Understanding The Papal Conclave: Choosing The Next Pope
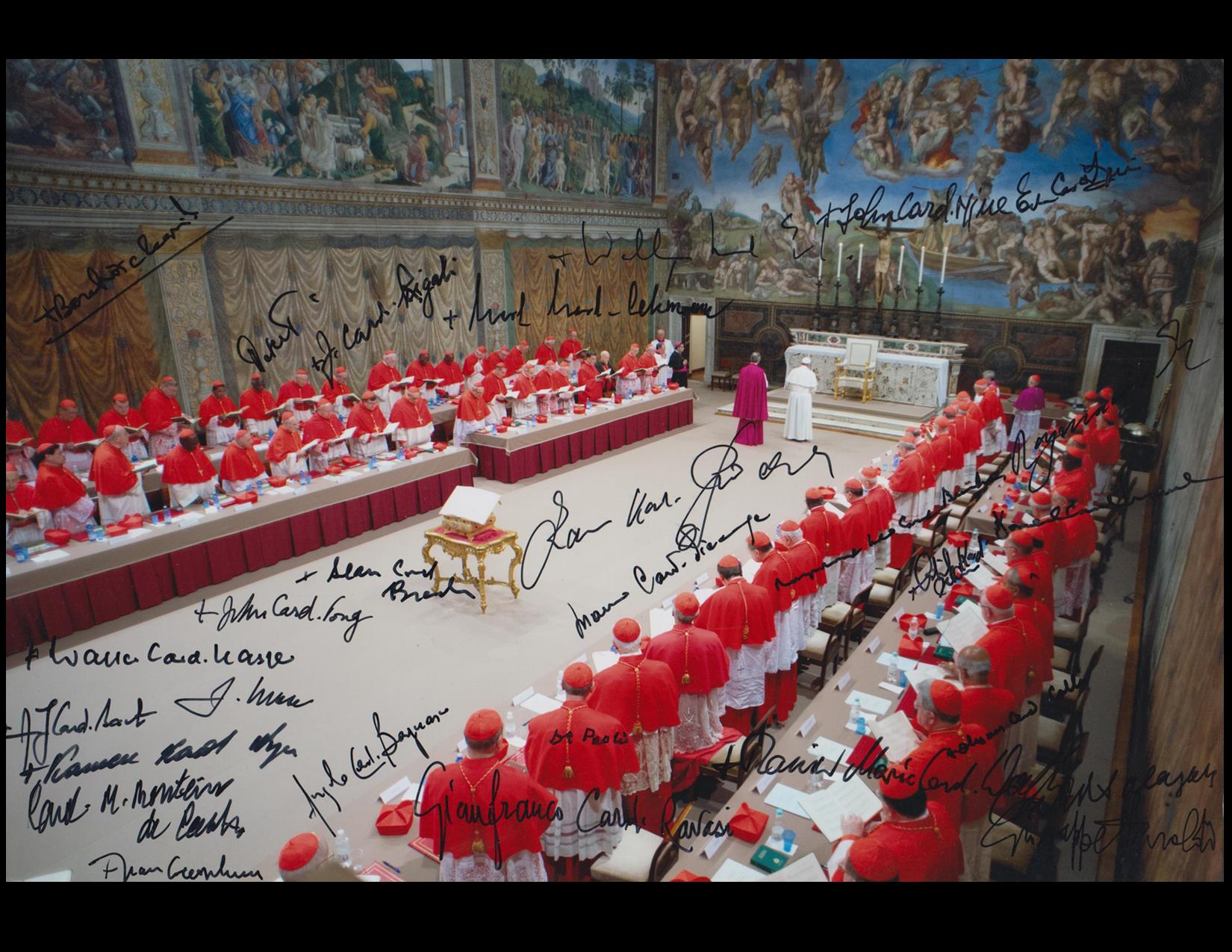

Table of Contents
The History and Evolution of the Papal Conclave
The history of the Papal Conclave is a long and fascinating journey, reflecting the evolving political and religious landscape of the Church. Early methods of papal election were often chaotic and tumultuous, sometimes involving popular votes that could easily descend into disputes and violence. The process of electing the Pope wasn't always a formal affair; in the early centuries, the selection process frequently lacked structure and clarity, leading to contentious situations and even schisms within the Church.
- Early methods of papal election: These ranged from informal deliberations among clergy to sometimes tumultuous popular votes within the Roman populace, often leading to protracted conflicts and questionable outcomes.
- The gradual formalization of the conclave process: Over the centuries, the Church gradually implemented rules and regulations to formalize the selection process, aiming to minimize conflict and ensure a more orderly and legitimate election. The need for a more structured approach arose directly from the difficulties caused by earlier, less regulated procedures.
- Key changes in the rules and procedures throughout history: The Second Vatican Council (1962-1965) significantly impacted the conclave, introducing reforms that aimed to modernize and streamline the process. These changes, amongst others, sought to create a more transparent process, while still preserving the necessary secrecy.
- Notable historical conclaves and their outcomes: Certain historical conclaves stand out for their complexity, length, or the significant impact of the Pope elected. For example, the conclave of 1268-1271, which lasted nearly three years, highlights the challenges faced in earlier centuries. Studying these historical events provides a valuable context for understanding the evolution of the current conclave procedures.
The Participants: Cardinal Electors
The Papal Conclave is not open to all; only Cardinal electors are eligible to participate in the choosing of the next Pope. Understanding the eligibility requirements and the role of the College of Cardinals is crucial to understanding the Papal election process.
- Requirements for becoming a Cardinal elector: To be eligible, a Cardinal must be under the age of 80 at the time the vacancy occurs. This age limit was established to ensure the vitality and long-term leadership of the Church. Their status as Cardinal is also a prerequisite for participation.
- The role of the College of Cardinals in the selection process: The College of Cardinals, composed of Cardinals from around the world, is responsible for electing the Pope. Their collective wisdom and diverse perspectives are believed to be essential in choosing a suitable leader for the global Catholic Church.
- The number of Cardinal electors and their geographic distribution: The number of Cardinal electors varies, but it is always a substantial group representing the Church's global presence. This geographic diversity is intentional, reflecting the Church's worldwide reach and ensuring representation from different cultures and regions.
- The process of electing Cardinal electors: The Pope appoints Cardinals, and the selection process considers various factors such as their theological expertise, administrative abilities, and pastoral experience. This ensures a diverse and qualified pool of potential electors for the Papal election.
The Conclave Procedure: Steps and Regulations
The conclave itself follows a specific procedure, carefully designed to ensure a fair and orderly election, even amidst the immense pressure and significance of the event. Secrecy is paramount.
- The conclave's location and security measures: The conclave is traditionally held within the Vatican City, and robust security measures are implemented to ensure the privacy and integrity of the process. All aspects of security are meticulously planned and executed to protect both the participants and the sanctity of the election process.
- The process of electing the new Pope, including the secret ballot system: The election is conducted through a series of secret ballots, ensuring that each Cardinal can vote freely and independently without external influence or pressure. The secrecy is of utmost importance.
- The required two-thirds majority vote: A two-thirds majority is required to elect a Pope. This high threshold is intended to ensure broad consensus within the College of Cardinals and to provide a strong mandate for the newly elected Pope.
- The announcement of the new Pope (the "Habemus Papam!"): Once a two-thirds majority is achieved, the new Pope is announced from the balcony of St. Peter's Basilica, accompanied by the traditional proclamation: "Habemus Papam!" ("We have a Pope!"). This moment is a highly anticipated event for Catholics worldwide.
- Scrutiny and procedures in case of a deadlock: Procedures are in place to handle situations where a two-thirds majority cannot be achieved, including additional ballots and considerations to avoid an extended impasse.
The Secrecy Surrounding the Conclave
The secrecy surrounding the conclave is not merely a tradition; it's a crucial element that ensures the integrity and independence of the election. This secrecy prevents external pressures from influencing the outcome.
- Reasons for maintaining secrecy during the conclave: The secrecy protects the cardinals from undue influence, promoting a free and fair election. This allows for open discussions and candid assessments without external pressures.
- Measures to prevent leaks and external influence: Strict rules and regulations govern communication during the conclave to prevent any unauthorized disclosure of information. Technology and communication methods are carefully monitored to maintain the utmost secrecy.
- The role of the Master of Ceremonies and other officials in maintaining secrecy: The Master of Ceremonies and other officials play a critical role in ensuring the strict adherence to the rules of secrecy. They are responsible for monitoring communications and maintaining a secure environment.
- Historical examples of breaches of conclave secrecy (and their consequences): While extremely rare, historical instances of breaches have served to underscore the importance of maintaining the secrecy surrounding the process and the potential consequences of failing to do so.
Conclusion
The Papal Conclave is a complex and significant event, a blend of ancient tradition and carefully defined procedures. Understanding the history, participants, and process of this election provides insight into the heart of the Catholic Church's governance. This intricate process, shrouded in secrecy, ultimately results in the selection of a leader for over a billion Catholics globally. Learn more about the fascinating history and intricacies of the Papal Conclave and the selection of the next Pope by exploring further resources on the Vatican website and other reliable sources. Deepen your understanding of this vital process by researching past Papal elections and the evolving rules governing the choosing of the next Pope.

Featured Posts
-
 Scathing Report On Angels Minor League Prospects
May 08, 2025
Scathing Report On Angels Minor League Prospects
May 08, 2025 -
 Chkn Mtn Awr Byf Lahwr Myn Gwsht Ky Qymtwn Ka Bhran
May 08, 2025
Chkn Mtn Awr Byf Lahwr Myn Gwsht Ky Qymtwn Ka Bhran
May 08, 2025 -
 Inter Milan Defeat Feyenoord Advance To Europa League Quarter Finals
May 08, 2025
Inter Milan Defeat Feyenoord Advance To Europa League Quarter Finals
May 08, 2025 -
 La Accion De Pulgar Que Llego Al Corazon De Los Hinchas Del Flamengo
May 08, 2025
La Accion De Pulgar Que Llego Al Corazon De Los Hinchas Del Flamengo
May 08, 2025 -
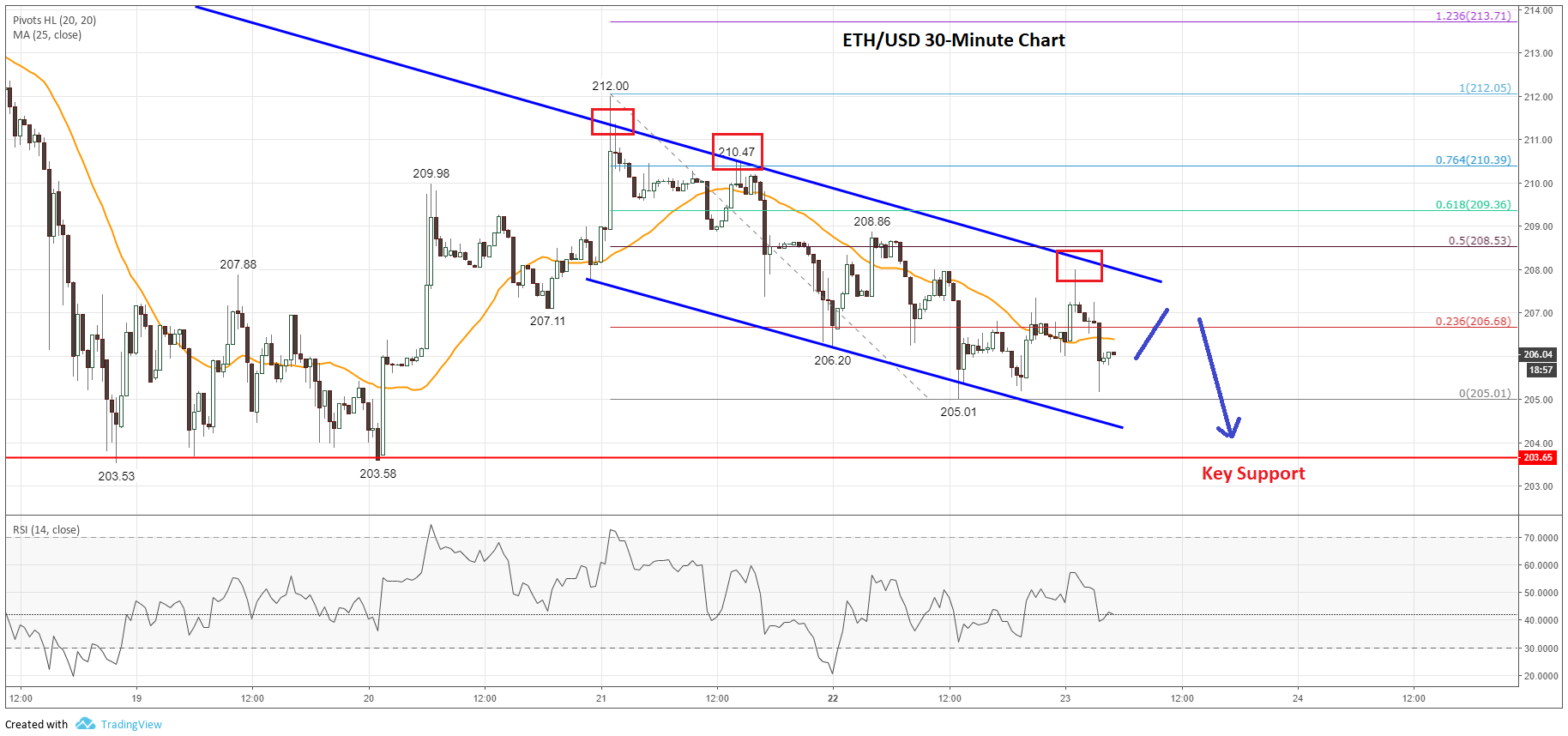 Ethereum Price Analysis Support Holds But Is A Fall To 1500 Likely
May 08, 2025
Ethereum Price Analysis Support Holds But Is A Fall To 1500 Likely
May 08, 2025
