The Future Of American Manufacturing: Will Factory Jobs Return Under Trump's Policies?
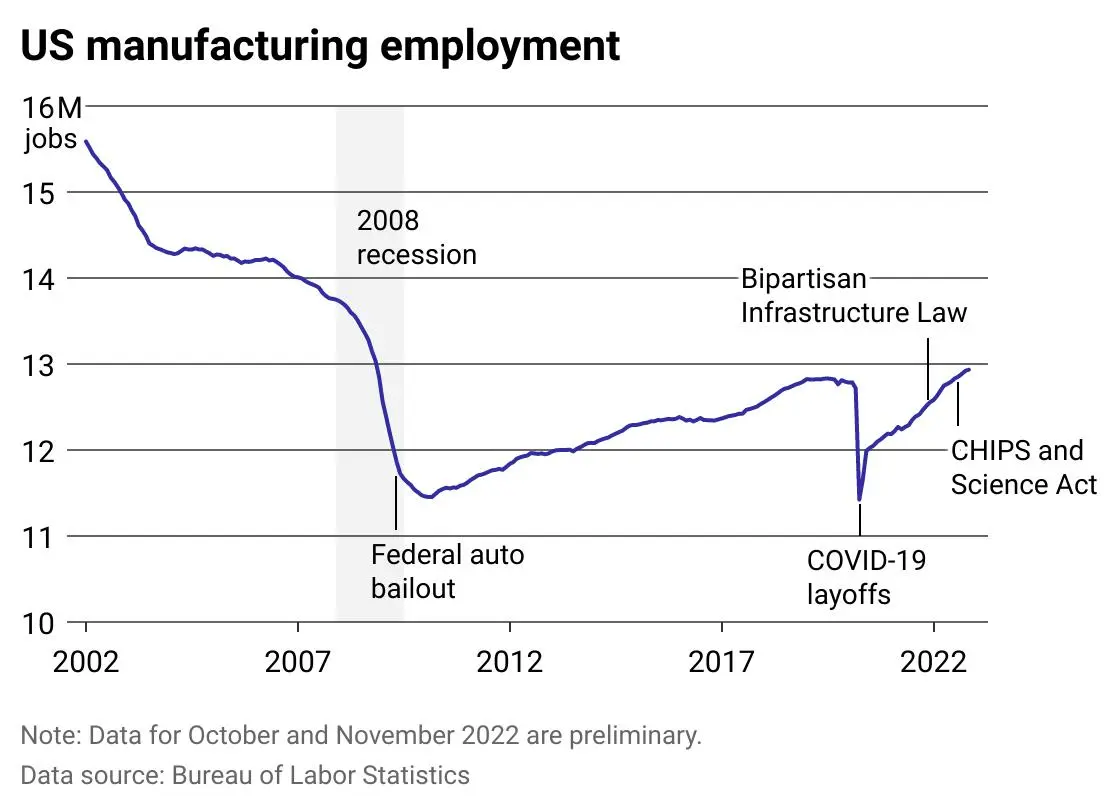
Table of Contents
Trump Administration Policies Aimed at Boosting Manufacturing
The Trump administration implemented several policies designed to boost domestic manufacturing and create jobs. These strategies, while ambitious, faced significant headwinds and yielded mixed results.
Trump Tariffs and Trade Wars: A Double-Edged Sword
A cornerstone of the Trump administration's approach was the imposition of tariffs on imported goods. The intention was to protect American industries from foreign competition, encouraging domestic production and job creation. However, this strategy proved to be a double-edged sword.
-
Benefits: Tariffs on steel and aluminum, for example, offered some protection to domestic producers, potentially saving some jobs in those sectors. The renegotiation of NAFTA into the USMCA (United States-Mexico-Canada Agreement) also aimed to level the playing field for American manufacturers.
-
Drawbacks: The tariffs triggered retaliatory tariffs from other countries, leading to increased prices for American consumers and harming some export-oriented industries. The trade war with China, in particular, significantly impacted various manufacturing sectors.
-
Specific Examples: The steel industry saw some short-term gains from tariffs, but the long-term effects remain debated. Conversely, the agricultural sector suffered significantly due to retaliatory tariffs imposed by China.
The impact of Trump tariffs and the resulting trade wars on manufacturing jobs remains a subject of ongoing debate among economists. While some sectors experienced short-term gains, the overall effect is complex and difficult to isolate. The long-term consequences of these protectionist measures are yet to be fully understood.
Tax Cuts and Deregulation: Stimulating Investment or Widening Inequality?
The administration also pursued significant tax cuts, aiming to stimulate business investment and job creation. Simultaneously, deregulation efforts sought to reduce the regulatory burden on businesses, making them more competitive.
-
Tax Cuts: The Tax Cuts and Jobs Act of 2017 lowered corporate tax rates, theoretically making it more attractive for businesses to invest and expand, including in manufacturing.
-
Deregulation: The administration reduced regulations across various sectors, including environmental regulations, potentially lowering manufacturing costs.
-
Actual Impact: While some businesses did invest, the impact on manufacturing employment was less clear-cut. The tax cuts' benefits were unevenly distributed, and the long-term effect on manufacturing jobs remains a topic of ongoing economic research. The impact of deregulation on worker safety and environmental protection also sparked considerable controversy.
Infrastructure Spending Plans: A Promise Yet to Be Fully Realized
Another key policy was a proposed increase in infrastructure spending. The idea was to stimulate demand for manufactured goods and create jobs in construction and related industries.
-
Proposed Investments: The administration proposed significant investments in roads, bridges, and other infrastructure projects.
-
Actual Spending: The actual level of infrastructure spending fell short of initial promises, limiting its impact on manufacturing job creation.
-
Sectors Benefiting: Increased infrastructure spending would have benefited sectors like steel, cement, and construction equipment manufacturing. However, the limited spending meant a comparatively smaller impact on these sectors.
Counterarguments and Challenges to Manufacturing Resurgence
Despite the administration's efforts, several factors hindered a significant resurgence of American manufacturing jobs.
Automation and Technological Advancements: The Rise of the Machines
Automation and technological advancements continue to transform the manufacturing landscape, reducing the demand for human labor.
-
Robotics and Automation: The increased adoption of robots and automated systems in factories has led to significant job displacement in some sectors.
-
Technological Unemployment: This technological unemployment is a global phenomenon and is not unique to the United States. It necessitates a shift towards reskilling and upskilling initiatives.
-
Reskilling and Upskilling Programs: Investing in programs to retrain workers for new roles in advanced manufacturing is crucial to mitigate job losses due to automation.
Global Competition and Offshoring: The Pressure from Abroad
Global competition, particularly from low-cost manufacturing hubs in Asia and elsewhere, remains a significant challenge for American manufacturers.
-
Low-Cost Manufacturing: The cost advantages enjoyed by countries with lower labor costs continue to pressure American manufacturers.
-
Offshoring and Reshoring: Companies continue to make decisions about offshoring versus reshoring manufacturing operations based on a complex interplay of factors including labor costs, transportation costs, and access to skilled labor.
-
Maintaining Competitiveness: American manufacturers need to focus on innovation, efficiency, and high-value manufacturing to compete effectively in the global market.
Skills Gap and Workforce Development: Bridging the Gap
A significant skills gap exists in the American workforce, hindering the ability to fill available manufacturing jobs.
-
Lack of Skilled Workers: Many manufacturing jobs require specialized skills that a significant portion of the workforce lacks.
-
Workforce Development Programs: Effective workforce development programs are essential to train and retrain workers for the demands of modern manufacturing.
-
Education and Vocational Training: Investing in education and vocational training programs is crucial to equip workers with the necessary skills for the evolving manufacturing sector.
Conclusion: The Long Road to Manufacturing Revival
The question of whether Trump's policies successfully reversed the decline of American manufacturing jobs is complex and requires ongoing analysis. While some policies, like tariffs, offered short-term protection to specific sectors, the long-term impact remains debated. Significant challenges, including automation and global competition, continue to affect the sector. Addressing the skills gap through robust workforce development programs is critical to ensuring the long-term competitiveness and health of American manufacturing. A sustainable revival of American manufacturing requires a comprehensive and multifaceted approach extending beyond individual policies. To gain a deeper understanding of the future of American manufacturing, further research into the long-term effects of these policies and the adaptation of the manufacturing sector is vital. Continue exploring the complexities of the future of American manufacturing to inform future policy decisions and investments.

Featured Posts
-
 Lufthansa Co Pilot Fainting Flight Continues Pilotless For 10 Minutes
May 20, 2025
Lufthansa Co Pilot Fainting Flight Continues Pilotless For 10 Minutes
May 20, 2025 -
 Unveiling The Richard Mille Rm 72 01 Designed With Charles Leclerc
May 20, 2025
Unveiling The Richard Mille Rm 72 01 Designed With Charles Leclerc
May 20, 2025 -
 Todays Nyt Mini Crossword Answers February 25th
May 20, 2025
Todays Nyt Mini Crossword Answers February 25th
May 20, 2025 -
 Tadic Ve Dzeko Mourinho Nun Elestirileri Ve Gelecekleri
May 20, 2025
Tadic Ve Dzeko Mourinho Nun Elestirileri Ve Gelecekleri
May 20, 2025 -
 Mikhael Shumakher Novaya Glava Semeynoy Zhizni
May 20, 2025
Mikhael Shumakher Novaya Glava Semeynoy Zhizni
May 20, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Recent D Wave Quantum Qbts Stock Market Performance A Detailed Look
May 20, 2025
Recent D Wave Quantum Qbts Stock Market Performance A Detailed Look
May 20, 2025 -
 Qbts Stocks Upcoming Earnings What To Expect
May 20, 2025
Qbts Stocks Upcoming Earnings What To Expect
May 20, 2025 -
 Understanding The D Wave Quantum Qbts Stock Rally Key Factors
May 20, 2025
Understanding The D Wave Quantum Qbts Stock Rally Key Factors
May 20, 2025 -
 Understanding The Recent D Wave Quantum Qbts Stock Price Jump
May 20, 2025
Understanding The Recent D Wave Quantum Qbts Stock Price Jump
May 20, 2025 -
 D Wave Quantum Inc Qbts Stock Surge Reasons Behind Todays Jump
May 20, 2025
D Wave Quantum Inc Qbts Stock Surge Reasons Behind Todays Jump
May 20, 2025
