Taiwan's Nuclear Phase-Out: The Rise Of LNG Imports

Table of Contents
The Decline of Nuclear Power in Taiwan
Taiwan's nuclear power program, once a cornerstone of its electricity generation, is undergoing a significant decline. The island currently operates three nuclear power plants: Kuosheng, Maanshan, and the now-decommissioned Chinshan. The government's decision to phase out nuclear power, driven primarily by the 2011 Fukushima Daiichi disaster and a strong anti-nuclear movement in Taiwan, has initiated a complex energy transition.
The political and social factors behind the phase-out are multifaceted. Public anxieties surrounding nuclear safety, coupled with growing concerns about nuclear waste disposal, have fueled a sustained anti-nuclear movement. This public pressure, combined with the government's commitment to a greener energy future, ultimately led to the decision to decommission existing plants and forego the construction of new ones.
- Timeline of nuclear plant closures: Chinshan Nuclear Power Plant was decommissioned in 2018, with Kuosheng and Maanshan slated for eventual closure as per the government's timeline.
- Public opinion shifts regarding nuclear energy: Post-Fukushima, public support for nuclear power significantly diminished, creating a strong political mandate for a nuclear phase-out.
- Government policies promoting renewable energy sources: The government has actively promoted the development of renewable energy sources such as solar and wind power to compensate for the loss of nuclear power generation. This includes substantial investments in renewable energy infrastructure and supportive regulatory frameworks. These policies are aimed at achieving greater energy independence and reducing reliance on fossil fuels. Keywords: Taiwan nuclear power phase-out, anti-nuclear movement Taiwan, Taiwan renewable energy.
The Rise of LNG as a Primary Energy Source
The decline of nuclear power has resulted in a substantial increase in Taiwan LNG imports. To fill the energy gap, Taiwan has dramatically increased its reliance on LNG, making it a primary energy source. This transition required significant investment in new infrastructure.
The increased LNG imports have necessitated the development of new LNG terminals and associated pipelines to handle the influx of liquefied natural gas. This infrastructure development has involved substantial foreign investment and collaborations with international energy companies.
- Statistics on LNG import growth: Data from Taiwan's Ministry of Economic Affairs shows a substantial percentage increase in LNG imports since the start of the nuclear phase-out. Specific figures should be inserted here referencing official sources.
- Major LNG suppliers to Taiwan: Taiwan sources LNG from various international suppliers, diversifying its supply chains to mitigate potential risks associated with relying on any single source. (Insert supplier information with sourcing).
- Investment in LNG infrastructure projects: Millions of dollars have been invested in developing the necessary infrastructure for receiving, processing and distributing the increased volume of LNG. (Insert investment data with sourcing) Keywords: Taiwan LNG imports, LNG terminals Taiwan, Taiwan energy infrastructure
Challenges and Risks Associated with LNG Dependency
While LNG provides a relatively cleaner alternative to coal, Taiwan's growing dependence on imported LNG presents significant challenges and risks. The most pressing concern is the inherent vulnerability to price volatility and potential supply disruptions in the global LNG market.
- Price fluctuations and their impact on Taiwan's energy costs: Fluctuations in global LNG prices directly impact Taiwan's energy costs, potentially leading to economic instability and impacting consumers and industries alike.
- Geopolitical risks and potential disruptions to LNG supply: Political instability in LNG-producing regions or disruptions to global shipping routes pose significant risks to Taiwan's energy security. Geopolitical tensions can disrupt supply chains, leaving Taiwan vulnerable to energy shortages.
- Diversification strategies to mitigate reliance on single suppliers: To mitigate these risks, Taiwan is actively pursuing strategies to diversify its LNG suppliers and explore alternative energy sources.
Keywords: Taiwan energy security, LNG price volatility, Taiwan energy diversification
Opportunities and Potential for Sustainable Development
Despite the challenges, Taiwan's energy transition presents significant opportunities for sustainable development. Integrating renewable energy sources alongside LNG is crucial for achieving a balanced and sustainable energy mix.
- Government initiatives to promote renewable energy (solar, wind): The Taiwanese government is actively investing in solar and wind power generation, aiming to significantly increase the share of renewable energy in its overall energy mix. (Insert details about government initiatives and target percentages)
- Smart grid technologies and energy efficiency programs: Investing in smart grid technologies and energy efficiency programs can help optimize energy consumption and reduce overall reliance on imported LNG. (Include examples of initiatives)
- Opportunities for technological advancements in LNG handling and storage: Advancements in LNG handling and storage technologies can improve efficiency and reduce environmental impact. (Mention specific technological advancements)
Keywords: Taiwan renewable energy integration, Taiwan energy efficiency, sustainable energy Taiwan
Conclusion
Taiwan's nuclear phase-out has necessitated a significant shift towards LNG imports to meet its energy demands. While this transition offers opportunities for economic development and technological advancement, it also presents considerable challenges related to energy security, price volatility, and geopolitical risks. Diversification strategies, coupled with a strong commitment to renewable energy and energy efficiency, are crucial for ensuring Taiwan's long-term energy sustainability.
Call to Action: Understanding the intricacies of Taiwan's LNG imports and the broader implications of its nuclear phase-out is crucial for navigating the island's energy future. Further research and discussion on sustainable energy solutions are needed to address the challenges and maximize the opportunities presented by this significant energy transition. Continue learning about Taiwan LNG imports and its impact on the nation's energy policy.

Featured Posts
-
 Alito And Roberts A Look Back At Their Time On The Supreme Court
May 20, 2025
Alito And Roberts A Look Back At Their Time On The Supreme Court
May 20, 2025 -
 Hegseths Announcement New Us Missile System Deployed To The Philippines
May 20, 2025
Hegseths Announcement New Us Missile System Deployed To The Philippines
May 20, 2025 -
 Michael Schumachers Failed Comeback A Case Study In Ignoring Expert Advice
May 20, 2025
Michael Schumachers Failed Comeback A Case Study In Ignoring Expert Advice
May 20, 2025 -
 Leclercs Frustration Hamiltons Role In Ferraris Team Orders Controversy
May 20, 2025
Leclercs Frustration Hamiltons Role In Ferraris Team Orders Controversy
May 20, 2025 -
 Poslednie Novosti O Shumakhere Drug Podelilsya Trevozhnymi Podrobnostyami
May 20, 2025
Poslednie Novosti O Shumakhere Drug Podelilsya Trevozhnymi Podrobnostyami
May 20, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 D Wave Quantum Qbts Stock Mondays Drop And Its Implications
May 20, 2025
D Wave Quantum Qbts Stock Mondays Drop And Its Implications
May 20, 2025 -
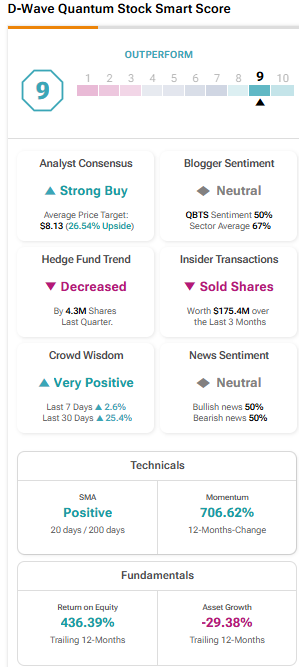 Understanding The D Wave Quantum Qbts Stock Dip On Monday
May 20, 2025
Understanding The D Wave Quantum Qbts Stock Dip On Monday
May 20, 2025 -
 Why Did D Wave Quantum Qbts Stock Fall On Monday
May 20, 2025
Why Did D Wave Quantum Qbts Stock Fall On Monday
May 20, 2025 -
 D Wave Quantum Qbts Understanding Its Significant Stock Decline In 2025
May 20, 2025
D Wave Quantum Qbts Understanding Its Significant Stock Decline In 2025
May 20, 2025 -
 Market Volatility And D Wave Quantum Qbts Understanding Mondays Drop
May 20, 2025
Market Volatility And D Wave Quantum Qbts Understanding Mondays Drop
May 20, 2025
