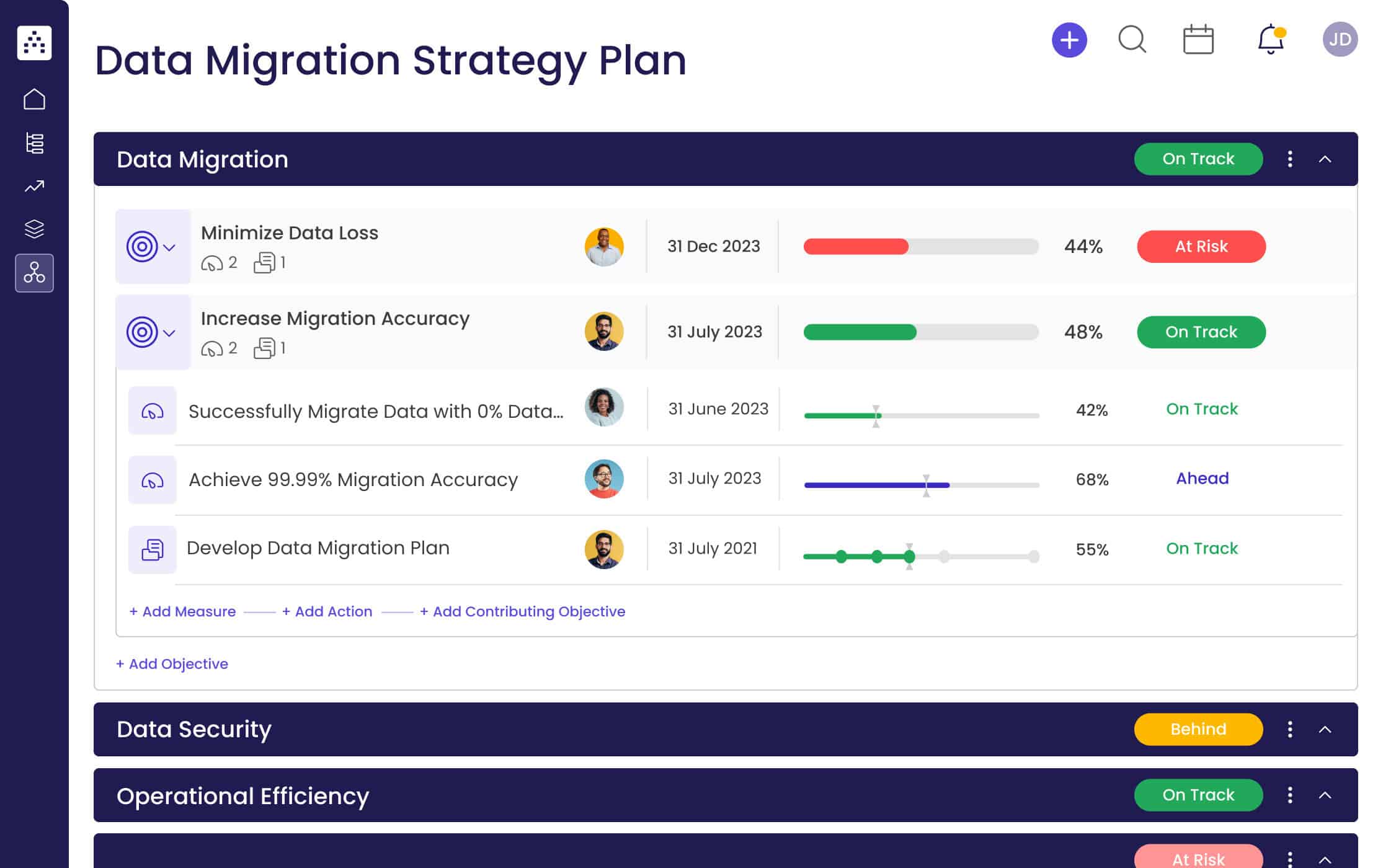
Table of Contents
Planning Your Data Migration Strategy
Effective data migration starts with a well-defined plan. This involves a thorough assessment of your current data landscape, careful selection of a migration method, and the establishment of clear goals and KPIs.
Assessing Your Current Data Landscape
Before initiating any data transfer, you need a complete understanding of your current data environment. This includes:
- Defining the Scope: What specific data needs to be migrated? Include databases, files, applications, and cloud storage. Be precise—avoid ambiguity.
- Identifying Data Sources and Formats: Categorize your data sources (e.g., SQL databases, NoSQL databases, CSV files, XML files). Knowing the format is crucial for choosing appropriate migration tools.
- Determining Data Volume and Growth Rate: Estimate the total size of your data and project its growth over time. This helps determine the required resources and timeframe for the migration.
- Evaluating Data Quality: Identify inconsistencies, duplicates, and errors. Data cleansing is often a necessary pre-migration step to ensure data integrity.
- Conducting a Risk Assessment: Identify potential risks and vulnerabilities during the data transfer process, such as data loss, security breaches, and application downtime.
Choosing the Right Migration Method
Several methods exist for data migration, each with its own advantages and disadvantages:
- Big Bang Migration: All data is transferred at once. This offers a fast transfer but carries significant risk if problems arise.
- Phased Migration: Data is transferred in stages, minimizing disruption but extending the project timeline.
- Parallel Migration: Old and new systems run concurrently during the transition. This minimizes downtime but increases complexity.
The optimal method depends on factors like your downtime tolerance, budget, technical expertise, and the complexity of your data. A phased approach is often preferred for its reduced risk.
Setting Clear Goals and KPIs
Clearly defined goals and KPIs are crucial for tracking progress and ensuring a successful migration.
- SMART Goals: Define Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound goals. For example: "Migrate 100% of customer data to the new system by December 31st, 2024, with less than 2 hours of downtime."
- Key Performance Indicators (KPIs): Track metrics like:
- Downtime: The total time the system is unavailable during migration.
- Data Integrity: The percentage of data transferred without errors or loss.
- Budget Adherence: Tracking actual costs against the planned budget.
- Completion Rate: The percentage of the data migration completed.
Regularly monitoring these KPIs allows for timely adjustments to the migration strategy.
Ensuring Data Security During Transfer
Data security is paramount during any data migration. Robust security measures must be implemented throughout the entire process.
Implementing Robust Security Measures
Protecting your data during transfer requires a multi-layered approach:
- Encryption: Employ strong encryption methods (AES-256) for data at rest and in transit. This protects data from unauthorized access.
- Access Control: Implement strict access control measures, granting only authorized personnel access to the data during transfer.
- Secure Protocols: Use secure protocols like HTTPS and SSH for all communication during the migration.
- Intrusion Detection/Prevention: Deploy intrusion detection and prevention systems to monitor for and block unauthorized access attempts.
- Security Audits & Penetration Testing: Regularly conduct security audits and penetration testing to identify and address vulnerabilities.
Data Loss Prevention (DLP) Strategies
Preventing data loss is critical. Employ these strategies:
- Backups: Create multiple backups of your data before, during, and after the migration.
- Data Validation & Verification: Use checksums and hashing algorithms to verify data integrity throughout the process. This ensures that the data transferred is an exact copy of the original.
- Data Corruption Prevention: Use error-checking mechanisms and redundant systems to prevent data corruption.
- Compliance: Ensure compliance with relevant data privacy regulations (GDPR, CCPA, etc.).
Testing and Validation of Transferred Data
Thorough testing is essential to ensure the accuracy and completeness of the transferred data.
Developing a Comprehensive Testing Plan
A comprehensive testing plan is crucial for identifying and resolving issues before going live:
- Testing Methodologies: Utilize various testing methods including unit testing, integration testing, system testing, and user acceptance testing (UAT).
- Data Validation: Verify the accuracy and completeness of the migrated data against the original source.
- Real-World Simulation: Test the system under realistic conditions to identify potential problems.
- Reporting & Documentation: Maintain detailed records of all testing activities, including results and identified issues.
Monitoring and Post-Migration Support
Post-migration monitoring is as crucial as the migration itself:
- Continuous Monitoring: Implement continuous monitoring to detect and address any issues that may arise after the migration.
- Ongoing Support: Provide ongoing support to users and address any problems they encounter.
- KPI Tracking: Continue to track KPIs to measure the long-term success of the migration.
- Regular Security Audits & Updates: Regularly conduct security audits and apply updates to maintain data security.
- Support & Maintenance Plan: Create a comprehensive support and maintenance plan to address ongoing issues and ensure system stability.
Conclusion
Successfully managing the transfer of data requires meticulous planning, robust security measures, and thorough testing. By following the strategies outlined in this guide, you can ensure a smooth, secure, and efficient data migration that minimizes downtime and protects your valuable information. Don't leave your sensitive data vulnerable – implement a secure data migration strategy today. Learn more about optimizing your approach to transferred data and ensuring the safety of your information.

Featured Posts
-
 Is Bitcoin Poised For A Rally Analysts May 6 Chart Prediction
May 08, 2025
Is Bitcoin Poised For A Rally Analysts May 6 Chart Prediction
May 08, 2025 -
 Xrp Etfs Potential For 800 Million In Week 1 Inflows Upon Approval
May 08, 2025
Xrp Etfs Potential For 800 Million In Week 1 Inflows Upon Approval
May 08, 2025 -
 Canadas Economic Sovereignty Carneys Firm Response To Trump Administration
May 08, 2025
Canadas Economic Sovereignty Carneys Firm Response To Trump Administration
May 08, 2025 -
 Istoriya Matchiv Ps Zh Ta Aston Villi V Yevrokubkakh
May 08, 2025
Istoriya Matchiv Ps Zh Ta Aston Villi V Yevrokubkakh
May 08, 2025 -
 Urgent Dwp Issues 3 Month Warning On Benefit Stoppage For 355 000 Claimants
May 08, 2025
Urgent Dwp Issues 3 Month Warning On Benefit Stoppage For 355 000 Claimants
May 08, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Is This Confirmation Jayson Tatum And Ella Mais Baby In New Commercial
May 08, 2025
Is This Confirmation Jayson Tatum And Ella Mais Baby In New Commercial
May 08, 2025 -
 Nba Star Jayson Tatum Welcomes Son With Singer Ella Mai Commercial Confirmation
May 08, 2025
Nba Star Jayson Tatum Welcomes Son With Singer Ella Mai Commercial Confirmation
May 08, 2025 -
 Jayson Tatum Seemingly Confirms Sons Birth With Ella Mai In New Commercial
May 08, 2025
Jayson Tatum Seemingly Confirms Sons Birth With Ella Mai In New Commercial
May 08, 2025 -
 Jayson Tatum And Ella Mai Commercial Hints At New Baby
May 08, 2025
Jayson Tatum And Ella Mai Commercial Hints At New Baby
May 08, 2025 -
 Empate Entre Liga De Quito Y Flamengo En La Copa Libertadores
May 08, 2025
Empate Entre Liga De Quito Y Flamengo En La Copa Libertadores
May 08, 2025
