Understanding The Expanding Vaccine Packaging Market
Table of Contents
Driving Forces Behind Market Growth
Several key factors are propelling the expansion of the vaccine packaging market. Understanding these drivers is crucial for stakeholders involved in vaccine development, distribution, and administration.
Increasing Vaccination Programs
Global immunization initiatives are a primary driver of market expansion. The increased focus on preventing vaccine-preventable diseases has led to a significant rise in demand for robust and reliable vaccine packaging solutions.
- Expansion of national immunization programs: Many countries are expanding their national immunization programs to cover a wider range of diseases and age groups.
- Increased focus on preventable diseases: Greater awareness of the devastating impact of preventable diseases like measles, polio, and influenza is driving vaccination efforts.
- Growing demand for novel vaccines: The development and deployment of novel vaccines, such as mRNA vaccines for COVID-19, have further increased demand for specialized packaging solutions.
The World Health Organization (WHO) reports a steady increase in global vaccination coverage, highlighting the significant role of effective vaccine packaging in ensuring vaccine potency and efficacy. Successful vaccination campaigns like the global eradication of smallpox demonstrate the importance of reliable cold chain packaging and logistical support.
Technological Advancements in Packaging Materials
Innovation in materials science is playing a crucial role in improving the safety and efficacy of vaccine delivery. Advanced materials provide better temperature control, enhanced protection against contamination, and improved sustainability.
- Development of advanced cold chain packaging solutions: This includes the use of temperature-sensitive indicators, vacuum insulated panels (VIPs), and phase-change materials (PCMs) to maintain the required temperature range during transport and storage.
- Use of biodegradable and sustainable materials: Growing environmental concerns are driving the development of eco-friendly packaging materials made from renewable resources, reducing the environmental footprint of vaccine distribution.
- Improved barrier properties to prevent contamination: Advanced materials provide better protection against moisture, oxygen, and other environmental factors that can compromise vaccine stability and potency.
Examples include the use of innovative polymers with enhanced barrier properties and the development of biodegradable alternatives to traditional polystyrene foam insulation.
Stringent Regulatory Requirements
Strict regulations governing vaccine manufacturing and distribution ensure vaccine integrity and safety throughout the supply chain. Compliance with these regulations necessitates the use of high-quality, compliant packaging materials and processes.
- Compliance with GMP (Good Manufacturing Practices): Vaccine packaging must adhere to strict GMP guidelines to ensure product quality and safety.
- Adherence to international standards: International standards, such as those set by the WHO, provide a framework for vaccine packaging design, testing, and performance.
- Traceability and track-and-trace systems: Regulations often mandate the implementation of track-and-trace systems to ensure the authenticity and integrity of vaccines throughout the supply chain, combatting counterfeit products.
Regulatory bodies like the FDA (Food and Drug Administration) and EMA (European Medicines Agency) play a crucial role in setting and enforcing these standards, impacting the design and manufacturing processes of vaccine packaging.
Types of Vaccine Packaging Solutions
Vaccine packaging encompasses various levels of protection to ensure safe and effective delivery. Understanding these different levels is critical for optimizing the entire vaccine supply chain.
Primary Packaging
Primary packaging is the material that directly contacts the vaccine product. The choice of material is critical for maintaining vaccine stability and preventing contamination.
- Vials: Glass vials are commonly used, offering good chemical inertness and visibility. However, plastic vials are increasingly used due to their lighter weight and reduced risk of breakage.
- Syringes (pre-filled and non-pre-filled): Pre-filled syringes offer convenience and reduce the risk of contamination during administration, while non-pre-filled syringes require separate filling, increasing the risk of error.
- Cartridges: Cartridges are used in auto-injectors for convenient self-administration.
The selection of primary packaging materials depends on the specific vaccine, its stability requirements, and the intended route of administration. Factors such as cost, ease of use, and environmental impact are also considered.
Secondary Packaging
Secondary packaging provides additional protection during transport and storage, acting as a buffer against physical damage and environmental fluctuations.
- Cartons: Cartons provide protection and labeling information, clearly identifying the vaccine product and its handling requirements.
- Cases: Cases offer more robust protection during transportation and often incorporate features like cushioning and tamper-evident seals.
- Pallets: Pallets facilitate efficient handling and transport of large quantities of vaccines.
- Specialized cold chain packaging: This includes insulated containers and thermal shippers designed to maintain the required temperature range during transport, using materials like EPS foam, PCMs, or VIPs.
The selection of secondary packaging is vital for maintaining the cold chain and protecting the vaccines from damage during shipping and handling.
Tertiary Packaging
Tertiary packaging is used for large-scale transportation and storage, focusing on efficient logistics and minimizing waste. It typically involves bulk shipping containers and pallets. The focus is on optimizing space utilization and ensuring safe and secure transport over long distances.
Challenges and Opportunities in the Vaccine Packaging Market
Despite the significant growth, the vaccine packaging market faces several challenges, creating opportunities for innovation and improvement.
Maintaining the Cold Chain
Maintaining the cold chain is paramount for ensuring vaccine efficacy. Temperature excursions can significantly reduce vaccine potency, rendering them ineffective.
- Challenges in maintaining the cold chain during transportation and storage: This is particularly challenging in developing countries with limited cold chain infrastructure.
- Solutions: Real-time temperature monitoring systems, improved cold chain infrastructure, and the use of advanced cold chain packaging technologies are crucial for addressing these challenges.
Successful cold chain management strategies often involve multi-faceted approaches, including efficient logistics, appropriate packaging, and reliable temperature monitoring systems.
Sustainability Concerns
The environmental impact of vaccine packaging is a growing concern. The use of non-biodegradable materials and the generation of packaging waste are significant sustainability challenges.
- Development of eco-friendly materials: The use of biodegradable and recyclable materials is crucial for minimizing the environmental impact.
- Waste reduction strategies: Optimizing packaging design to minimize material usage and exploring innovative waste management solutions are essential.
- Recycling programs: Establishing robust recycling programs for used vaccine packaging materials can reduce landfill waste.
The transition towards more sustainable packaging solutions requires collaboration across the vaccine supply chain, from manufacturers to end-users.
Counterfeit Vaccine Prevention
Protecting against counterfeit vaccines is paramount to public health. Counterfeit vaccines can be ineffective, harmful, or even fatal.
- Implementation of security features in packaging: This includes the use of tamper-evident seals, holograms, and unique identification numbers.
- Use of track-and-trace technologies: Track-and-trace systems enable the monitoring of vaccine movement throughout the supply chain, helping to identify and prevent counterfeit products.
Implementing robust security features and track-and-trace systems is critical for ensuring the authenticity and safety of vaccines.
Conclusion
The global vaccine packaging market is dynamic and expanding, driven by increasing vaccination efforts, technological advancements, and regulatory demands. Addressing the challenges of cold chain management, sustainability, and counterfeit prevention is critical for ensuring the continued safe and effective delivery of vaccines worldwide. Companies involved in the vaccine packaging market need to adapt to these evolving needs and invest in innovative, sustainable, and secure packaging technologies. Further research into sustainable and efficient vaccine packaging solutions is vital for a healthier future. Learn more about the latest trends and innovations in the vaccine packaging market today!

Featured Posts
-
 Daniel Cormiers Explosive Revelation What He Told Jon Jones Publicist
May 30, 2025
Daniel Cormiers Explosive Revelation What He Told Jon Jones Publicist
May 30, 2025 -
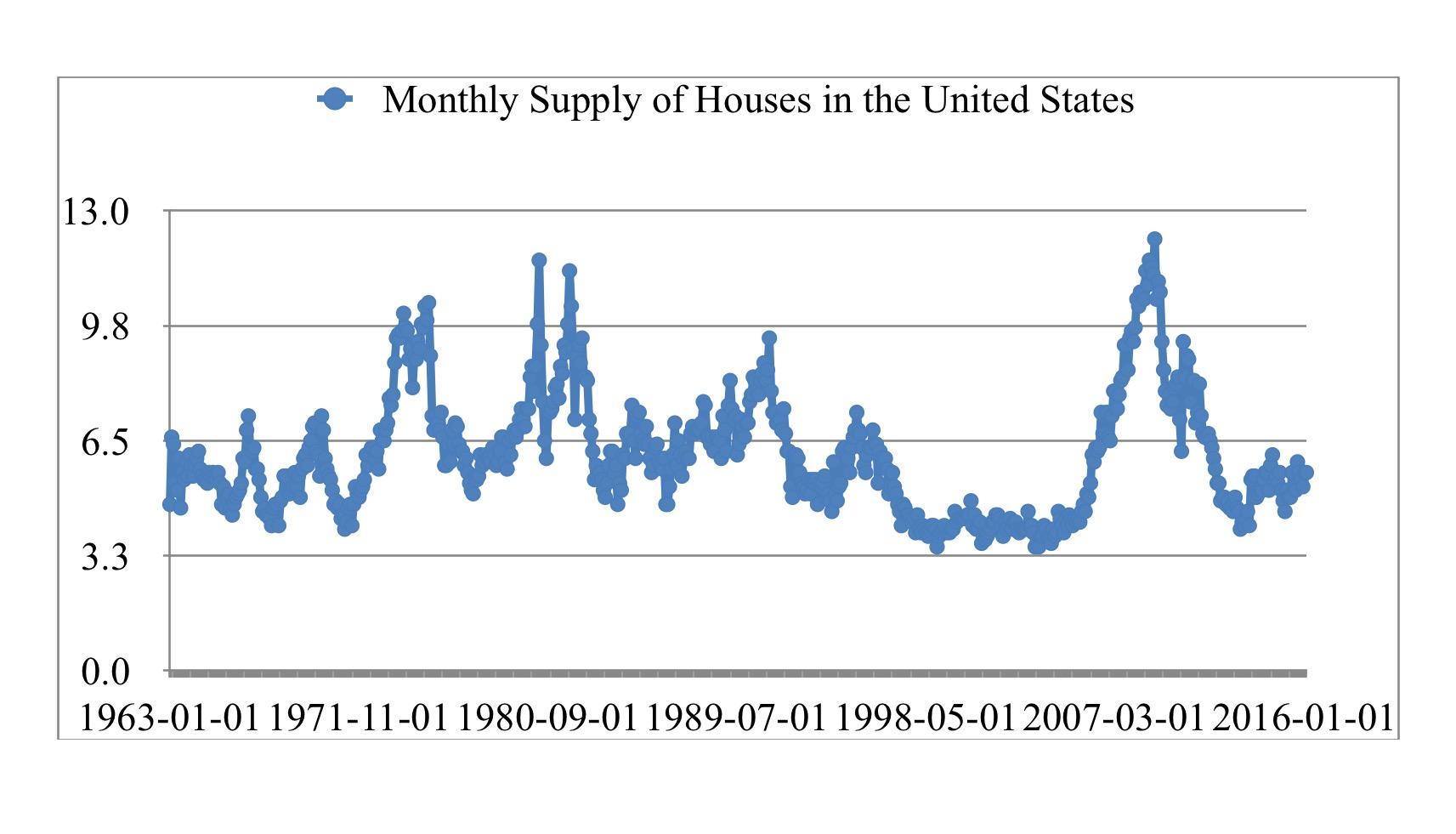 Record Low Home Sales Indicate Housing Market Crisis
May 30, 2025
Record Low Home Sales Indicate Housing Market Crisis
May 30, 2025 -
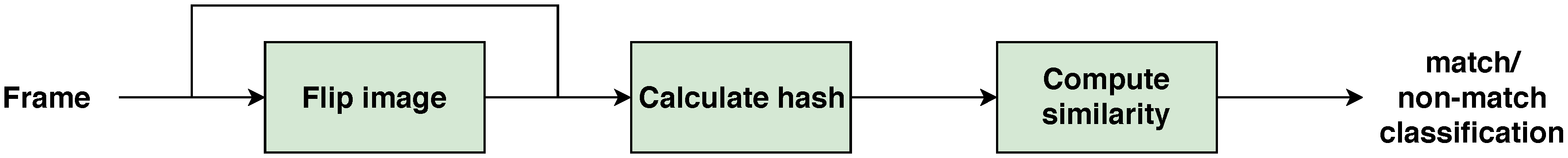 Do Algorithms Contribute To Mass Shooter Radicalization A Critical Analysis
May 30, 2025
Do Algorithms Contribute To Mass Shooter Radicalization A Critical Analysis
May 30, 2025 -
 Ticketmaster Vista Previa Virtual De Tu Asiento Antes De Comprar
May 30, 2025
Ticketmaster Vista Previa Virtual De Tu Asiento Antes De Comprar
May 30, 2025 -
 Analyse Anderlechts Handtering Af Et Godt Tilbud
May 30, 2025
Analyse Anderlechts Handtering Af Et Godt Tilbud
May 30, 2025
