Understanding The Value Proposition Of Middle Managers In Modern Organizations

Table of Contents
Bridging the Gap Between Leadership and Frontline Employees
Middle managers serve as a vital link, connecting senior leadership's strategic vision with the daily operations of frontline employees. They translate complex, high-level goals into actionable tasks, ensuring everyone understands their role in achieving organizational objectives. This crucial translation process minimizes misunderstandings and maximizes efficiency. Middle managers act as a two-way conduit, relaying feedback and insights from the frontlines to upper management, allowing for course correction and strategic adaptation.
- Facilitating communication and information flow: Middle managers ensure that information flows seamlessly between different levels of the organization, preventing communication breakdowns.
- Translating complex directives into clear, understandable instructions: They break down complex strategic plans into smaller, manageable tasks that frontline employees can easily understand and execute.
- Gathering and relaying feedback from frontline employees to senior leadership: They act as a voice for their teams, ensuring that senior management is aware of challenges, opportunities, and employee concerns.
- Identifying and addressing potential problems before they escalate: Their close proximity to daily operations allows them to identify and address issues proactively, preventing them from escalating into larger problems.
Fostering Team Development and Employee Engagement
Beyond operational tasks, middle managers play a critical role in fostering team development and driving employee engagement. They are responsible for mentoring, coaching, and motivating their teams to achieve peak performance. This involves creating a positive and supportive work environment where employees feel valued and empowered.
- Conducting performance reviews and providing constructive feedback: Regular performance reviews provide opportunities for growth and improvement, strengthening the employee-manager relationship.
- Identifying training needs and development opportunities for team members: Middle managers identify skill gaps and provide opportunities for professional development, leading to increased employee competency and satisfaction.
- Creating a positive and supportive work environment: A positive work environment fosters collaboration, innovation, and productivity.
- Building strong team cohesion and collaboration: Effective middle managers build strong teams by promoting collaboration and mutual respect.
- Delegating tasks effectively and empowering team members: Empowerment boosts morale and allows team members to take ownership of their work.
Driving Operational Efficiency and Productivity
Middle managers are instrumental in driving operational efficiency and productivity within their teams. They monitor performance, identify areas for improvement, and implement strategies to optimize workflows. This involves leveraging resources effectively, ensuring adherence to company policies, and making informed decisions to enhance overall output.
- Monitoring team performance and identifying areas for improvement: Regular monitoring allows for early detection of performance issues and prompt corrective action.
- Implementing new processes and technologies to enhance efficiency: Middle managers are often at the forefront of adopting and implementing new technologies and processes to improve team efficiency.
- Managing resources effectively to optimize output: Efficient resource allocation ensures that teams have the necessary tools and resources to achieve their objectives.
- Ensuring adherence to company policies and procedures: Compliance with company policies and procedures minimizes risk and maintains organizational consistency.
- Problem-solving and decision-making within their area of responsibility: Middle managers make quick, informed decisions to resolve issues and keep projects on track.
Adaptability and Change Management in a Dynamic Environment
In today's volatile business environment, adaptability is paramount. Middle managers play a crucial role in navigating organizational change and guiding their teams through transitions. They communicate change initiatives clearly, support team members through periods of adjustment, and mitigate potential risks associated with change management. They adapt strategies and processes to meet evolving business needs, ensuring organizational agility.
- Communicating change initiatives effectively to their teams: Clear and consistent communication reduces uncertainty and anxiety during periods of change.
- Supporting team members through periods of transition: Providing support and guidance during times of change helps employees adapt and thrive.
- Identifying and mitigating potential risks associated with change: Proactive risk management minimizes disruptions and ensures a smooth transition.
- Adapting strategies and processes to meet evolving business needs: Flexibility and adaptability are essential for navigating a rapidly changing environment.
The Evolving Role of Middle Managers in the Digital Age
The digital age presents both challenges and opportunities for middle managers. Technology and automation are transforming many aspects of their roles, requiring them to upskill and adapt to new tools and technologies. However, this evolution also empowers them with new capabilities for data-driven decision-making and improved communication.
- Utilizing data analytics to inform decision-making: Data-driven insights allow for more informed decisions and improved operational efficiency.
- Leveraging technology to improve communication and collaboration: Technology facilitates communication and collaboration across teams and geographical locations.
- Adapting to remote work environments and virtual teams: Middle managers must adapt their management styles to effectively lead remote and virtual teams.
- Developing digital literacy skills and staying current with technological advancements: Continuous learning is crucial for staying ahead in the rapidly evolving digital landscape.
Conclusion
Middle managers are indispensable to organizational success. Their contributions extend far beyond simply executing directives; they are the vital bridge between leadership and frontline employees, fostering team development, driving operational efficiency, and navigating the complexities of change. Organizations must recognize and invest in their middle management talent, providing them with the necessary training, support, and empowerment to fully leverage their potential. Re-evaluate your middle management strategy, optimize your middle management team, and unlock the full potential of your middle managers to achieve lasting organizational success.

Featured Posts
-
 Can Film Tax Credits Boost Minnesotas Tv And Film Industry
Apr 29, 2025
Can Film Tax Credits Boost Minnesotas Tv And Film Industry
Apr 29, 2025 -
 Did The Ny Times Bury The Real Story Of The January 29th Dc Air Disaster
Apr 29, 2025
Did The Ny Times Bury The Real Story Of The January 29th Dc Air Disaster
Apr 29, 2025 -
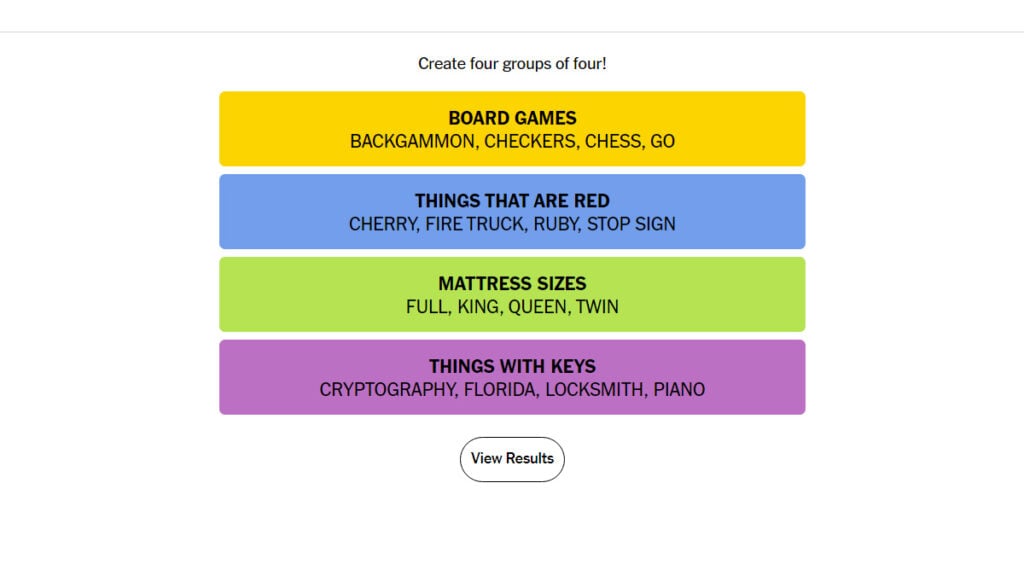 Solve Nyt Strands Hints And Answers For March 3rd 2025
Apr 29, 2025
Solve Nyt Strands Hints And Answers For March 3rd 2025
Apr 29, 2025 -
 Exclusive Technology Huaweis Ai Chip Aims To Disrupt The Market
Apr 29, 2025
Exclusive Technology Huaweis Ai Chip Aims To Disrupt The Market
Apr 29, 2025 -
 Videos Show Raid Of Underground Nightclub Over 100 Immigrants Detained
Apr 29, 2025
Videos Show Raid Of Underground Nightclub Over 100 Immigrants Detained
Apr 29, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 How You Tube Is Engaging Older Viewers With Classic And New Content
Apr 29, 2025
How You Tube Is Engaging Older Viewers With Classic And New Content
Apr 29, 2025 -
 Cardinal Trial Fresh Evidence Points To Prosecutorial Misconduct
Apr 29, 2025
Cardinal Trial Fresh Evidence Points To Prosecutorial Misconduct
Apr 29, 2025 -
 London Real Estate Fraud British Court Decision Against Vatican
Apr 29, 2025
London Real Estate Fraud British Court Decision Against Vatican
Apr 29, 2025 -
 Vatican Defrauded London Real Estate Deal Ruled Fraudulent By British Court
Apr 29, 2025
Vatican Defrauded London Real Estate Deal Ruled Fraudulent By British Court
Apr 29, 2025 -
 Becciu Case Fresh Evidence Casts Doubt On Conviction
Apr 29, 2025
Becciu Case Fresh Evidence Casts Doubt On Conviction
Apr 29, 2025
