Post-Nuclear Taiwan: The Growing Reliance On LNG
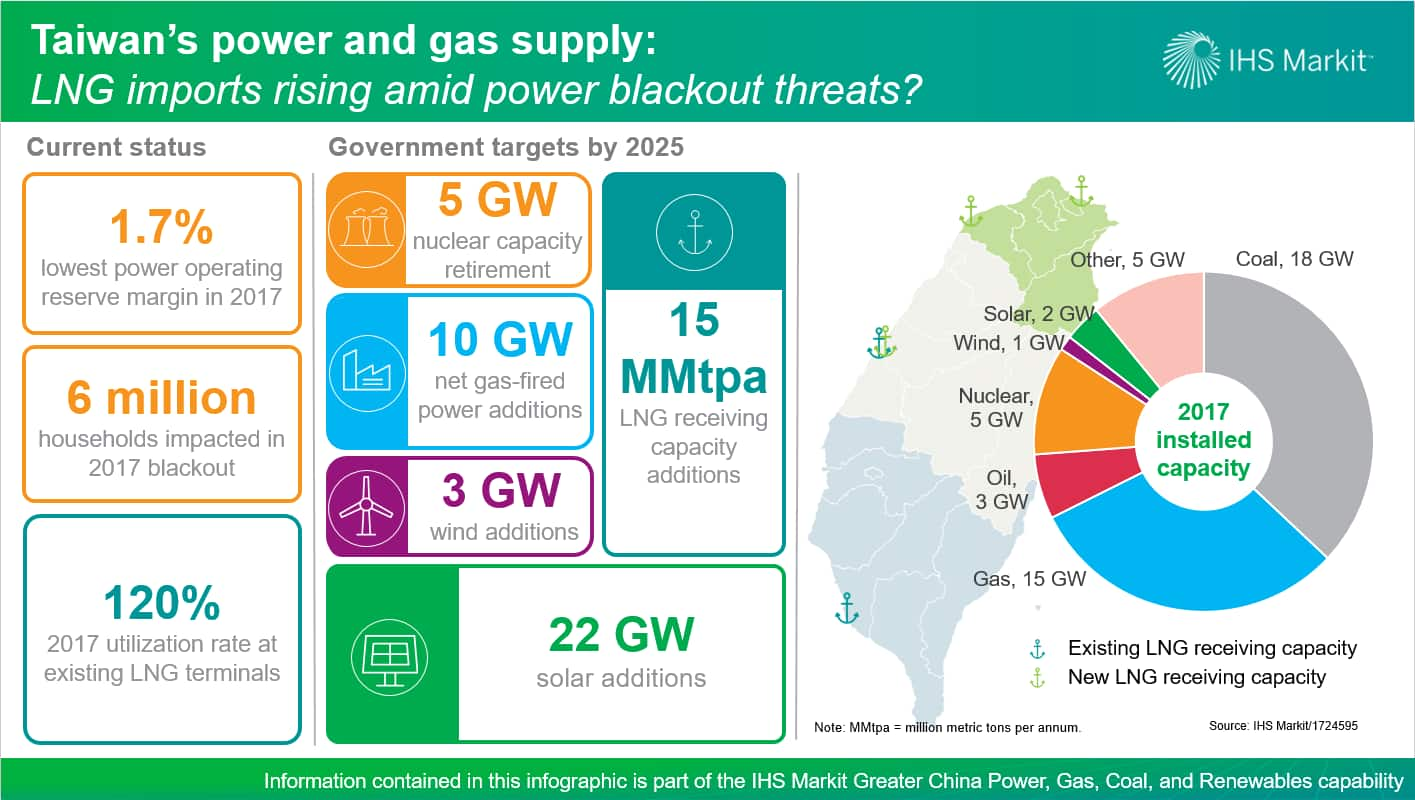
Table of Contents
The Decline of Nuclear Power in Taiwan
Phased Decommissioning of Nuclear Plants
Taiwan's decision to phase out nuclear power is a multifaceted one, driven by a combination of factors. The timeline for decommissioning involves a gradual shutdown of its existing nuclear power plants, a process fraught with political, economic, and social complexities.
- Nuclear Power Plant No. 1: Officially decommissioned in 2018.
- Nuclear Power Plant No. 2: Scheduled for decommissioning in the coming years.
- Nuclear Power Plant No. 3: Currently operating, but its future remains a subject of ongoing debate and policy changes.
Public opinion, deeply influenced by safety concerns following the Fukushima disaster, played a significant role in the decision to scale back nuclear energy production. The perceived risks associated with nuclear power, coupled with the high costs of maintaining and upgrading aging plants, further fueled the shift towards alternative energy sources.
Environmental Impacts of Nuclear Phase-out
The reduction in nuclear energy production has necessitated a significant increase in alternative energy sources, inevitably impacting the environment. While nuclear power offers a low-carbon energy source, the transition brings its own set of environmental challenges:
- Increased Greenhouse Gas Emissions: The reliance on fossil fuels like LNG to fill the energy gap leads to a higher carbon footprint compared to nuclear power.
- Nuclear Waste Management: The safe and long-term management of existing nuclear waste remains a crucial environmental concern, requiring substantial investment and technological solutions. This includes the development of suitable storage facilities and exploring advanced waste processing technologies.
The Rise of LNG as a Primary Energy Source
Increased LNG Imports and Infrastructure Development
To compensate for the decline in nuclear power, Taiwan has significantly increased its LNG imports. This surge in demand has spurred major investments in infrastructure development, including:
- New LNG Terminals: Expansion of existing and construction of new LNG import terminals to handle the rising volume of LNG shipments.
- Pipeline Network Upgrades: Significant upgrades and expansions to the island's pipeline network are crucial for efficient distribution of LNG across the country.
Both the private and public sectors are heavily involved in these infrastructure projects, collaborating to meet the country's increasing energy demands.
Economic Implications of LNG Reliance
The shift to LNG has profound economic implications for Taiwan. While providing energy security, it also presents economic challenges:
- Price Volatility: The global LNG market is subject to price fluctuations, impacting the stability of energy prices for consumers and businesses. Hedging strategies and diversification of supply sources become critical for mitigating this risk.
- Job Creation: The LNG sector, including import, storage, and distribution, is creating new jobs, boosting the economy. The development and maintenance of related infrastructure further stimulate employment opportunities.
Challenges and Opportunities in LNG Dependence
Geopolitical Risks and Energy Security
Taiwan's increased reliance on LNG imports exposes it to geopolitical risks and potential vulnerabilities:
- Supply Chain Disruptions: Dependence on specific LNG-exporting countries creates vulnerabilities to potential supply chain disruptions due to geopolitical tensions or unforeseen events.
- Diversification Strategies: Mitigating these risks requires strategic diversification of LNG sources, exploring alternative energy options, and enhancing the resilience of its energy infrastructure.
Environmental Considerations of LNG
While LNG is considered a cleaner-burning fossil fuel compared to coal, it's crucial to address its environmental impact:
- Greenhouse Gas Emissions: LNG combustion still produces greenhouse gas emissions, albeit less than coal. Efforts to reduce these emissions are vital for environmental sustainability.
- Methane Leaks: Methane, a potent greenhouse gas, can leak during the LNG production, transportation, and processing stages. Stricter regulations and technological advancements are needed to minimize methane leaks. Carbon capture and storage (CCS) technologies offer potential solutions to further reduce the environmental footprint.
Conclusion: Post-Nuclear Taiwan's Path Forward with LNG
Taiwan's transition from nuclear power to LNG is a complex undertaking, presenting both significant opportunities and substantial challenges. The increasing reliance on LNG necessitates strategic planning to ensure energy security, manage economic risks, and minimize environmental impact. Diversifying energy sources, investing in renewable energy technologies, and adopting efficient energy consumption practices are crucial steps for a sustainable energy future.
To delve deeper into this critical issue, search for "Taiwan LNG energy future" or "Post-nuclear Taiwan energy strategy." Understanding Taiwan's energy transition and its strategic reliance on LNG is paramount for the island's economic prosperity and environmental sustainability. A secure and sustainable energy future for Taiwan demands a comprehensive and forward-looking approach to its energy policy involving LNG and renewable energy sources.

Featured Posts
-
 Your Complete Guide To The Nyt Crossword April 25 2025
May 20, 2025
Your Complete Guide To The Nyt Crossword April 25 2025
May 20, 2025 -
 Todays Nyt Mini Crossword Answers For March 18
May 20, 2025
Todays Nyt Mini Crossword Answers For March 18
May 20, 2025 -
 Canadian Tires Potential Hudsons Bay Acquisition Challenges And Opportunities
May 20, 2025
Canadian Tires Potential Hudsons Bay Acquisition Challenges And Opportunities
May 20, 2025 -
 Bribery Allegations Rock The Navy Retired Admirals Fall From Grace
May 20, 2025
Bribery Allegations Rock The Navy Retired Admirals Fall From Grace
May 20, 2025 -
 Incendio De Escola Na Tijuca Recordacoes E Tristeza Marcam Comunidade
May 20, 2025
Incendio De Escola Na Tijuca Recordacoes E Tristeza Marcam Comunidade
May 20, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Big Bear Ai Bbai Stock Plummets Missed Revenue And Leadership Shakeup
May 20, 2025
Big Bear Ai Bbai Stock Plummets Missed Revenue And Leadership Shakeup
May 20, 2025 -
 Market Dip Consider This Ai Quantum Computing Stock
May 20, 2025
Market Dip Consider This Ai Quantum Computing Stock
May 20, 2025 -
 What Caused Big Bear Ai Bbai Stock To Plummet In 2025
May 20, 2025
What Caused Big Bear Ai Bbai Stock To Plummet In 2025
May 20, 2025 -
 Is Big Bear Ai Bbai One Of The Best Ai Penny Stocks To Buy Right Now
May 20, 2025
Is Big Bear Ai Bbai One Of The Best Ai Penny Stocks To Buy Right Now
May 20, 2025 -
 Big Bear Ai Bbai Stock Buy Rating Holds Despite Defense Sector Uncertainty
May 20, 2025
Big Bear Ai Bbai Stock Buy Rating Holds Despite Defense Sector Uncertainty
May 20, 2025
