Understanding The ADHD Brain: A Journey Inside Our ADHD Minds

Table of Contents
Neurological Differences in the ADHD Brain
The ADHD brain exhibits distinct neurological differences compared to neurotypical brains. These variations influence how individuals with ADHD process information, regulate emotions, and manage daily tasks.
Brain Structure and Function
Research indicates structural and functional differences in several key brain regions in individuals with ADHD. These differences contribute significantly to the core symptoms of the disorder.
- Smaller volume in certain brain regions: Studies have shown smaller volumes in areas like the prefrontal cortex (responsible for executive functions), basal ganglia (involved in motor control and reward processing), and cerebellum (crucial for coordination and motor control).
- Reduced activity in areas responsible for attention and impulse control: Brain imaging techniques reveal reduced activity in areas associated with attention, focus, and impulse inhibition, leading to difficulties with sustained attention and impulsive behaviors.
- Differences in neurotransmitter systems (dopamine, norepinephrine): Imbalances in neurotransmitters like dopamine and norepinephrine, which play critical roles in attention, motivation, and reward processing, are also implicated in ADHD.
- Impact on executive functions (planning, organization, working memory): These structural and functional differences directly affect executive functions, leading to challenges with planning, organization, working memory, and time management.
Neurotransmitter Imbalances
Neurotransmitters are chemical messengers that transmit signals between brain cells. In the ADHD brain, imbalances in dopamine and norepinephrine are thought to play a significant role.
- Dopamine's role in reward processing and motivation: Dopamine is essential for motivation, reward processing, and attention. Lower dopamine levels can lead to decreased motivation, difficulty with focus, and reduced reward sensitivity.
- Norepinephrine's role in alertness and arousal: Norepinephrine regulates alertness, arousal, and attention. Imbalances can result in difficulties with sustained attention, impulsivity, and hyperactivity.
- The impact of medication on neurotransmitter levels: Many ADHD medications work by modulating dopamine and norepinephrine levels, thereby improving attention, focus, and impulse control.
Genetic and Environmental Factors
The development of ADHD is a complex interplay of genetic and environmental factors.
- Heritability of ADHD: ADHD has a strong genetic component, with studies suggesting a high heritability rate. Genes influencing neurotransmitter function and brain development are implicated.
- Environmental factors influencing symptom expression: Environmental factors such as prenatal exposure to toxins, low birth weight, and early childhood trauma can also influence the expression of ADHD symptoms.
- Epigenetics and gene-environment interactions: Epigenetics explores how environmental factors can modify gene expression without altering the DNA sequence itself, contributing to the complexity of ADHD development.
Cognitive Challenges and Strengths of the ADHD Brain
While ADHD presents certain cognitive challenges, it's crucial to recognize that the ADHD brain also possesses unique strengths.
Executive Function Deficits
Individuals with ADHD often struggle with executive functions, which are higher-level cognitive processes that control and manage other cognitive functions.
- Impact on academic performance: Difficulties with planning, organization, and working memory can significantly impact academic performance.
- Challenges in workplace productivity: These challenges can also affect workplace productivity, leading to difficulties with time management, task completion, and organization.
- Strategies for improving executive function: Strategies such as time management techniques, organizational tools, and cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) can help improve executive functions.
Hyperfocus and Creativity
One of the often-overlooked strengths of the ADHD brain is the capacity for hyperfocus and enhanced creativity.
- The ability to intensely focus on tasks of interest: When highly engaged, individuals with ADHD can exhibit intense focus and concentration, often exceeding that of neurotypical individuals.
- Increased creativity and innovative thinking: This intense focus, coupled with a tendency towards unconventional thinking, can lead to increased creativity and innovative problem-solving skills.
- Harnessing these strengths for productive outcomes: Understanding and leveraging these strengths is crucial for maximizing potential and achieving success.
Emotional Regulation Difficulties
Emotional regulation is another area where individuals with ADHD may experience challenges.
- Emotional lability and heightened sensitivity: Individuals with ADHD may experience emotional lability (rapid shifts in mood) and heightened sensitivity to stimuli.
- Difficulty managing frustration and anger: This can lead to difficulties managing frustration, anger, and other intense emotions.
- Strategies for improving emotional regulation: Techniques such as mindfulness, emotional regulation exercises, and therapy can be highly beneficial in improving emotional control.
Understanding ADHD and its Impact on Daily Life
ADHD significantly impacts various aspects of daily life, varying across the lifespan and often presenting with co-occurring conditions.
ADHD in Children vs. Adults
The manifestation of ADHD symptoms changes over time.
- Developmental considerations: Symptoms in children often involve hyperactivity and impulsivity, while in adults, inattentiveness may be more prominent.
- Diagnosis and treatment variations: Diagnostic criteria and treatment approaches are tailored to the developmental stage of the individual.
- Impact on relationships and social interactions: ADHD can affect relationships and social interactions due to challenges with impulsivity, emotional regulation, and communication.
Co-occurring Conditions
ADHD frequently co-occurs with other mental health conditions.
- Increased risk for mental health challenges: Individuals with ADHD have a higher risk of developing anxiety disorders, depression, and other mental health conditions.
- Importance of comprehensive assessment and treatment: A comprehensive assessment is crucial to identify and address all co-occurring conditions.
- Integrated approach to managing co-occurring conditions: An integrated approach that addresses both ADHD and co-occurring conditions is essential for effective management.
Support and Management Strategies
Various strategies are available to help manage ADHD symptoms.
- Medication options and their effectiveness: Stimulant and non-stimulant medications can effectively improve attention, focus, and impulse control.
- Behavioral therapy and its benefits: Behavioral therapy, such as CBT, teaches coping mechanisms and strategies for managing ADHD challenges.
- Lifestyle adjustments for improved focus and organization: Lifestyle adjustments, including regular exercise, healthy diet, and sufficient sleep, can significantly impact symptom management.
Conclusion
Understanding the intricacies of the ADHD brain offers crucial insights into the challenges and strengths experienced by individuals with ADHD. From neurological differences and cognitive challenges to the impact on daily life, we've explored the complexities of this neurodevelopmental condition. While the ADHD brain presents unique challenges, it also harbors remarkable potential for creativity and innovative thinking. By understanding the underlying mechanisms and employing effective management strategies, individuals with ADHD can thrive and lead fulfilling lives. Continue your journey into understanding the ADHD brain and discover more resources to support yourself or your loved ones. Learn more about effective coping mechanisms and treatment options for managing ADHD minds by exploring additional resources. Embrace the neurodiversity of the ADHD brain and unlock its potential.

Featured Posts
-
 Landman Ali Larter Returns Season 2 Set Images Reveal Oil Rig Action
May 13, 2025
Landman Ali Larter Returns Season 2 Set Images Reveal Oil Rig Action
May 13, 2025 -
 Securing A Professorship In Fine Arts A Focus On Spatial Design
May 13, 2025
Securing A Professorship In Fine Arts A Focus On Spatial Design
May 13, 2025 -
 Tekikoe Trump Mokan Byd N Nousu Ja Teslan Uhka
May 13, 2025
Tekikoe Trump Mokan Byd N Nousu Ja Teslan Uhka
May 13, 2025 -
 Planning Your Winterwatch Adventure A Comprehensive Checklist
May 13, 2025
Planning Your Winterwatch Adventure A Comprehensive Checklist
May 13, 2025 -
 Doom The Dark Ages Review File Size And Early Impressions Unveiled
May 13, 2025
Doom The Dark Ages Review File Size And Early Impressions Unveiled
May 13, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Byd Seal Buyers Guide Everything You Need To Know
May 13, 2025
Byd Seal Buyers Guide Everything You Need To Know
May 13, 2025 -
 A Case Study Addendum How Byd Became A Leader In Ev Battery Manufacturing
May 13, 2025
A Case Study Addendum How Byd Became A Leader In Ev Battery Manufacturing
May 13, 2025 -
 Addendum Analyzing Byds Success In The Ev Battery Market A Case Study
May 13, 2025
Addendum Analyzing Byds Success In The Ev Battery Market A Case Study
May 13, 2025 -
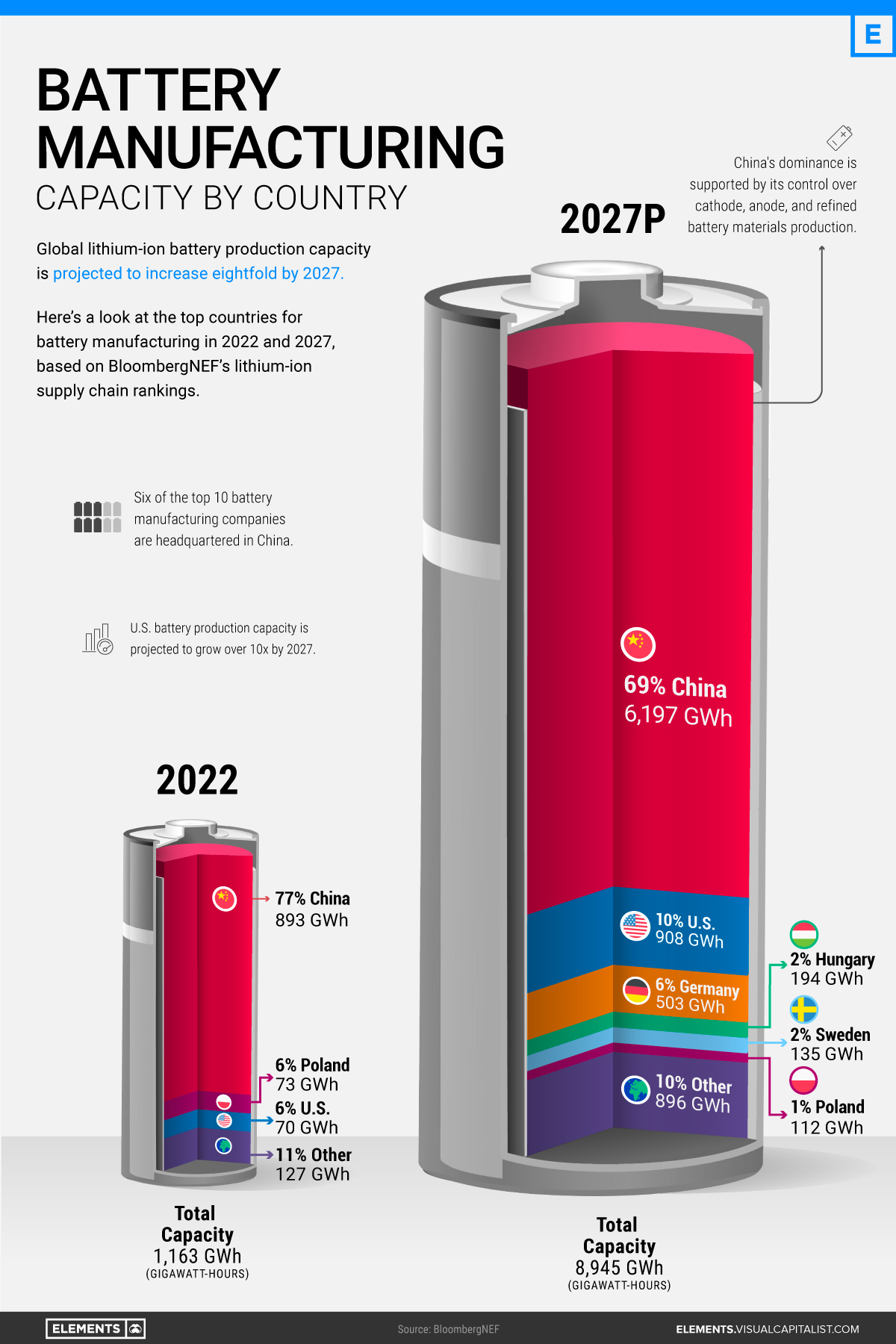 Byd Case Study Examining Their Leading Position In Ev Battery Manufacturing
May 13, 2025
Byd Case Study Examining Their Leading Position In Ev Battery Manufacturing
May 13, 2025 -
 Case Study Addendum Byds Leadership In Electric Vehicle Battery Production
May 13, 2025
Case Study Addendum Byds Leadership In Electric Vehicle Battery Production
May 13, 2025
